Archive for the ‘food’ category: Page 248
Feb 18, 2019
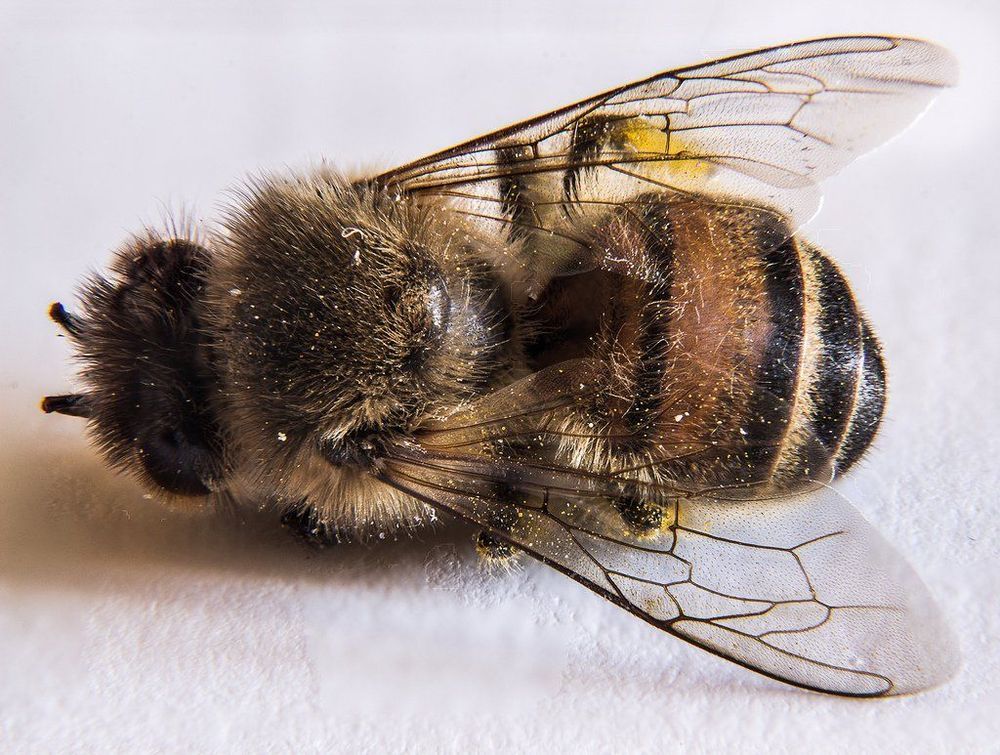
France Becomes First Country In Europe To Ban All Pesticides Linked To Bee Deaths
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: food
The excessive use of pesticides has brought about numerous disastrous effects on the environment, and among them, it has recently drastically reduced the bee population in various areas of the world. Yet, not many countries took remedial measures, even after realizing the dangers, but this was not the case with France.
It is on track to becoming the first European country to ban five pesticide varieties, as scientists believe that these neonicotinoids are extremely dangerous since they kill bees.
However, while bee-keepers and environmentalists are extremely happy with this decision, sugar beet and cereal farmers are not very excited about it, since they are afraid that in this way, their crops will be more prone to pests and insects.
Feb 18, 2019
Machine learning unlocks plants’ secrets
Posted by James Christian Smith in categories: biological, food, robotics/AI
Plants are master chemists, and Michigan State University researchers have unlocked their secret of producing specialized metabolites.
The research, published in the latest issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, combined plant biology and machine learning to sort through tens of thousands of genes to determine which genes make specialized metabolites.
Some metabolites attract pollinators while others repel pests. Ever wonder why deer eat tulips and not daffodils? It’s because daffodils have metabolites to fend off the critters who’d dine on them.
Continue reading “Machine learning unlocks plants’ secrets” »
Feb 18, 2019
Potential food allergens in medications
Posted by James Christian Smith in categories: biotech/medical, food, health
Imagine taking medicine oblivious to the fact that a food allergy can effect you taking simply medicine.
Certain substances derived from foodstuffs are used as excipients in drugs and vaccines for their pharmaceutical properties. Some of these food-derived excipients contain food proteins either intentionally or unintentionally as contaminants. As such, patients who have IgE antibodies directed against these food proteins are theoretically at risk for allergic reactions when exposed to the food proteins in the medications. However, such reactions are quite rare, usually because the amount of food protein is not present in a large enough quantity to elicit a reaction or because the particular protein is not a common allergen. When the food protein appears as an unintentional contaminant, the amount of protein, if any, that is present might be variable and might elicit reactions only from some lots of medication that happen to contain more of the food protein or illicit reactions only in patients who are exquisitely sensitive or happen to have IgE antibodies directed against a particular epitope in the contaminating protein. In most circumstances these medications should not be routinely withheld from patients who have particular food allergies because the overwhelming majority will tolerate the medications uneventfully. However, if a particular patient has had an apparent allergic reaction to the medication, allergy to the food component should be investigated as a possible cause. Even in this circumstance (ie, an allergic reaction to a medication in a patient allergic to a particular food and the presence of the food protein in the medication), the food protein would still have to be demonstrated to be causal by using appropriate testing because other allergens present in the medication could have been the cause or the medication might be capable of non–IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation.
