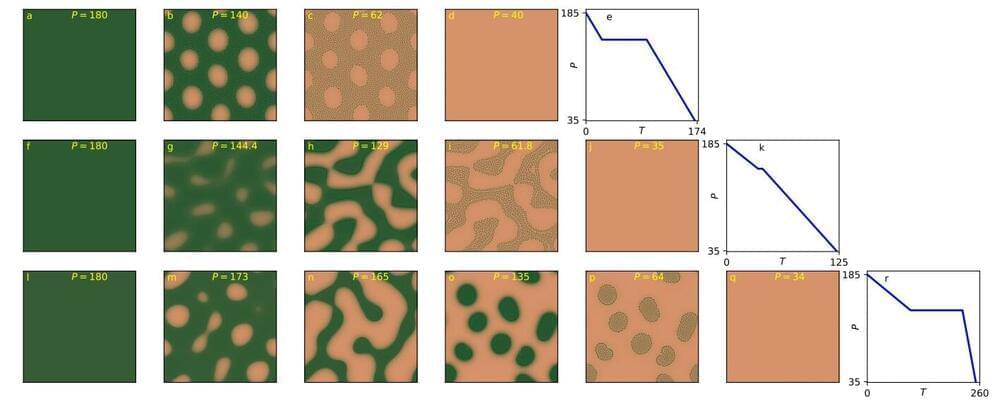
Fairy circles, a nearly hexagonal pattern of bare-soil circular gaps in grasslands, initially observed in Namibia and later in other parts of the world, have fascinated and baffled scientists for years. Theories for their appearance range from spatial self-organization induced by scale-dependent water-vegetation feedback to pre-existing patterns of termite nests.
Prof. Ehud Meron of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has been studying the Namibian fairy circles as a case study for understanding how ecosystems respond to water stress. He believes that all theories to date have overlooked the coupling between two robust mechanisms essential for understanding ecosystem response: phenotypic plasticity at the level of a single plant, and spatial self-organization in vegetation patterns at the level of a plant population.
Phenotypic plasticity is the plant’s ability to change its own traits in response to environmental stresses.