Aug 24, 2023
Starch discovery unlocks benefits for brewing, baking and milling industries
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: energy, food, health
Research has brought clarity to the longstanding question of how starch granules form in the seeds of Triticeae crops—wheat, barley, and rye—unlocking diverse potential benefits for numerous industries and for human health.
Starch in wheat, maize, rice and potatoes is a vital energy-giving part of our diet and a key ingredient in many industrial applications from brewing and baking to the production of paper, glue, textiles, and construction materials.
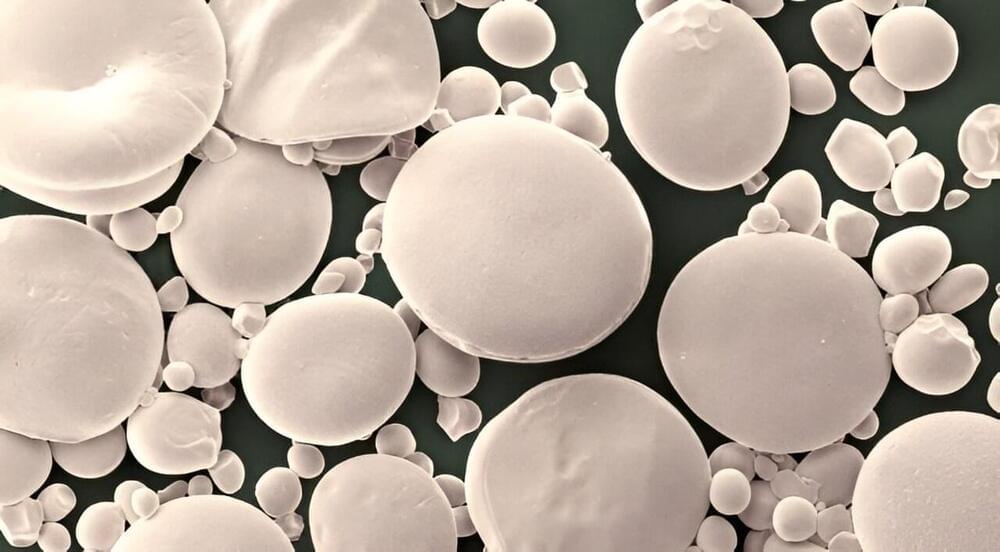
Starch granules of different crops vary greatly in size and shape. Wheat starch (and those of other Triticeae) uniquely have two distinct types of granules: large A-type granules and smaller B-type granules.