Oct 11, 2017
Intel Accelerates Its Quantum Computing Efforts With 17-Qubit Chip
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: computing, information science, quantum physics
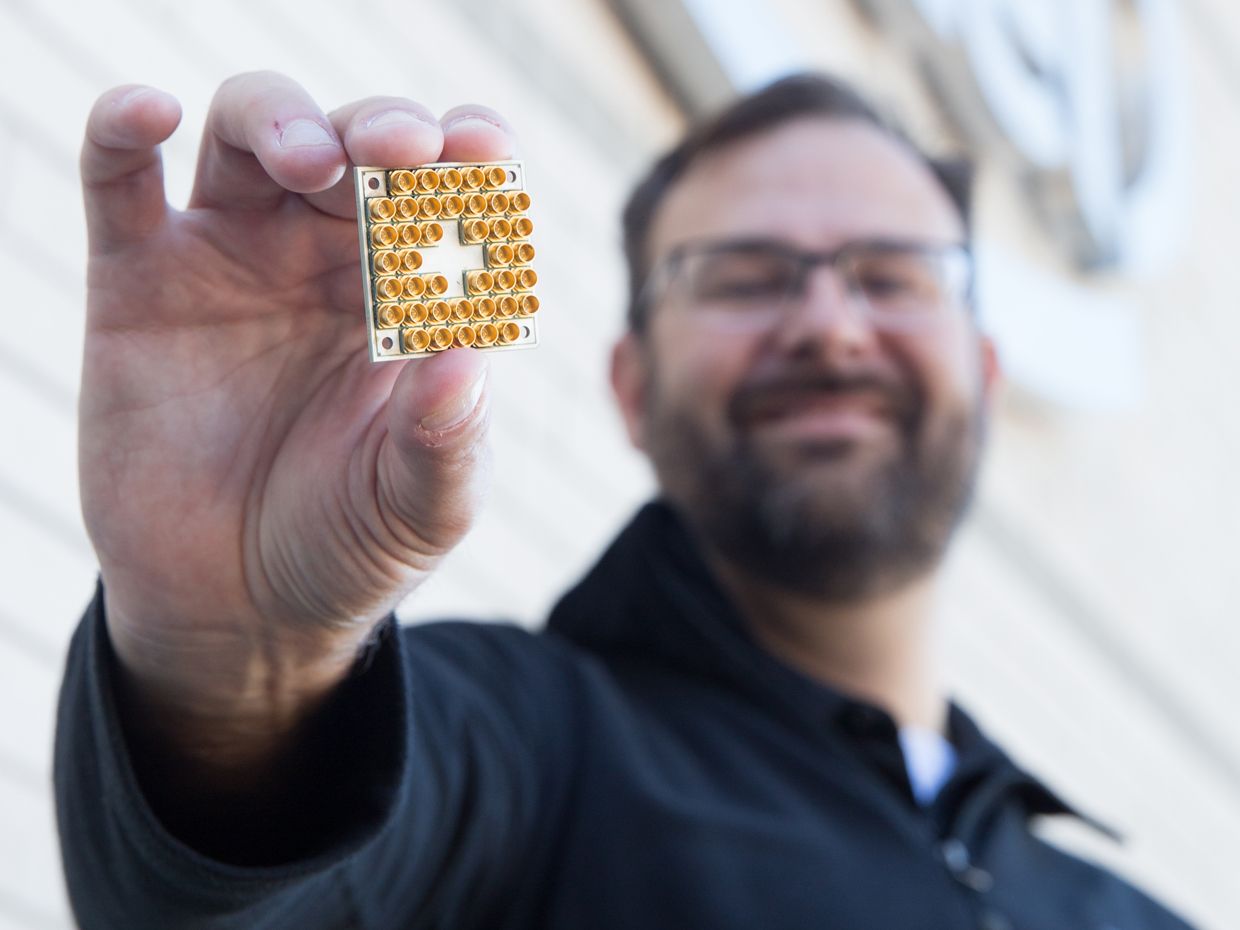
Intel says it is shipping an experimental quantum computing chip to research partners in The Netherlands today. The company hopes to demonstrate that its packaging and integration skills give it an edge in the race to produce practical quantum computers.
The chip contains 17 superconducting qubits—the quantum computer’s fundamental component. According to Jim Clarke, Intel’s director of quantum hardware, the company chose 17 qubits because it’s the minimum needed to perform surface code error correction, an algorithm thought to be necessary to scaling up quantum computers to useful sizes.
Intel’s research partners, at the TU Delft and TNO research center Qutech, will be testing the individual qubits’ abilities as well as performing surface code error correction and other algorithms.
Continue reading “Intel Accelerates Its Quantum Computing Efforts With 17-Qubit Chip” »