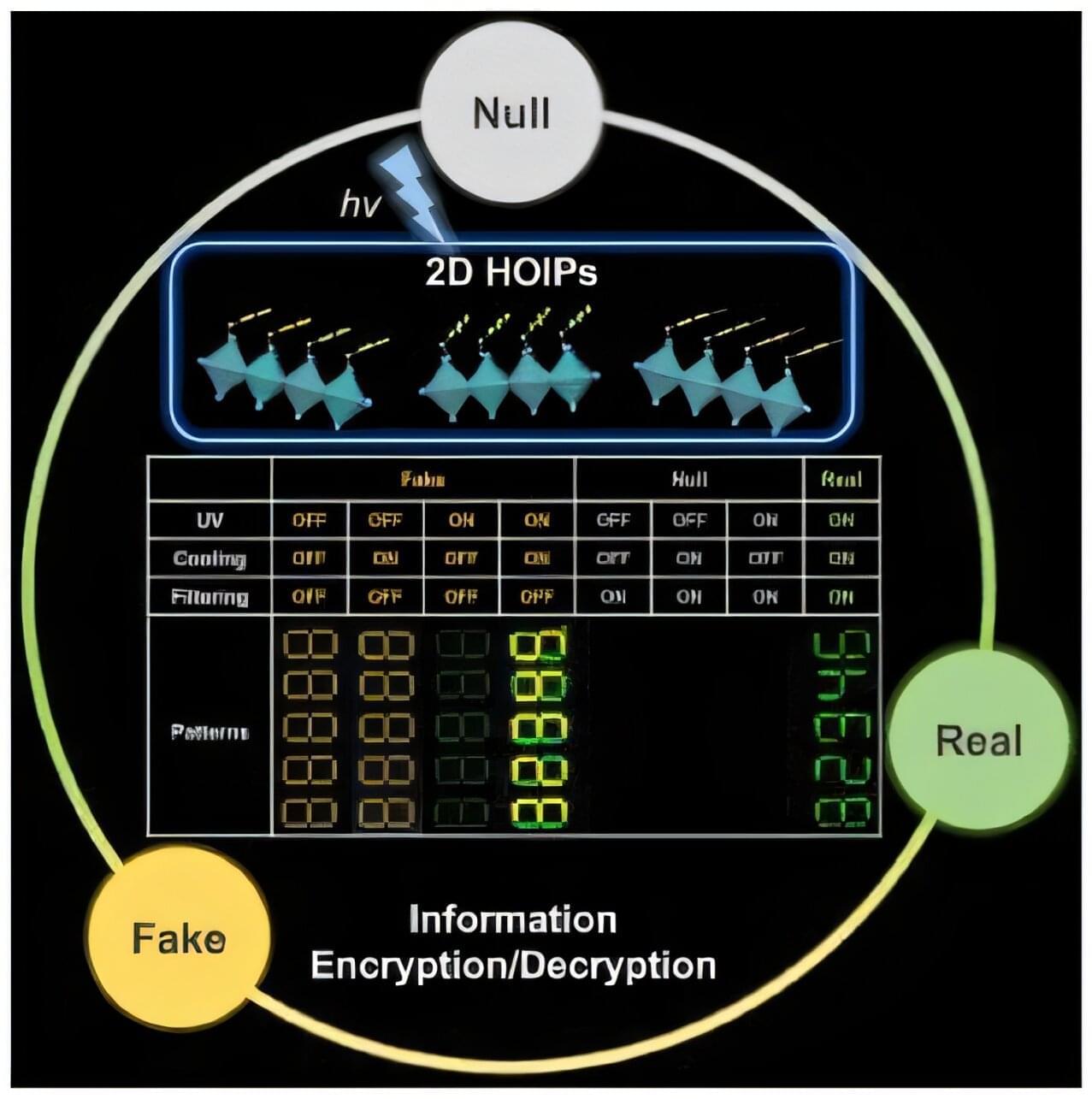
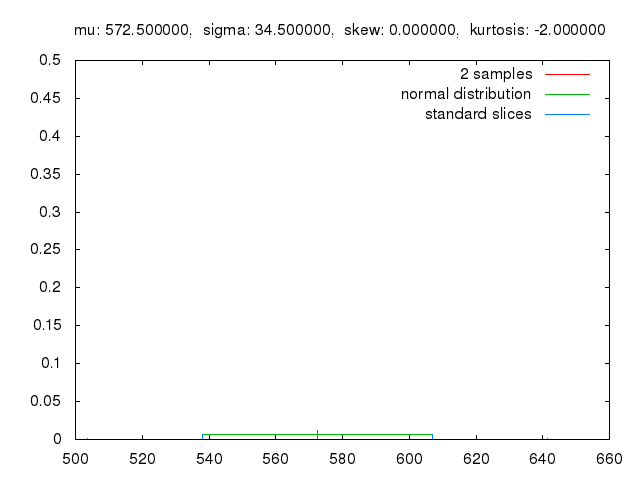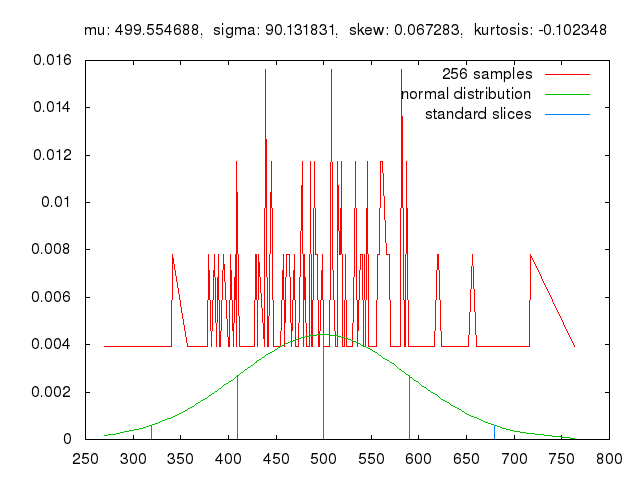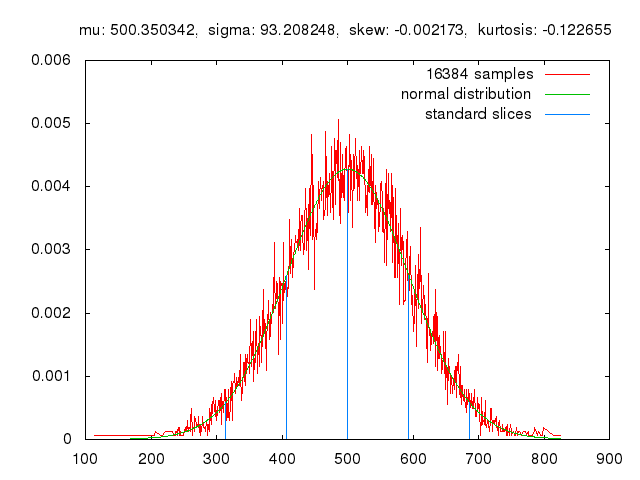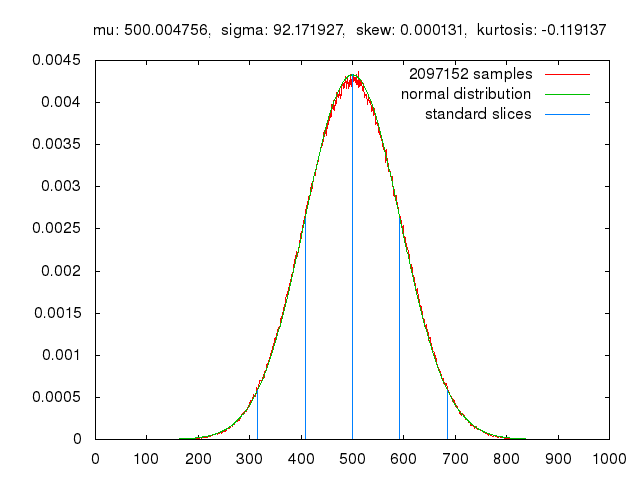To guarantee high data security, encryption must be unbreakable while the data remains rapidly and easily readable. A novel strategy for optical encryption/decryption of information has now been introduced in the journal Angewandte Chemie by a Chinese research team. It is based on compounds with carefully modulated luminescent properties that change in response to external stimuli.
The compounds are hybrid two-dimensional organic-inorganic metal-halide perovskites, whose structure consists of inorganic layers formed from lead and iodide ions (linked PbI6 octahedra) with organic cations arranged between them. They are easy to produce, inexpensive, and printable, while demonstrating interesting optoelectronic properties.
A team led by Shenlong Jiang, Qun Zhang, and Yi Luo at the University of Science and Technology of China (Hefei) worked with three perovskites with only slight variations in their cations (phenethylammonium lead iodide perovskite (PEA)2PbI4 and its fluoridated (2-F-PEA)2PbI4 and brominated (4-Br-PEA)2PbI4 derivatives).