Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics phenomena, could eventually tackle some optimization and computational problems faster and more efficiently than their classical counterparts. Instead of bits, the fundamental units of information in classical computers, quantum computers rely on qubits (quantum bits), which can be in multiple states at once.
Silicon-based quantum dots, semiconductor-based structures that trap individual electrons, have been widely used as qubits, as the spin state of the electrons they confine can be leveraged to encode information. Despite their promise, many quantum computers developed so far are susceptible to decoherence, which entails the disruption of qubit states due to their interaction with the surrounding environment.
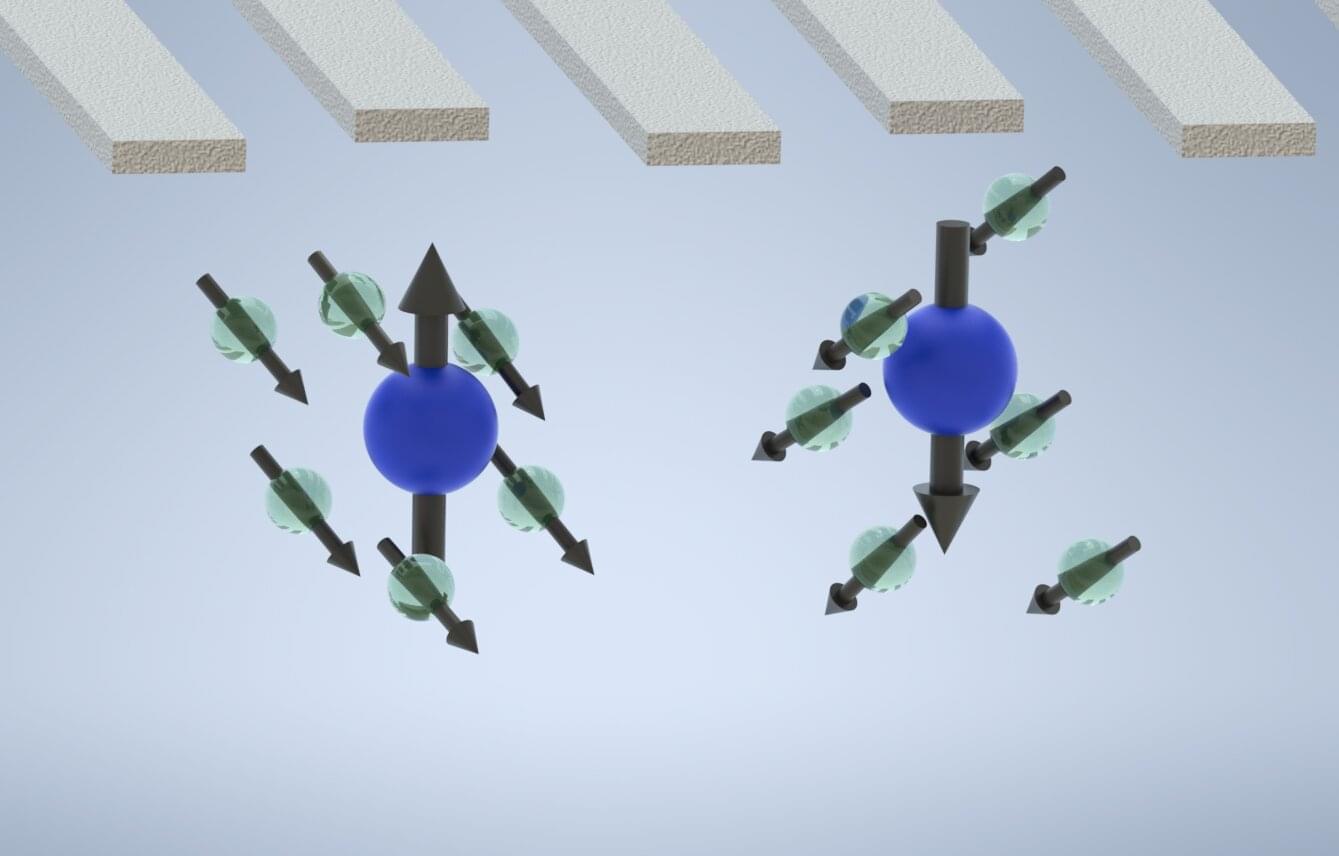
Researchers at the University of Rochester recently set out to experimentally realize a so-called nuclear-spin dark state, a condition that has been theorized to improve the performance of quantum computers, suppressing undesirable interactions and thus reducing decoherence. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, demonstrates the potential of this state for reducing decoherence in quantum systems and thus potentially improving control over quantum information processing.