Sep 27, 2022
Epigenetic aging and perceived psychological stress in old age
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: genetics, life extension, neuroscience
Additionally, epigenetic changes were suggested to be a possible link [30, 31] between adverse childhood experiences and mortality as well as higher morbidity burden in late life [32]. It was proposed that this link could be mediated by health-adverse coping mechanisms (activated as a result of high levels of anxiety and depression) that are associated with adverse childhood experiences [33]. Some of these coping strategies, such as smoking, alcohol abuse and and a high BMI resulting from unhealthy eating habits, were shown to be associated with DNAmAA in some studies [34,35,36]. However, these results were not unequivocally replicated [37,38,39] (reviewed in ref. [40]).
Previous studies that examined the relationship between DNAmAA and stress operationalized stress as low socioeconomic status (SES) [41, 42], (childhood) trauma [26, 43,44,45], racial discrimination [46], or exposure to violence [47]. Many previous studies on the topic focused on changes in DNAm age during childhood as this period is known to be particularly prone to stress-related epigenetic changes [29].
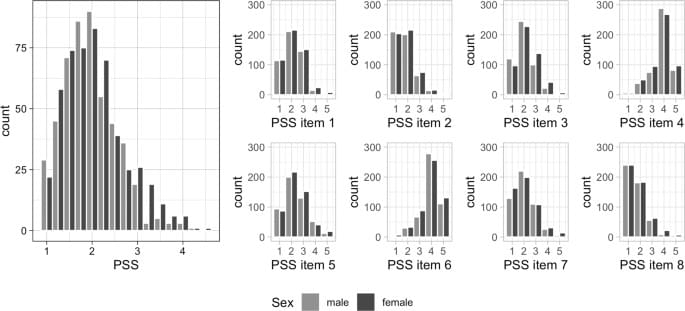
In contrast, in this work we focus on older age which was shown to be the second most vulnerable phase in a person’s life in terms of epigenetics [29]. As epigenetic modifications remain even after the psychological stimulus has ceased there is the possibility of cumulating effects on the epigenome exerted by repeated psychological stressors [29]. Specifically, we analyzed the association between the amount of experienced stress (measured by Cohen’s Perceived Stress Scale [PSS] [48]) and several DNAm age estimators (i.e. the 7-CpG clock [49], Horvath’s clock [50], Hannum’s clock [51], PhenoAge [34], GrimAge [52]) in 1,100 older adults. While the PSS represents a well-established marker of perceived stress [48], to our knowledge it has not been investigated in the context of epigenetic aging before. While we were able to replicate well-established associations with perceived stress, none of the five epigenetic clocks analyzed in the current study were associated with the perception of stress.