Beehive sensors offer hope in saving honeybee colonies.



A collaboration of researchers in Austria and China has built a universal inverse-design magnonic device that can efficiently produce new electronic components based solely on a definition of the desired performance, and do the job in minutes or hours. They published the result in Nature Electronics.
Designing an electronic component usually requires extensive manual design and simulation to achieve a desired functionality. Inverse design eliminates these steps. It is a two-step process: First, the developers divide a design area into an array of smaller, programmable elements. Then, they deploy iterative feedback-loop optimization to tune these elements to achieve a predefined functionality.
This new device manipulates magnons, the quasiparticle quanta of magnetic spin waves. There have been magnonic devices and inverse-design devices, but this is the first universal magnonic inverse design device. Hypothetically, this kind of device can duplicate the performance of anything from a diode to a neuromorphic circuit.

When a droplet of water falls on a hot pan, it dances across the surface, skimming on a thin layer of steam like a tiny hovercraft; this is known as the Leidenfrost effect. But now, researchers know what happens when a hot droplet falls on a cool surface.
These new findings, published in the journal Newton, demonstrate that hot and burning droplets can bounce off cool surfaces, propelled by a thin layer of air that forms beneath them. This phenomenon could inspire new strategies for slowing the spread of fires and improving engine efficiency.
“We started with a very fundamental question: What will happen when a burning droplet impacts a solid surface?” says senior author Pingan Zhu of City University of Hong Kong, China.
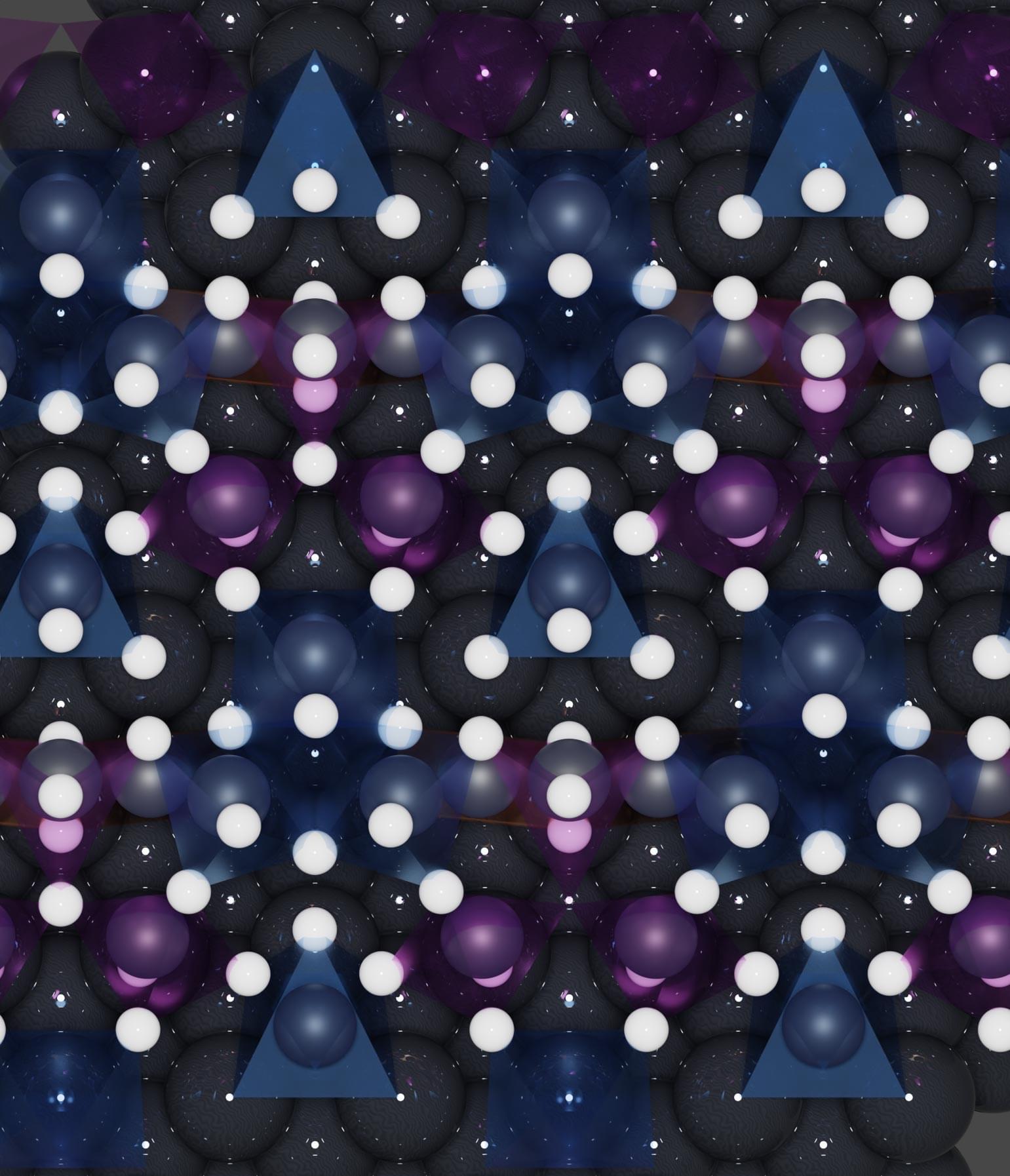
For years, scientists were baffled by a peculiar problem: why do platinum electrodes, usually stable, corrode so quickly in electrochemical devices? A collaboration between SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Leiden University cracked the case by using cutting-edge X-ray techniques.
They found that platinum hydrides, not sodium ions as once suspected, were responsible for the degradation. This discovery could revolutionize hydrogen production and electrochemical sensor durability, potentially slashing costs and improving efficiency.
Unraveling a Costly Mystery.

Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor (/ ˈ k æ n t ɔːr / KAN-tor; German: [ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfɛʁdinant ˈluːtvɪç ˈfiːlɪp ˈkantoːɐ̯] ; 3 March [O.S. 19 February] 1845 – 6 January 1918 [ 1 ] ) was a mathematician who played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between the members of two sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. Cantor’s method of proof of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal and ordinal numbers and their arithmetic. Cantor’s work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he was well aware of. [ 2 ]
Originally, Cantor’s theory of transfinite numbers was regarded as counter-intuitive – even shocking. This caused it to encounter resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré [ 3 ] and later from Hermann Weyl and L. E. J. Brouwer, while Ludwig Wittgenstein raised philosophical objections; see Controversy over Cantor’s theory. Cantor, a devout Lutheran Christian, [ 4 ] believed the theory had been communicated to him by God. [ 5 ] Some Christian theologians (particularly neo-Scholastics) saw Cantor’s work as a challenge to the uniqueness of the absolute infinity in the nature of God [ 6 ] – on one occasion equating the theory of transfinite numbers with pantheism [ 7 ] – a proposition that Cantor vigorously rejected.
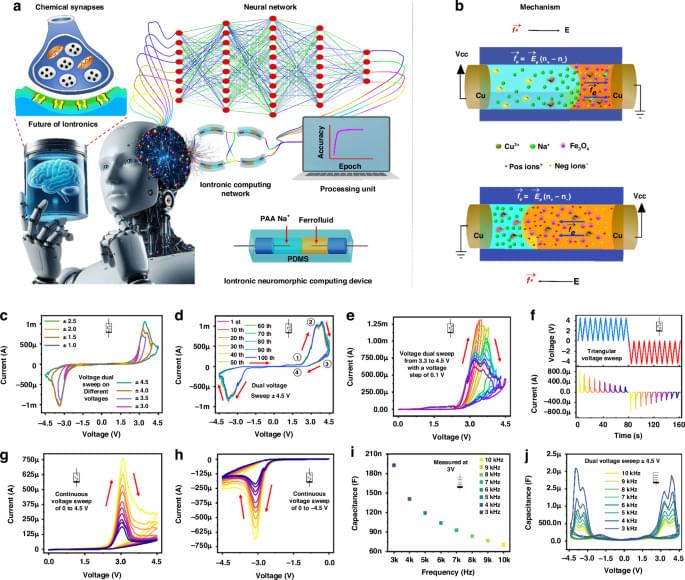
Khan, M.U., Hassan, B., Alazzam, A. et al. Brain inspired iontronic fluidic memristive and memcapacitive device for self-powered electronics. Microsyst Nanoeng 11, 37 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00882-x.


Keeping up with the Joneses…
The big elephant in the room here is Micro-LED. That’s because, like QDEL, Micro-LED pixels are self-emissive, with each pixel containing a tiny red, blue, and green LED, which combine to produce different colors as needed. It also means that Micro-LED displays have that pixel-level control for true blacks.
But QDEL could win here, too. Quantum dots seem to be able to produce more saturated and more pure colors than LEDs, which is why quantum dots are used on many high-end TVs today. Of course, it’s entirely possible that Micro-LED technology could be combined with a quantum dot layer for purer and more vibrant colors, which would create a stunning image with a high level of brightness.
Likely, however, QDEL could end up doing a similar job as Micro-LED for much cheaper. Micro-LED has proven expensive to produce. While QDEL isn’t being used on consumer screens just yet, it could end up being much cheaper given the fact that quantum dots at this point are relatively easy to manufacture.
Water isn’t just liquid, ice, or vapor — under extreme conditions, it can transform into exotic phases, such as the newly observed plastic ice VII.
This hybrid phase, predicted years ago but only recently confirmed using cutting-edge neutron spectrometers, exhibits both solid-like structure and liquid-like molecular motion.
Beyond the familiar: water’s many phases.