Feb 12, 2019
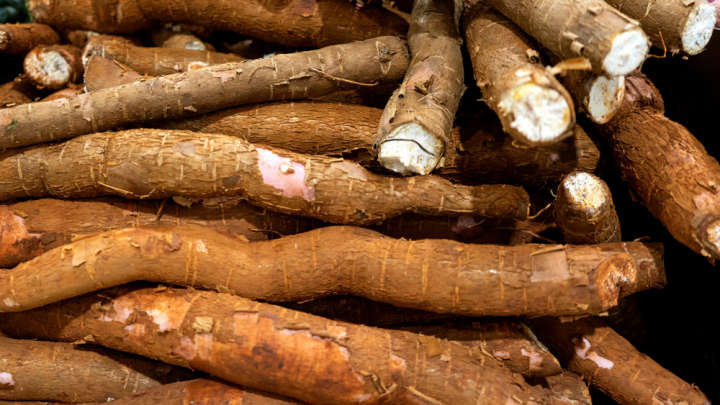
Genetically Modified Super-Charged Cassava Could Help Stamp Out Malnourishment In Africa
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, food, genetics
Over 800 million people depend on cassava as a main food staple. Also known as manioc and yuca, this root vegetable also makes up around 50 percent of the caloric intake of around one-third of people in sub-Saharan Africa.
Unfortunately, it isn’t the most nutritious of food sources. As a result, iron and zinc deficiencies are sky high in many parts of Africa. It’s estimated that up to 75 percent of preschool children and 67 percent of pregnant women in Nigeria are anemic as a result of iron deficiency.
However, researchers have now developed super-charged cassavas using genetic engineering to enrich the plant with significantly higher levels of both iron and zinc.
Feb 8, 2019
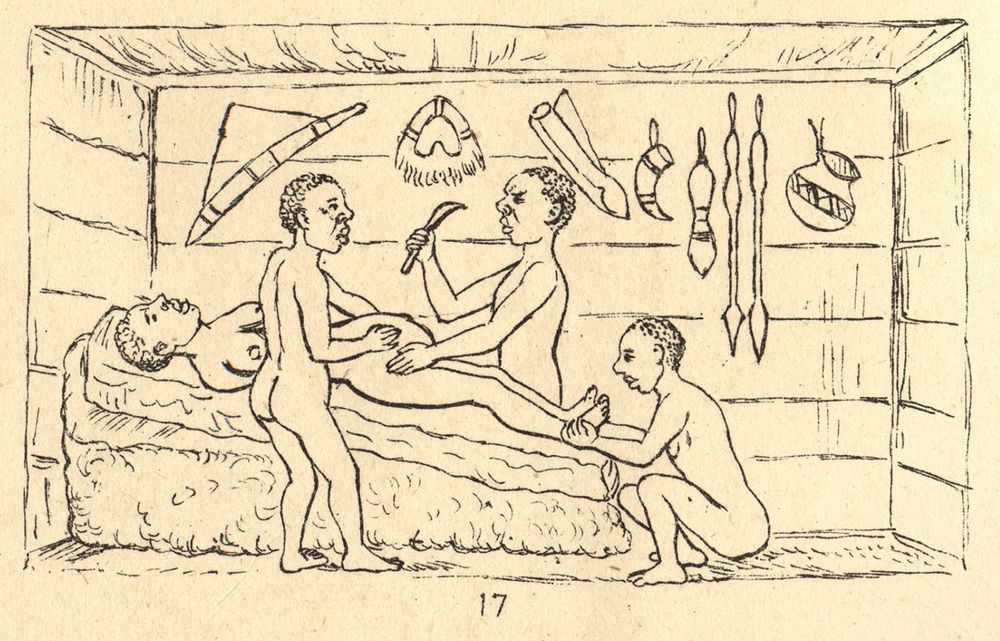
Cesarean Section — A Brief History
Posted by James Christian Smith in categories: biotech/medical, food
While Barry applied Western surgical techniques, nineteenth-century travelers in Africa reported instances of indigenous people successfully carrying out the procedure with their own medical practices. In 1879, for example, one British traveller, R.W. Felkin, witnessed cesarean section performed by Ugandans. The healer used banana wine to semi-intoxicate the woman and to cleanse his hands and her abdomen prior to surgery. He used a midline incision and applied cautery to minimize hemorrhaging. He massaged the uterus to make it contract but did not suture it; the abdominal wound was pinned with iron needles and dressed with a paste prepared from roots. The patient recovered well, and Felkin concluded that this technique was well-developed and had clearly been employed for a long time. Similar reports come from Rwanda, where botanical preparations were also used to anesthetize the patient and promote wound healing.
