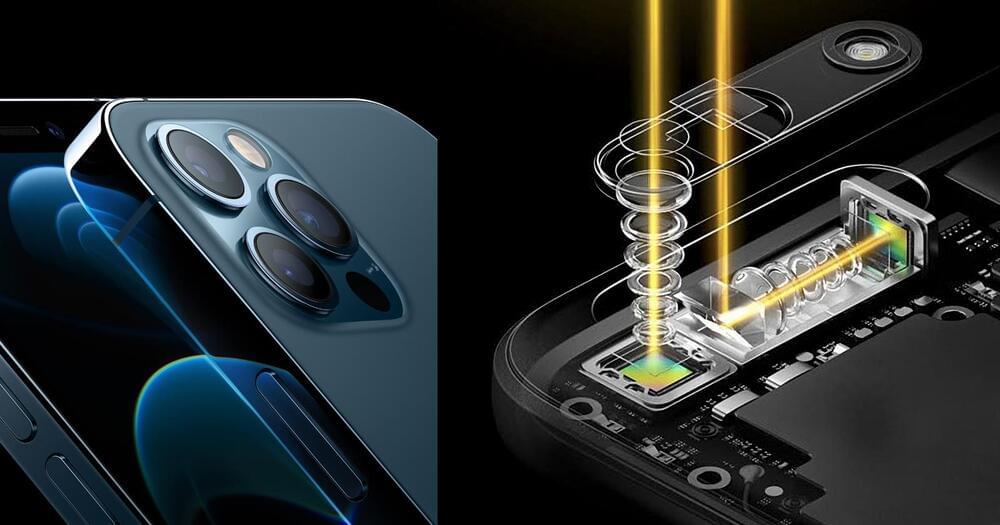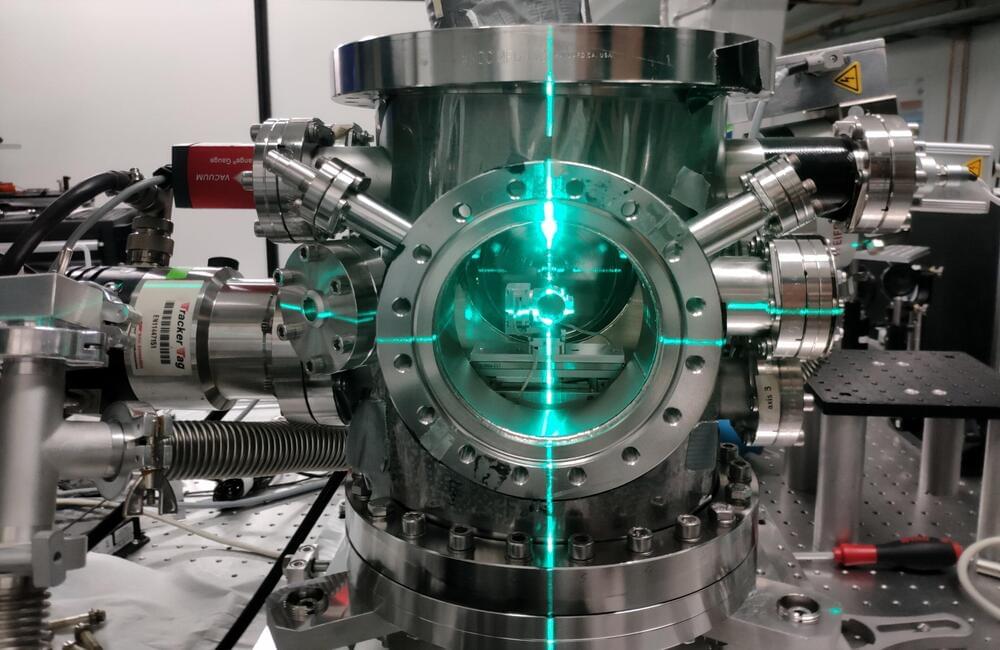
Scientists at DESY have built a compact electron camera that can capture the inner, ultrafast dynamics of matter. The system shoots short bunches of electrons at a sample to take snapshots of its current inner structure. It is the first such electron diffractometer that uses Terahertz radiation for pulse compression. The developer team around DESY scientists Dongfang Zhang and Franz Kärtner from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science CFEL validated their Terahertz-enhanced ultrafast electron diffractometer with the investigation of a silicon sample and present their work in the first issue of the journal Ultrafast Science, a new title in the Science group of scientific journals.
Electron diffraction is one way to investigate the inner structure of matter. However, it does not image the structure directly. Instead, when the electrons hit or traverse a solid sample, they are deflected in a systematic way by the electrons in the solid’s inner lattice. From the pattern of this diffraction, recorded on a detector, the internal lattice structure of the solid can be calculated. To detect dynamic changes in this inner structure, short bunches of sufficiently bright electrons have to be used. “The shorter the bunch, the faster the exposure time,” says Zhang, who is now a professor at Shanghai Jiao Tong University. “Typically, ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) uses bunch lengths, or exposure times, of some 100 femtoseconds, which is 0.1 trillionths of a second.”
Such short electron bunches can be routinely produced with high quality by state-of-the-art particle accelerators. However, these machines are often large and bulky, partly due to the radio frequency radiation used to power them, which operates in the Gigahertz band. The wavelength of the radiation sets the size for the whole device. The DESY team is now using Terahertz radiation instead with roughly a hundred times shorter wavelengths. “This basically means, the accelerator components, here a bunch compressor, can be a hundred times smaller, too,” explains Kärtner, who is also a professor and a member of the cluster of excellence “CUI: Advanced Imaging of Matter” at the University of Hamburg.