Archive for the ‘evolution’ category: Page 11
Aug 16, 2024
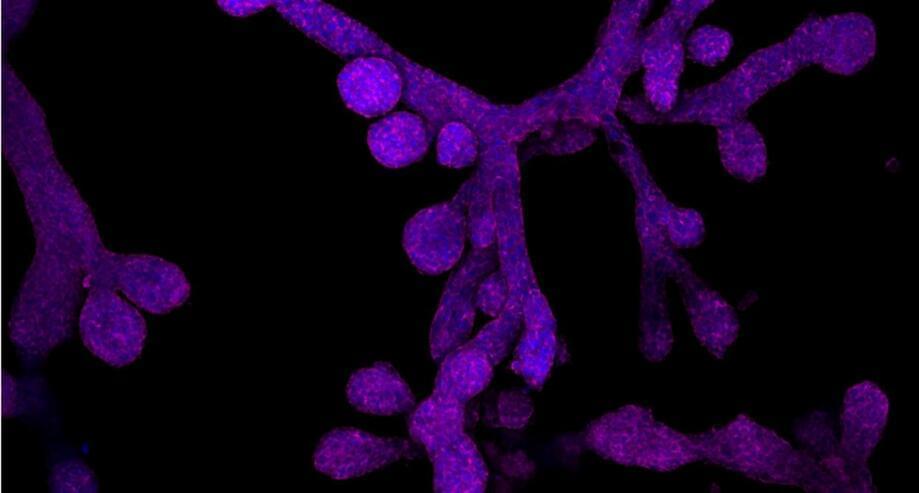
Mammary glands in a dish − what miniature organs reveal about evolution, lactation, regeneration and breast cancer
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, evolution, food
Organoids of mammary glands can help researchers more efficiently study lactation, with findings that could apply to fields ranging from agriculture to medicine.
Aug 14, 2024
Scientists capture clearest glimpse of how brain cells embody thought
Posted by Cecile G. Tamura in categories: evolution, neuroscience
This explores how the human brain forms abstract concepts and adapts to changing environments, specifically looking at how neurons in certain brain regions contribute to complex thinking.
It takes brains to infer how any two things in the world relate to each other, whether it’s the way bad weather links to commuting delays or how environmental conditions lead to the evolution of species. A new study based on recordings in the brains of people has yielded a pathbreaking trove of data that researchers now have used to reveal, with more clarity than ever, the neural incarnations of inferential reasoning.
Aug 14, 2024
Webb Telescope Unveils Evidence of Water and Hydration on Asteroid Psyche
Posted by Laurence Tognetti, Labroots Inc. in categories: evolution, space
“Asteroids are leftovers from the planetary formation process, so their compositions vary depending on where they formed in the solar nebula,” said Dr. Anicia Arredondo. “Hydration that is endogenous could suggest that Psyche is not the remnant core of a protoplanet.”
Could a metallic asteroid contain water and what can this teach us about the asteroid’s formation and evolution? This is what a recent study due for publication in the Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers led by the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) investigated whether the metallic asteroid Psyche —which is one of the largest objects in the main asteroid belt—could contain evidence of water and hydration.
This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of asteroids and what this can teach us about the history of the solar system. This study also comes as NASA’s Psyche spacecraft is currently en route to the Psyche asteroid and is scheduled to arrive in August 2029.
