The HEOS project is searching space for signs of Dyson Spheres. Funded by the Swedish government, the project not only believes that these extraterrestrial power plants are possible, but also assumes that we can detect them. Dyson spheres are power plants that hypercivilizations build in space to harness incredible amounts of energy. Will HEOS soon enable us to make contact with an extraterrestrial species for the first time?
Category: energy – Page 27


Pure nickel oxide research refutes hydrogen-superconductivity link
Physicists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have synthesized very pure superconducting materials and redefined the critical role of hydrogen in the newly discovered nickel-oxide superconductors.
Their findings were published concurrently in the journals Nature Communications and Physical Review Letters.
Superconductivity is an exciting phenomenon where electrical resistance disappears, and it holds transformative potential for revolutionizing energy technologies. Despite its potential, the origin and fundamental mechanism of superconductivity remain one of the greatest mysteries in physics.
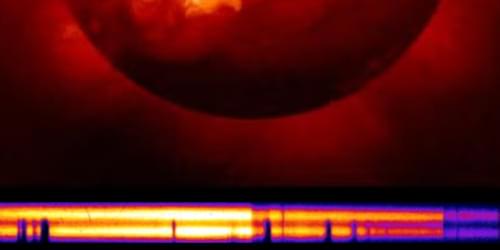
X-Ray Spectral Imaging Probes How Sun-Like Plasma Blocks Light
Temporal measurements in conditions similar to those in the Sun rebut a leading hypothesis for why models and experiments disagree on how much light iron absorbs.
Understanding how light interacts with matter inside stars is crucial for predicting stars’ evolution, structure, and energy output. A key factor in this process is opacity—the degree to which a material absorbs radiation. Recent experimental findings have challenged long-standing models, showing that iron, a major contributor to stellar opacity, absorbs more light than expected. This discrepancy has profound implications for our understanding of the Sun and of other stars. Over the past two decades, three groundbreaking studies [1–3] have taken major steps toward resolving this mystery, using advanced laboratory experiments to measure iron’s opacity under extreme conditions similar to those of the Sun’s interior. However, the discrepancy remained, with researchers hypothesizing that it came from systematic errors from temporal gradients in plasma properties.

Affordable hydrogen production with a low-cost palladium-based nanosheet
Hydrogen energy promises a clean and sustainable future, but its production often depends on expensive platinum-based catalysts, making it costly. The industry needs more affordable alternatives to platinum to make hydrogen energy more viable.
Researchers from the Tokyo University of Science (TUS) have developed a new catalyst called bis(diimino)palladium coordination nanosheets (PdDI). These low-cost palladium-based nanosheets match platinum’s performance in producing hydrogen.

