Sep 5, 2023
Better cybersecurity with quantum random number generation based on a perovskite light emitting diode
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: cybercrime/malcode, encryption, finance, quantum physics
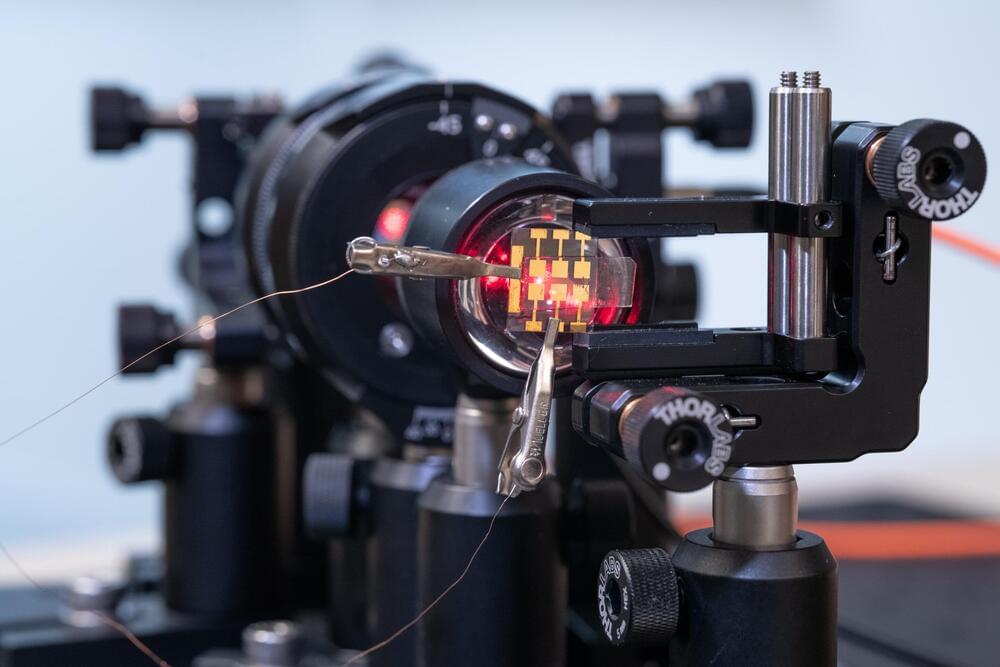
Digital information exchange can be safer, cheaper and more environmentally friendly with the help of a new type of random number generator for encryption developed at Linköping University, Sweden. The researchers behind the study believe that the new technology paves the way for a new type of quantum communication.
In an increasingly connected world, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important to protect not just the individual, but also, for example, national infrastructure and banking systems. And there is an ongoing race between hackers and those trying to protect information. The most common way to protect information is through encryption. So when we send emails, pay bills and shop online, the information is digitally encrypted.
To encrypt information, a random number generator is used, which can either be a computer program or the hardware itself. The random number generator provides keys that are used to both encrypt and unlock the information at the receiving end.