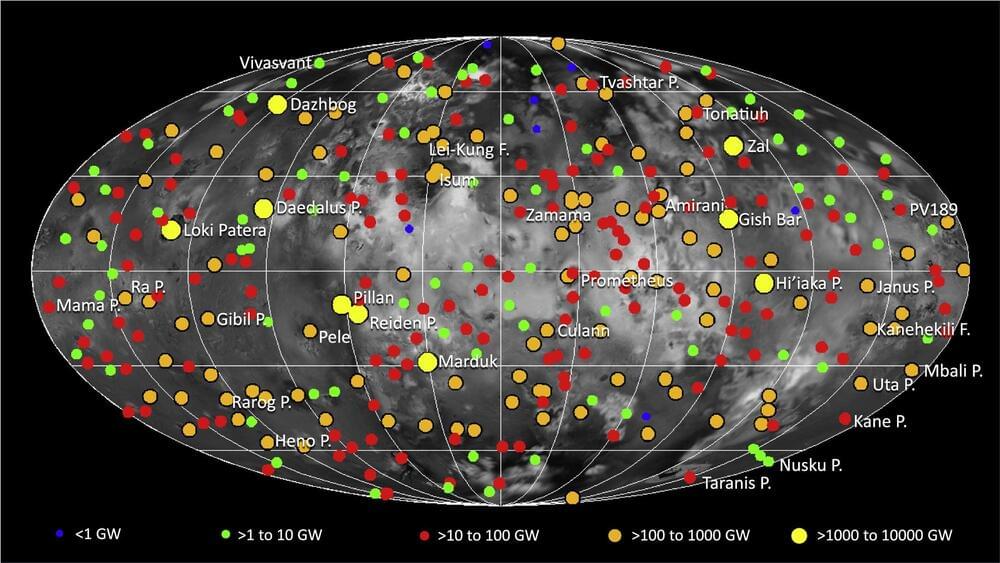
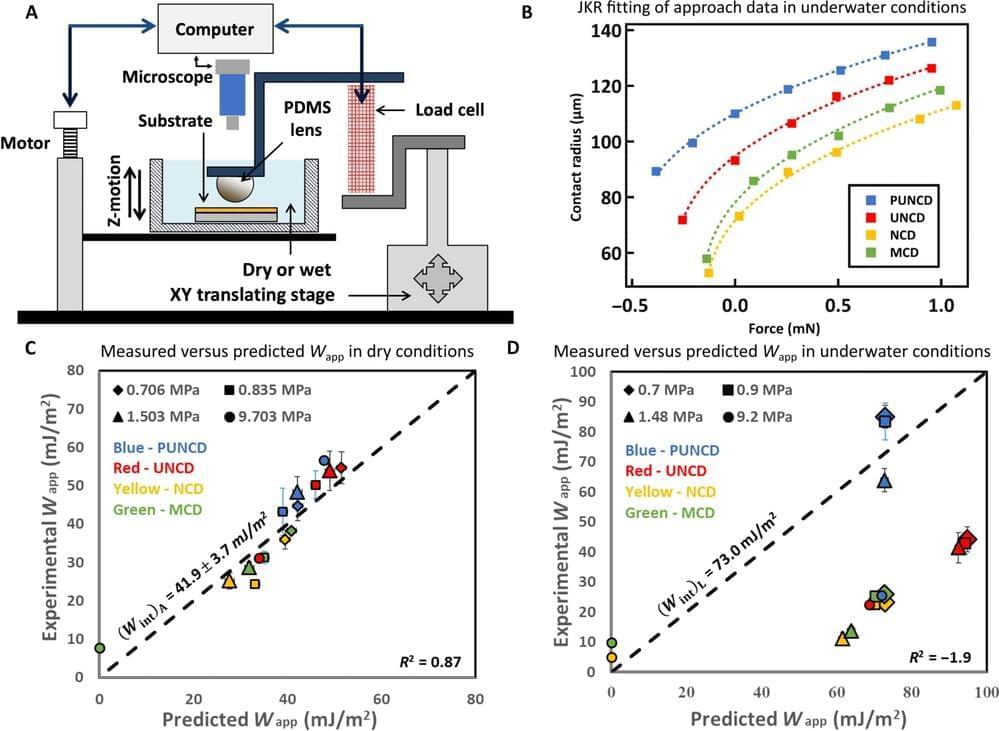
Don’t fall into the determinism trap. Everything is, in fact, random, says chemist Lee Cronin.
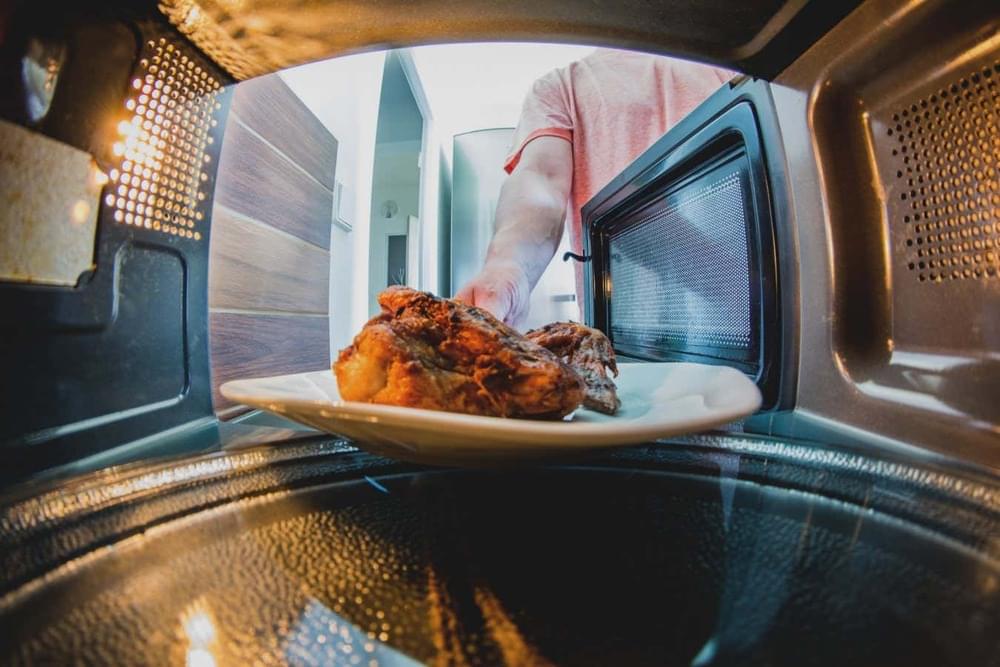