In Western society women for the most part were barred from carrying out cesarean sections until the late nineteenth century, because they were largely denied admission to medical schools. The first recorded successful cesarean in the British Empire, however, was conducted by a woman. Sometime between 1815 and 1821, James Miranda Stuart Barry performed the operation while masquerading as a man and serving as a physician to the British army in South Africa.
If pairing wine with food is an art, then consider this episode a masterpiece. The guys drink their way around town, from donut shops to Thai food in a tattoo parlor.
Weed MARIJUANA Travel Steak Culture Cannabis Munchies meatballs Documentary Hip-Hop seafood Pasta Brooklyn DABBING cooking moonshine duck feast wine rap Queens Tattoos history Italian food NEW YORK CITY Red Hook BBQ Fine Dining Smoking Tattooing friendship concert Thai Food Donuts vice_videos: premiere spirits sauce Natural Wine barbeque food pairings clams chicken parm chiense food carrol gardens.
Feb 7, 2019
A very small number of crops are dominating globally. That’s bad news for sustainable agriculture
Posted by Xavier Rosseel in categories: food, sustainability
A new U of T study suggests that globally we’re growing more of the same kinds of crops, and this presents major challenges for agricultural sustainability on a global scale.
The study, done by an international team of researchers led by U of T assistant professor Adam Martin, used data from the U.N.’s Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) to look at which crops were grown where on large-scale industrial farmlands from 1961 to 2014.
They found that within regions crop diversity has actually increased — in North America for example, 93 different crops are now grown compared to 80 back in the 1960s. The problem, Martin says, is that on a global scale we’re now seeing more of the same kinds of crops being grown on much larger scales.
Feb 3, 2019
Plastics are being glued together in the ocean by bacteria, scientists find
Posted by Xavier Rosseel in categories: chemistry, food, particle physics
Researchers at Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh used water collected from the Faroe-Shetland Channel and the Firth of Forth to set up their experiments. Plastics were added to the seawater and then incubated in conditions simulating the ocean’s surface. Within minutes, the minuscule pieces of plastic grouped together with bacteria, algae and other organic particles. The scientists are said to have been surprised to discover large masses of biopolymers formed the bulk of these plastic agglomerates. Team member Stephen Summers said: “This is a first step towards understanding how nanoplastics interact with natural biopolymers throughout the world’s oceans. ”This is very important, as it is at this small scale that much of the world’s biogeochemistry occurs. ”We found that the biopolymers envelope or engulf the nanoplastic particles, which caused the plastics to agglomerate into clumps. ”The nanoplastics, which are 100–200 times smaller than a bacterial cell, were actually incorporated into the agglomerates, which became visible to the naked eye in our lab experiments. ”The fact that these agglomerates become large enough to see raises concern, as they are likely to be seen as a food source by small marine animals.” We found that the biopolymers envelope or engulf the nanoplastic particles, which caused the plastics to agglomerate into clumps.
Researchers said micro and nano plastic particles mix with the bacteria secretions within minutes, forming clumps.

Continue reading “Plastics are being glued together in the ocean by bacteria, scientists find” »
Feb 2, 2019
An Arkansas Teen Helped Turn Tea Leaves and Molasses Into a Supercapacitor
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: food, materials
In the search for people working on cheaper supercapacitors, she found herself in the lab of Noureen Siraj, Ph.D., an assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Arkansas, Little Rock. One of Siraj’s students, Samantha Macchi, had already been working on such a project for about a year and a half, figuring out how to make supercapacitor electrodes from common materials like used tea leaves, molasses, and a basic kitchen microwave oven — humble beginnings for a high-tech device. Siraj and Macchi brought Bollimpalli onto the project to learn about the work, which she later presented at ISEF. Meanwhile, Macchi and Siraj published the resulting research in January in the journal Chemistry Select.
Bollimpalli was initially assigned to a different project in the lab, but when she found out about the work on supercapacitors, she asked to switch tasks. Siraj, who is used to having high school students learn about her team’s work, quickly obliged.
“She quickly learned all the protocols, and she actually was able to explain. She brought an understanding that is missing in a lot of the high school students,” Siraj tells Inverse. “She really is good at absorbing the information.” They worked together tirelessly to help Bollimpalli nail the presentation she would later give at ISEF.
Continue reading “An Arkansas Teen Helped Turn Tea Leaves and Molasses Into a Supercapacitor” »