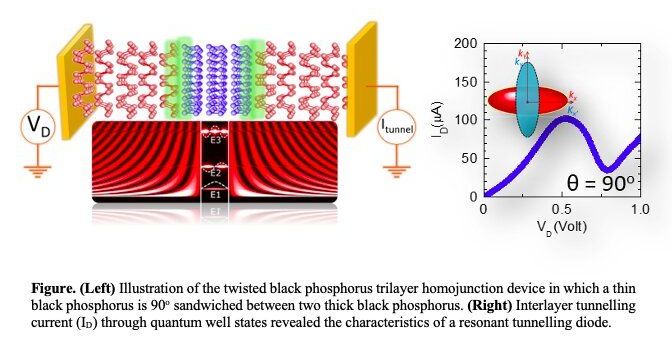
In recent years, electronics engineers worldwide have been trying to develop new semiconductor heterostructure devices using atomically thin materials. Among the many devices that can be fabricated using these materials are resonant tunneling diodes, which typically consist of a quantum-well structure placed between two barrier layers.
Past research has shown that stacking two-dimensional (2D) layers that are twisted in relation to each other can enhance or suppress the interlayer coupling at their interface. This suppression or enhancement can in turn modulate the electronic, optical and mechanical properties of the resulting device.
For instance, some studies found that the intralayer current transport in small angle twisted bilayer graphene prompted some exotic phenomena, such as superconductivity and ferromagnetism. These observations inspired a fundamentally new approach to device engineering, known as ‘twistronics’ (i.e., twist electronics).