Physics theory suggests that exotic excitations can exist in the form of bound states confined in the proximity of topological defects, for instance, in the case of Majorana zero modes that are trapped in vortices within topological superconducting materials. Better understanding these states could aid the development of new computational tools, including quantum technologies.
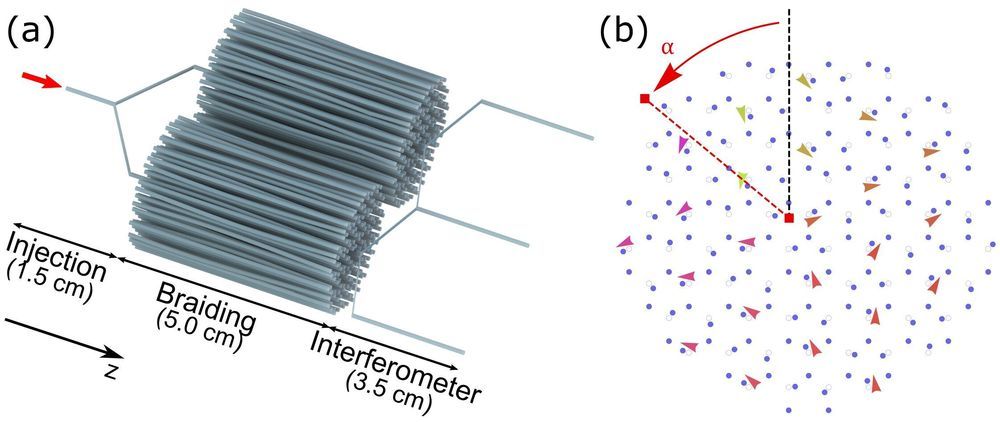
One phenomenon that has attracted attention over the past few years is “braiding,” which occurs when electrons in particular states (i.e., Majorana fermions) are braided with one another. Some physicists have theorized that this phenomenon could enable the development of a new type of quantum technology, namely topological quantum computers.
Researchers at Pennsylvania State University, University of California-Berkeley, Iowa State University, University of Pittsburgh, and Boston University have recently tested the hypothesis that braiding also occurs in particles other than electrons, such as photons (i.e., particles of light). In a paper published in Nature Physics, they present the first experimental demonstration of braiding using photonic topological zero modes.