Microwaves in homes, offices and laboratories have been found to host diverse microbiomes, highlighting the importance of regular cleaning.
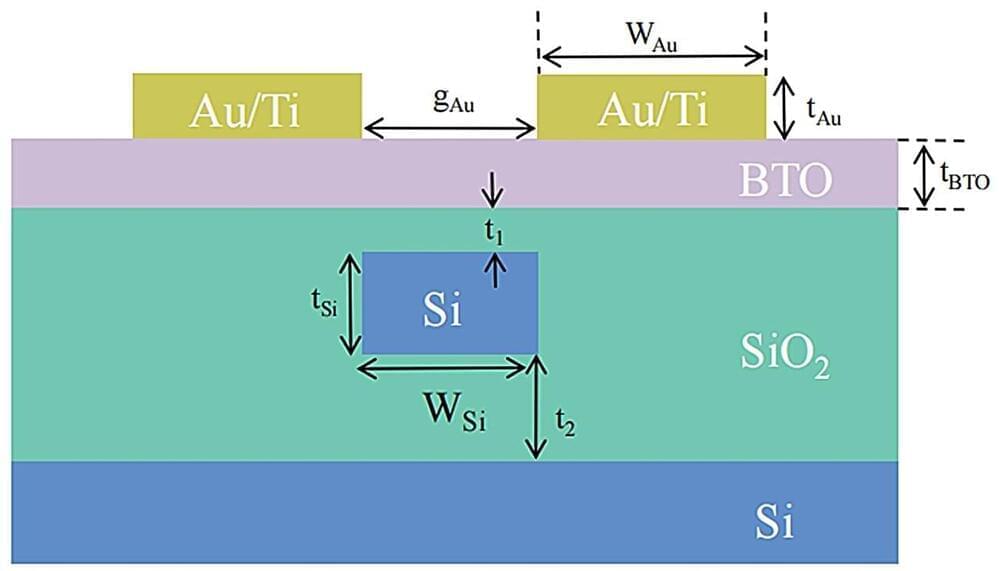
Future optical communication and signal processing systems will require high-volume optical links, wherein photonic integrated devices play a key role. Si photonics is currently among the most advanced techniques for realizing low-cost PIC. However, despite their enormous potential, there remain basic restraints on light modulation in SOI waveguides. The absence of a linear EO coefficient is challenging because of the crystal structure of Si.

New cooling technologies that incorporate energy storage could help by charging themselves when renewable electricity is available and demand is low, and still providing cooling services when the grid is stressed.
“We say, take the problem, and turn it into a solution,” says Yaron Ben Nun, founder and chief technology officer of Nostromo Energy.
One of Nostromo Energy’s systems, which it calls an IceBrick, is basically a massive ice cube tray. It cools down a solution made of water and glycol that’s used to freeze individual capsules filled with water. One IceBrick can be made up of thousands of these containers, which each hold about a half-gallon, or roughly two liters, of water.

If you thought the Great Reset was a lot to process and fight, hang on to your hats. The global elite, never satisfied with their power and always seeking more, have introduced a new phase of their agenda. Called the “Great Narrative,” it capitalizes upon the decay in Western values to realign power. It is not a coincidence that in the World Economic Forum’s “8 Predictions for the World in 2030” video, #2 was “The U.S. won’t be the world’s leading superpower. A handful of countries will dominate” and #8 was “Western values will have been tested to the breaking point.”
This Great Narrative framework is enabled by more than just pure societal malaise. It harnesses advanced technologies, from artificial intelligence to robotics to help shift the power structure in a new world order. Glenn Beck covers this plan and how to fight back in his truly important new book, “Dark Future.”

When an interdisciplinary conference lasts a little longer…
929 likes, — adamdthompson on July 22, 2024: ‘Mine in this week’s @newyorkermag’