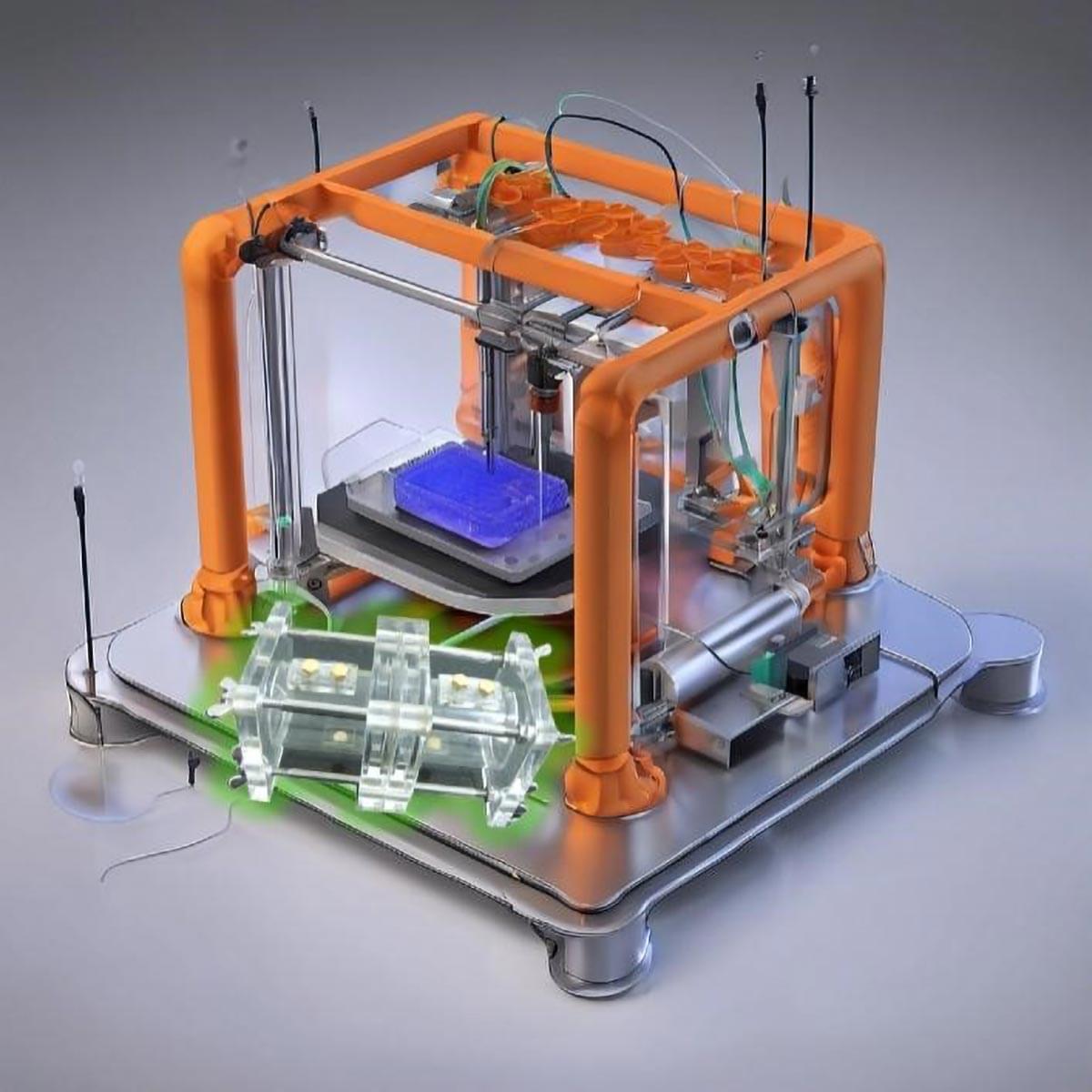
How 3D Printing Is Powering a Cleaner Environment in the Future
3D printing is revolutionizing microbial electrochemical systems (MES) by enabling precise reactor design, custom electrode fabrication, and enhanced bioprinting applications. These innovations optimize pollutant degradation and energy production, with significant implications for sustainability and environmental management.
Microbial electrochemical systems (MES) are emerging as a promising technology for addressing environmental challenges by leveraging microorganisms to transfer electrons. These systems can simultaneously degrade pollutants and generate electricity, making them valuable for sustainable wastewater treatment and energy production.
However, conventional methods for constructing MES components often lack design flexibility, limiting performance optimization. To overcome these limitations and enhance MES efficiency, innovative fabrication techniques are needed—ones that allow precise control over reactor structures and functions.
Mussel-inspired nanoparticle assembly tech to aid energy applications
This method enables applications in photonics, electronics, and advanced materials for energy and environmental use.
This technique will control functional nanoparticle assembly into uniform monolayers over large surfaces.
Employing nanoparticle components is often challenging despite its versatility, especially when fabricating a device. Therefore, scientists presented an electrostatic assembly as a potential solution, where nanoparticles attach to oppositely charged surfaces.
However, this process can take a lot of work, and thus, the South Korean scientists devised the “mussel-inspired” one-shot nanoparticle assembly technique that transports materials from water in microscopic volumes to two-inch wafers in 10 seconds.

Center for Energy Systems Research
Welcome to the age of wireless electricity.
Nikola Tesla once envisioned a world where electricity could be transmitted wirelessly, eliminating the need for wires and revolutionizing energy distribution.
Over a century later, that dream is on the brink of becoming reality.
Companies worldwide, from America’s Wave Inc. to Japan’s Space Power Technologies and New Zealand’s Emrod, are pioneering wireless power transmission technologies. These innovations range from microwave and laser-based energy transfer to solar satellites that beam electricity from space. New Zealand is already testing Emrod’s wireless energy infrastructure, which could provide clean, sustainable power across difficult terrains. Meanwhile, advancements like wireless EV charging roads and underground charging systems are making the technology more practical than ever.
As promising as wireless electricity sounds, challenges remain—chief among them, public skepticism and efficiency concerns.
Despite this, major institutions like Caltech and Purdue University are pushing forward, with projects aimed at developing large-scale wireless power solutions. Whether through inductive charging for electric vehicles, space-based solar power, or rectenna-driven energy grids, the world is inching closer to Tesla’s vision. If successful, wireless electricity could revolutionize industries, eliminate the limitations of traditional power grids, and usher in a new era of energy sustainability.
The future of power might just be as simple as turning on a switch—without plugging in.