Continue reading “Webb Telescope Unveils Evidence of Water and Hydration on Asteroid Psyche” »
Aug 14, 2024
Rewriting the evolutionary history of critical components of the nervous system
Posted by The Neuro-Network in category: evolution
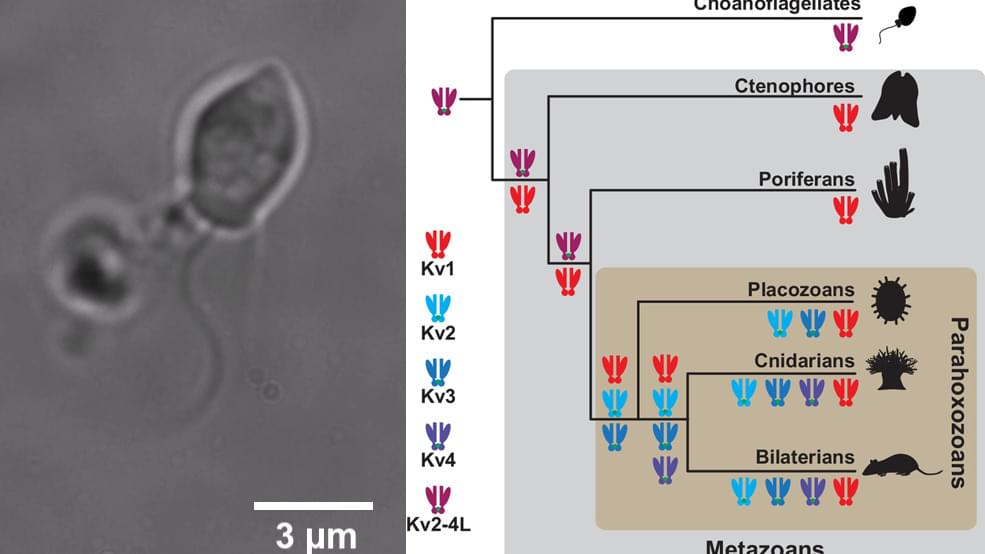
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new study has rewritten the conventionally understood evolutionary history of certain proteins critical for electrical signaling in the nervous system. The study, led by Penn State researchers, shows that the well-studied family of proteins — potassium ion channels in the Shaker family — were present in microscopic single cell organisms well before the common ancestor of all animals. This suggests that, rather than evolving alongside the nervous system as previously thought, these ion channels were present before the origin of the nervous system.
The study appeared in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We tend to think of evolution as a one-way march toward greater and greater complexity, but that often isn’t what occurs in the natural world,” said Timothy Jegla, associate professor of biology in the Penn State Eberly College of Science and leader of the research team. “For example, it was thought that as different kinds of animals evolved and the nervous system became more complex, ion channels arose and diversified to match that complexity. But our research suggests that this is not the case. We have previously shown that the oldest living animals, those with simple nerve nets, have the highest ion channel diversity. This new finding adds to growing evidence that many of the building blocks for the nervous system were already in place in our protozoan ancestors — before the nervous system even existed.”
Aug 10, 2024
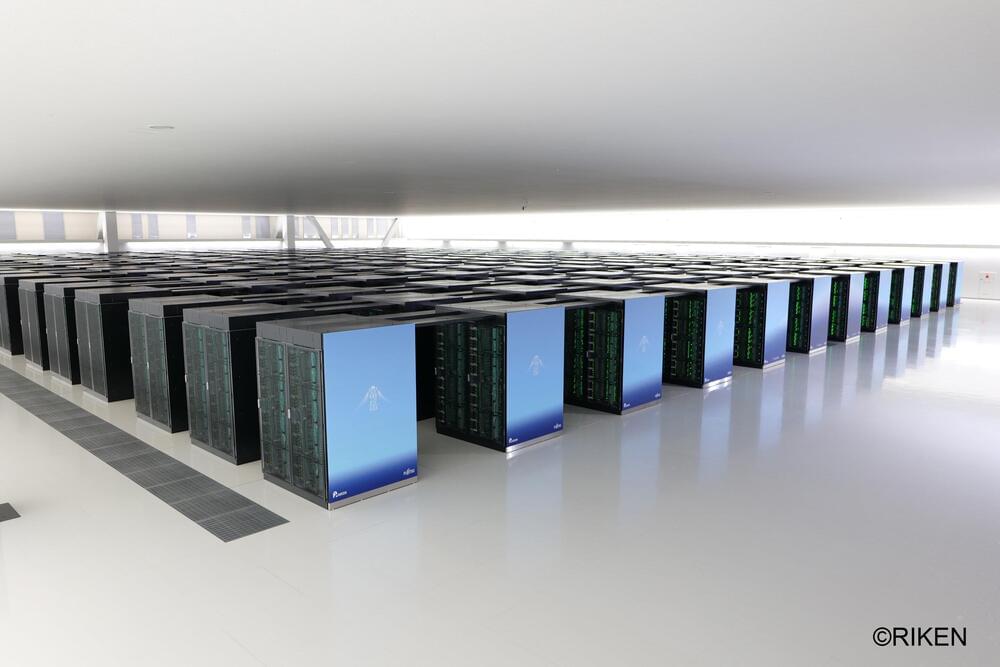
Exploring the evolution of social norms with a supercomputer
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: evolution, supercomputing
Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Computational Science (Japan) and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology (Germany) have published new findings on how social norms evolve over time. They simulated how norms promote different social behavior, and how the norms themselves come and go. Because of the enormous number of possible norms, these simulations were run on RIKEN’s Fugaku, one of the fastest supercomputers worldwide.
