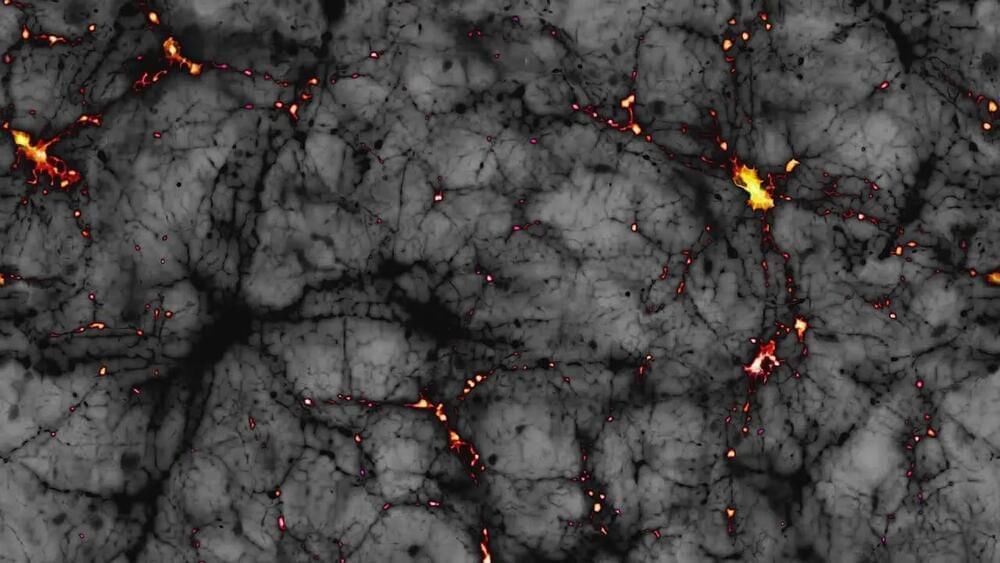
Researchers have created a composite image showing dark matter’s role in linking galaxies, using data from 23,000 galaxy pairs located 4.5 billion light-years away. This discovery, through weak gravitational lensing, offers direct evidence of the dark matter web predicted for decades, moving from theoretical assumptions to measurable proof. The finding helps confirm dark matter’s critical role in keeping galaxies intact, at a time when some scientists are questioning its existence. Though still largely invisible, this breakthrough brings us closer to truly understanding the unseen forces binding the universe together.
The idea of dark matter originated out of sheer necessity. Given the amount of matter we can observe, the universe shouldn’t be able to exist and function the way it does—this visible matter simply can’t produce the gravitational forces required to hold galaxies together. Dark matter offers scientists a solution to this problem. They suggest the universe must contain a type of matter that we are unable to detect, one that doesn’t absorb, reflect, or emit light—hence, a truly “dark” form of matter.
To maintain the accuracy of our scientific models, dark matter would need to make up more than a quarter of the universe’s total matter. However, what exactly constitutes dark matter remains a mystery, and attempting to find evidence for something invisible is a difficult endeavor. Until now, scientists have primarily relied on observing its gravitational influence as indirect proof of dark matter’s existence. But researchers from the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada, have gone a step further—they’ve produced a composite image that confirms galaxies are linked by dark matter.