When it is a matter of survival, predation trumps symbiosis.
Corals eat their algal partners during food scarcity.
When it is a matter of survival, predation trumps symbiosis.
Corals eat their algal partners during food scarcity.

BEIJING, Aug. 24, 2023 /PRNewswire/ — On August 22, the 2023 World Robot Conference (WRC), which was held in Beijing with the theme of “Spurring Innovation for the Future,” came to a big success. The 2023 World Robotics Expo and the 2023 World Robot Contest took place at the same time, bringing together about 160 robotics companies and scientific research institutions from around the globe, and showcasing close to 600 advanced technologies and products, over 320 representatives from international organizations, academicians, renowned experts, and entrepreneurs at home and abroad have been invited to attend.
As a general robotics company, Dreame Technology took center stage for the first time at the World Robot Conference. It unveiled a wide range of robots, including general-purpose humanoid robots, consumer-grade bionic quadruped robots, industrial-grade quadruped robots, wireless Robotic Pool Cleaner, commercial food delivery robots and floor-cleaning robots. This range highlighted Dreame’s broad competitiveness across the fields of R&D for robotic ecosystems and technologies, supply chains, production and manufacturing, talent development, and commercialization.
Oral tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are a class of cancer drugs that can be highly susceptible to issues with solubility in the gastrointestinal tract. Most crystalline TKI drugs have pH-dependent solubility that affects their bioavailability in an oral dosage form. Consequently, natural variations in gastric pH, or variations due to eating or taking antacids, can significantly impact drug absorption and, in turn, therapeutic efficacy.
Alternative formulation techniques such as amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) can still deliver the convenience of a pill while reducing TKIs’ sensitivity to physiological variation. This ensures more consistent—and higher—bioavailability. This whitepaper outlines the challenges associated with pH-dependent solubility for oral TKI drugs and reviews how leveraging ASD formulation can help create more effective, patient-friendly drug products.
It can be time consuming to test food and drink for potentially harmful bacteria, but viruses that naturally attack the bacteria can be gene edited to speed up the process.
Research has brought clarity to the longstanding question of how starch granules form in the seeds of Triticeae crops—wheat, barley, and rye—unlocking diverse potential benefits for numerous industries and for human health.
Starch in wheat, maize, rice and potatoes is a vital energy-giving part of our diet and a key ingredient in many industrial applications from brewing and baking to the production of paper, glue, textiles, and construction materials.
Starch granules of different crops vary greatly in size and shape. Wheat starch (and those of other Triticeae) uniquely have two distinct types of granules: large A-type granules and smaller B-type granules.
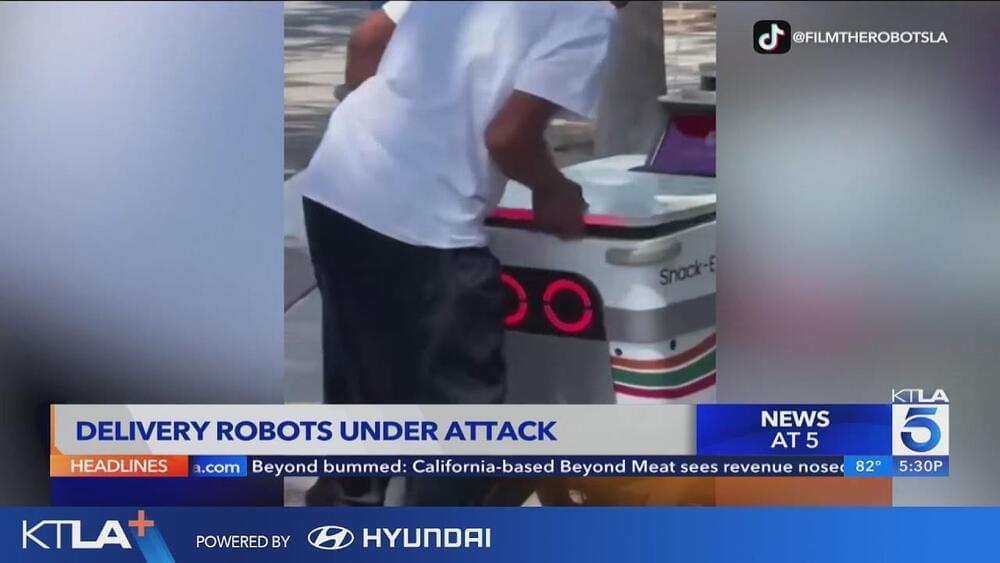
The popularity of remote food delivery skyrocketed during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the trend has continued to help businesses thrive years later. Unfortunately, some of the robotic delivery vehicles are taking a beating, with several viral videos showing people kicking the autonomous bots over and even stealing the products inside.
KTLA 5’s Rachel Menitoff reports. (Aug. 7, 2023)
KTLA 5 News — Keeping Southern Californians informed since 1947.
“The invention, which cooks cylinder-shaped pizzas and other foods, recently moved on to the final phase of NASA’s Deep Space Food Challenge.”
The invention, which cooks cylinder-shaped pizzas and other foods, is now being adjusted for zero-gravity with the help of BioServe Space Technologies.
Throughout the history of human civilization, energy has been holding an imperative role in humanity’s progress1. Especially in the past few centuries, innovations in the harnessing of power have catalyzed humanity’s rapid growth2. Energy remains a key driver of human development3, with each revolution in industry and agriculture highlighting human’s reliance on it. Revolution in the eighteenth century was a turning point. The development of steam engines powered by fossil fuels led to significant technological progress4. Electricity has then opened new possibilities for the future5. Humanity has grown at a compound annual rate of 2.43% from 1965 to 2020, demonstrating our continued increasing demand for and consumption of energy6,7. However, the pace at which human being can progress as a civilization in the future remains uncertain.
While mankind was establishing its identity in the universe, insatiable human curiosity over the realm of civilization peaked in the 1960s8, which led to deeper cogitation of the concept of civilization. Providing that some of the extraterrestrial civilizations are highly likely million years more advanced than mankind, Soviet astrophysicist Nikolai Kardashev proposed a scale to classifies a civilization’s technological development based on its energy consumption9, which was later known as the Kardashev Scale. The scale initially categorized civilizations into three types. Type 1 is known as the planetary civilization, which features the capability of harnessing and utilizing all forms of energies that can be reached on the host planet, such as wind, solar, and geothermal power; Type 2 and 3, known as the stellar and galactic civilizations, respectively, are capable of extracting and utilizing all energy created by their respective systems9. Yet, such a scale proved lackluster in the quantitative presentation of the civilization types. Subsequently, Carl Sagan furthered the Kardashev Scale with data extrapolation, and proposed a continuous function quantifying the Kardashev Scale in index K10
$$K=\frac{.
A new discovery by the Polytechnic University of Milan opens up new perspectives in the field of sustainable chemical synthesis, promoting innovative solutions that allow chemicals to be created in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way. The findings were recently published in the journal Nature Synthesis.
Using the innovative technique of dispersing isolated atoms on carbon nitride supports, the team developed a catalyst that is more active and selective in esterification reactions. This is an important reaction in which carboxylic acids and bromides are combined to form products used in the manufacture of medicines, food additives, and polymers.
The revolutionary feature of this new catalyst is that it reduces the use of rare metals, a significant step towards conserving critical resources and making processes more sustainable. In addition, the catalyst can be activated by sunlight, eliminating the need for energy-intensive methods. This discovery holds enormous potential in reducing dependence on finite resources and lowering the environmental impact of catalytic processes.