Aug 8, 2024
Images from NASA’s DART spacecraft reveal insights into near-Earth asteroid
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: evolution, space
Images that NASA’s DART spacecraft captured of an asteroid moments before it intentionally collided with the object in 2022 have now allowed researchers to gain fresh insights into the celestial bodies.
The slew of studies published this week using data gathered from the asteroids Didymos and Dimorphos are an indication, researchers say, that the DART mission accomplished far more than just proving that potentially dangerous asteroids can be redirected from a trajectory toward Earth.
The findings published Tuesday across five research papers help to characterize the origin, evolution and physical characteristics of the two asteroids, located within 7 million miles of Earth. What the researchers discovered could help scientists better understand binary asteroids, such as Didymos and Dimorphos, in which the smaller body orbits the other.
Aug 8, 2024
Revolutionary GPS Method Reveals Earth’s Crust Movements Post-Earthquake
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: evolution, innovation
A groundbreaking study using sub-daily GPS has improved our understanding of early afterslip following earthquakes, offering a more accurate assessment of seismic hazards and enhancing emergency response and preparedness strategies.
A groundbreaking study has revealed new insights into the Earth’s crust’s immediate behavior following earthquakes. Researchers have utilized sub-daily Global Positioning System (GPS) solutions to accurately measure the spatial and temporal evolution of early afterslip following the 2010 Mw 8.8 Maule earthquake. This innovative approach marks a significant advancement in seismic analysis, offering a more precise and rapid depiction of ground deformations, which is essential for assessing seismic hazards and understanding fault line activities.
The aftermath of an earthquake is marked by intricate postseismic adjustments, particularly the elusive early afterslip. Daily seismic monitoring has struggled to capture the rapid and complex ground movements occurring in the critical hours post-quake. The intricacies of these initial activities and their profound implications for seismic hazard assessment highlight an urgent need for more refined and immediate monitoring techniques.
Aug 6, 2024
Scientists unveil a fascinating new perspective on human consciousness
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: evolution, neuroscience
Scientists propose that human consciousness evolved primarily for social survival, enabling better communication and interaction within communities, rather than just individual benefit, challenging traditional views on the evolution of subjective awareness.
Aug 6, 2024
Impact of Intense UV Radiation on Planet Habitability Around Red Dwarf Stars
Posted by Laurence Tognetti, Labroots Inc. in categories: evolution, space
“This study has changed the picture of the environments around stars less massive than our Sun, which emit very little UV light outside of flares,” said Jason Hinkle.
How can red dwarf stars, which are both smaller and cooler than our Sun, influence the habitability potential for exoplanets orbiting them? This is what a recent study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society hopes to address as a team of international researchers led by the University of Hawai’i investigated how stellar flares emanating from red dwarf stars could help ascertain the habitability potential for exoplanetary systems. This study holds the potential to help astronomers better understand the formation and evolution of exoplanetary systems throughout the cosmos and the conditions necessary for life to exist on these worlds.
For the study, the researchers analyzed near-ultraviolet (near-UV) and far-ultraviolet (far-UV) data obtained from the now-retired NASA GALEX space telescope of 182 stellar flares emitting from 158 stars within 100 parsecs (326 light-years) from Earth. The goal of the study was to ascertain how UV emissions influence whether a planet can host life.
Continue reading “Impact of Intense UV Radiation on Planet Habitability Around Red Dwarf Stars” »