Oct 9, 2019
New horizons for connecting future quantum computers into a quantum network
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: computing, internet, quantum physics
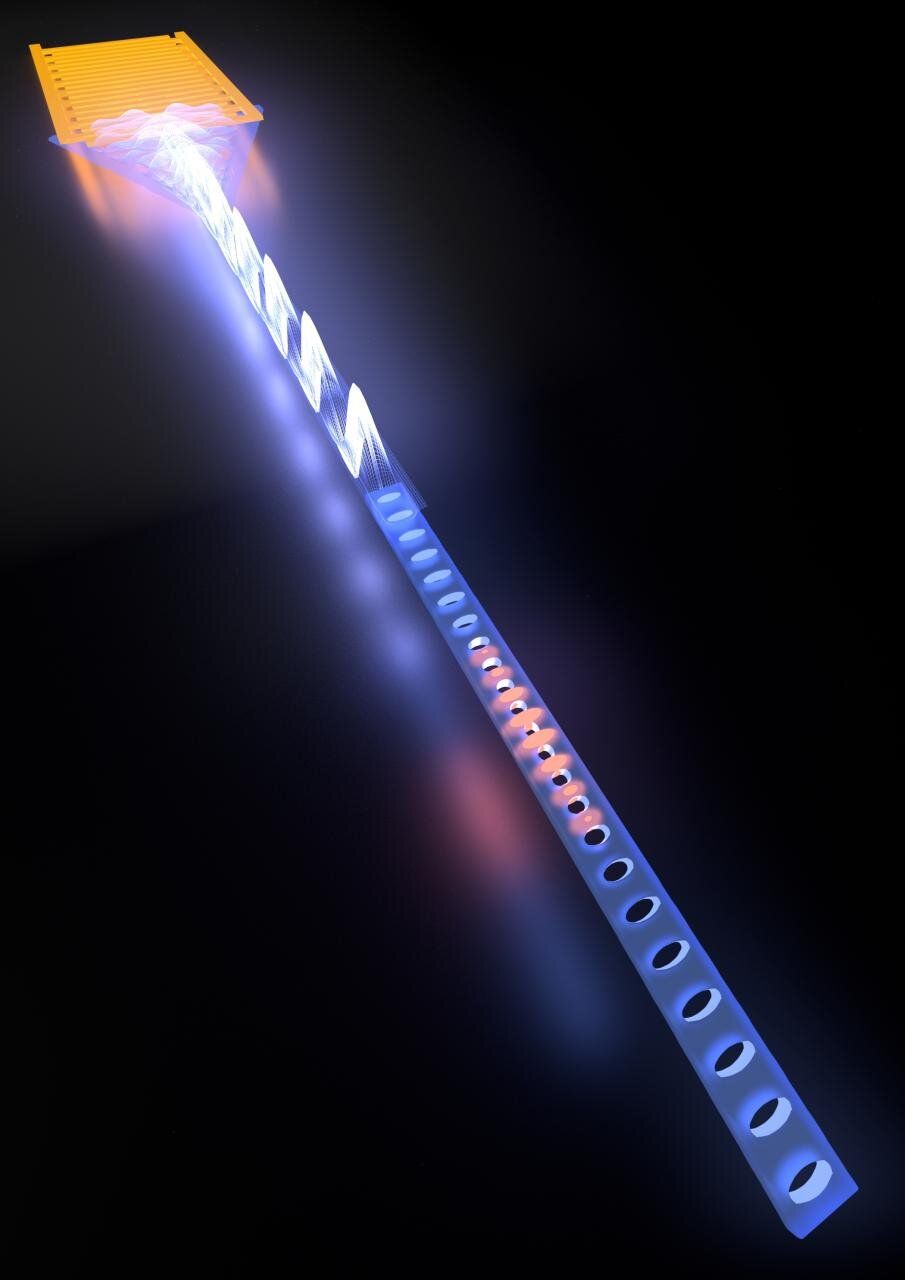
Researchers led by Delft University of Technology personnel have made two steps in the conversion of quantum states between signals in the microwave and optical domains. This is of great interest for connecting future superconducting quantum computers into a global quantum network. This week they report on their findings in Nature Physics and in Physical Review Letters.
Conversion between signals in the microwave and optical domains is of great interest, particularly for connecting future superconducting quantum computers into a global quantum network. Many leading efforts in quantum technologies, including superconducting qubits and quantum dots, share quantum information through photons in the microwave regime. While this allows for an impressive degree of quantum control, it also limits the distance the information can realistically travel before being lost to a mere few centimeters.
At the same time, the field of optical quantum communication has already seen demonstrations over distance scales capable of providing real-world applications. By transmitting information in the optical telecom band, fiber-based quantum networks over tens or even hundreds of kilometers can be envisaged. “In order to connect several quantum computing nodes over large distances into a quantum internet, it is therefore vital to be able to convert quantum information from the microwave to the optical domain, and back,” says Prof. Simon Groeblacher of Delft University of Technology. “This will not only be extremely interesting for quantum applications, but also for highly efficient, low-noise conversion between classical optical and electrical signals.”