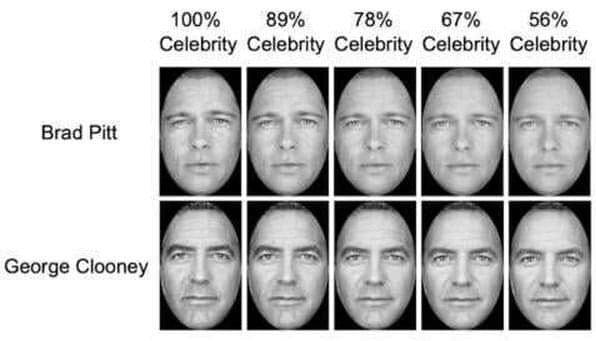
Their popularity makes celebrities easy to spot. Strangers, however, can also get mistaken for celebrities, resulting in cases of false “celebrity sightings.” In attempting to explain the contradiction, a University of California, Riverside, study reports that celebrity faces are remembered more precisely but less accurately.
Precision, in this context, refers to how memories for a particular face resemble each other over repeated memory retrievals, which can be likened to the clustering of arrows on a target in archery. Accuracy measures how remembered faces resemble newly encountered faces—or the deviation from the target in archery.
“What our findings say is that people might accept errors by misidentifying someone as a celebrity in the interest of securing a ‘celebrity sighting,’” said Weiwei Zhang, an associate professor of psychology, who led the study that appears in the journal Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. “Our study explains why people are good and bad at spotting celebrities and highlights the importance of assessing both memory imprecision and bias in memory performance.”