Jan 22, 2024
New study reveals surprising behavior of iron under extreme conditions
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: evolution, space
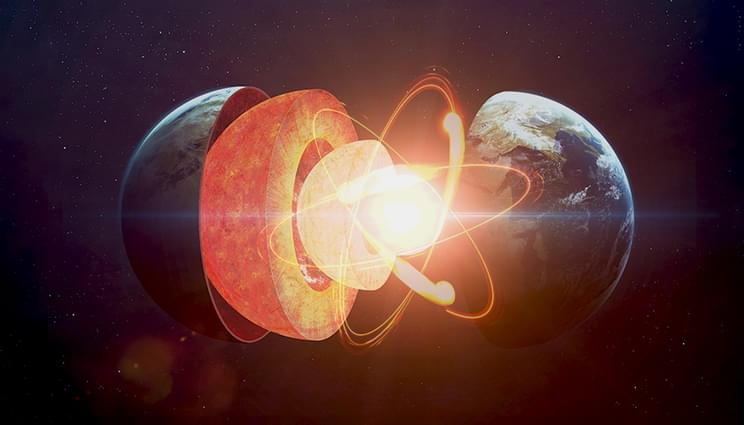
Iron is one of the world’s most abundant elements and a primary component of the Earth’s core. Understanding the behavior of iron under extreme conditions, such as ultra-high pressures and temperatures, has implications for the science of geology and the Earth’s evolution.
In a study conducted by a team led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. researchers combined lasers and X-ray diffraction methods to examine how different crystal structures of iron are related to each other and what happens when it melts at ultrahigh pressures and temperatures. The paper was published in the journal Physical Review B.
Using the Dynamic Compression Sector beamline at Argonne National Laboratory, researchers applied nanosecond laser shock compression to iron at pressures up to 275 gigapascals (GPa) — more than 2 million times atmospheric pressure — and used in situ picosecond X-ray diffraction to study the structure of the iron under these extreme conditions. Authors said the ability to gather this novel data on iron provides insights into materials science and the internal dynamics of Earth and other terrestrial exoplanets.