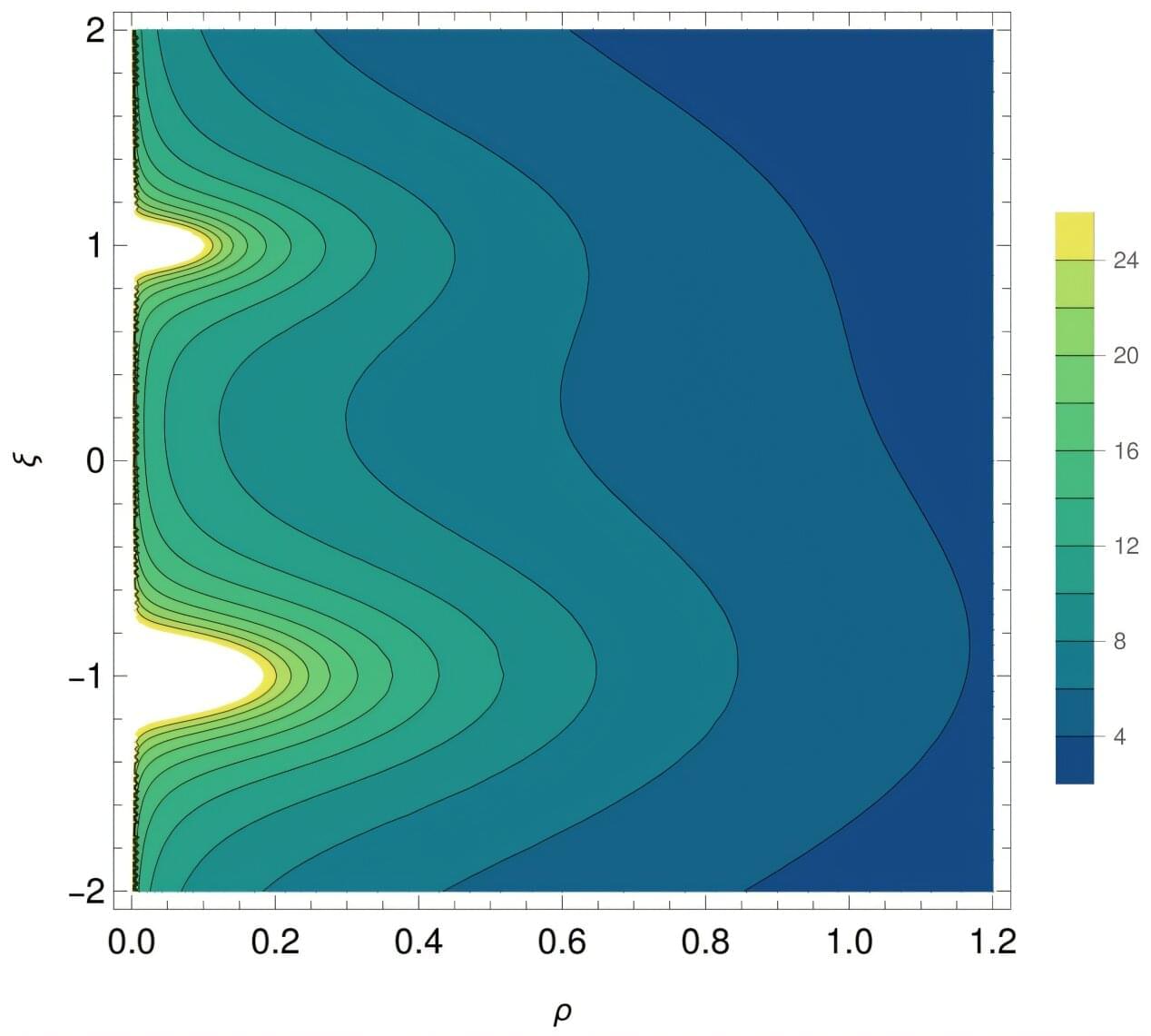
The CMS collaboration at CERN has observed an unexpected feature in data produced by the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), which could point to the existence of the smallest composite particle yet observed. The result, reported at the Rencontres de Moriond conference in the Italian Alps this week, suggest that top quarks—the heaviest and shortest lived of all the elementary particles—can momentarily pair up with their antimatter counterparts to produce an object called toponium.
Other explanations cannot be ruled out, however, as the existence of toponium was thought too difficult to verify at the LHC, and the result will need to be further scrutinized by CMS’s sister experiment, ATLAS.
High-energy collisions between protons at the LHC routinely produce top quark–antiquark pairs (tt-bar). Measuring the probability, or cross section, of tt-bar production is both an important test of the Standard Model of particle physics and a powerful way to search for the existence of new particles that are not described by the 50-year-old theory. Many of the open questions in particle physics, such as the nature of dark matter, motivate the search for new particles that may be too heavy to have been produced in experiments so far.