Jun 7, 2023
Engineered Liver-On-A-Chip Platform to Mimic Liver Functions and Its Biomedical Applications: A Review
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, computing, engineering
Year 2019 😗😁
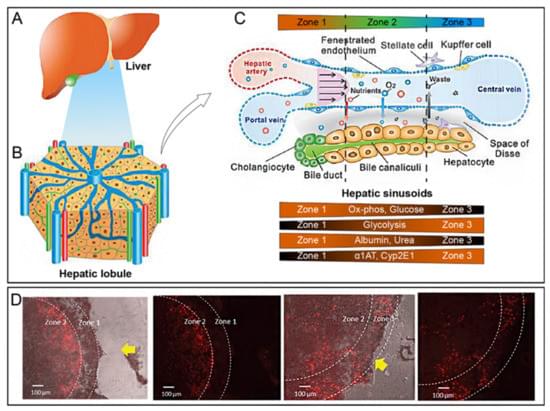
Hepatology and drug development for liver diseases require in vitro liver models. Typical models include 2D planar primary hepatocytes, hepatocyte spheroids, hepatocyte organoids, and liver-on-a-chip. Liver-on-a-chip has emerged as the mainstream model for drug development because it recapitulates the liver microenvironment and has good assay robustness such as reproducibility. Liver-on-a-chip with human primary cells can potentially correlate clinical testing. Liver-on-a-chip can not only predict drug hepatotoxicity and drug metabolism, but also connect other artificial organs on the chip for a human-on-a-chip, which can reflect the overall effect of a drug. Engineering an effective liver-on-a-chip device requires knowledge of multiple disciplines including chemistry, fluidic mechanics, cell biology, electrics, and optics.