“At first, we thought it was absurd. How else could you respond to the idea that black holes generate swirling clouds of planet-sized particles that could be the dark matter thought to hold galaxies together? We tend to think about particles as being tiny but, theoretically, there is no reason they can’t be as big as a galaxy,” said theoretical physicist Asimina Arvanitaki, at the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics referring to the heated debate about the standard model for dark matter that proposes that it is ‘cold,’ meaning that the particles move slowly compared to the speed of light which is tied to the mass of dark matter particles. The lower the mass of the particle, the ‘warmer’ it is and the faster it will move.
On January 9, NASA physicists using the Hubble Space Telescope reported that although the type of particle that makes up dark matter is still a mystery, a compelling observational test for the cold dark matter passed “with flying colors,” The NASA team used a new “cosmic magnifying glasses” technique that found that dark matter forms much smaller clumps than previously known, confirming one of the fundamental predictions of the widely accepted “cold dark matter” theory.
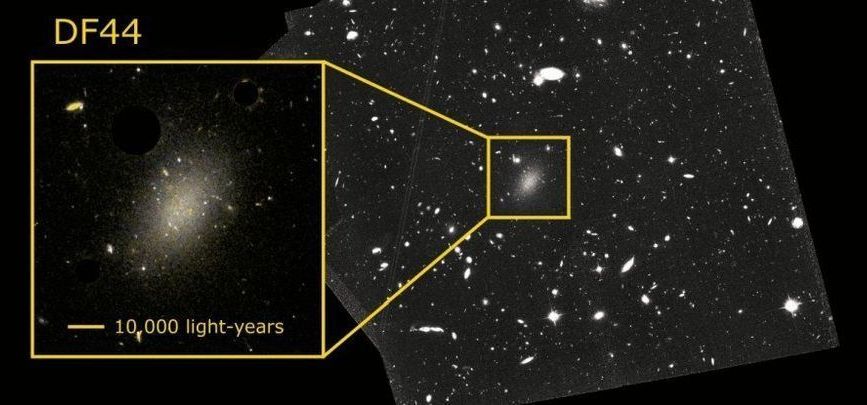
Physicists at the University of California, Davis, taking the temperature of dark matter, the mysterious substance that makes up about a quarter of our universe now report that the model of cold (more massive) dark matter holds at very large scales” said Chris Fassnacht, a physics professor at UC Davis, “but doesn’t work so well on the scale of individual galaxies.” That’s led to other models including ‘warm’ dark matter with lighter, faster-moving particles and ‘hot’ dark matter with particles moving close to the speed of light that have been ruled out by observations.