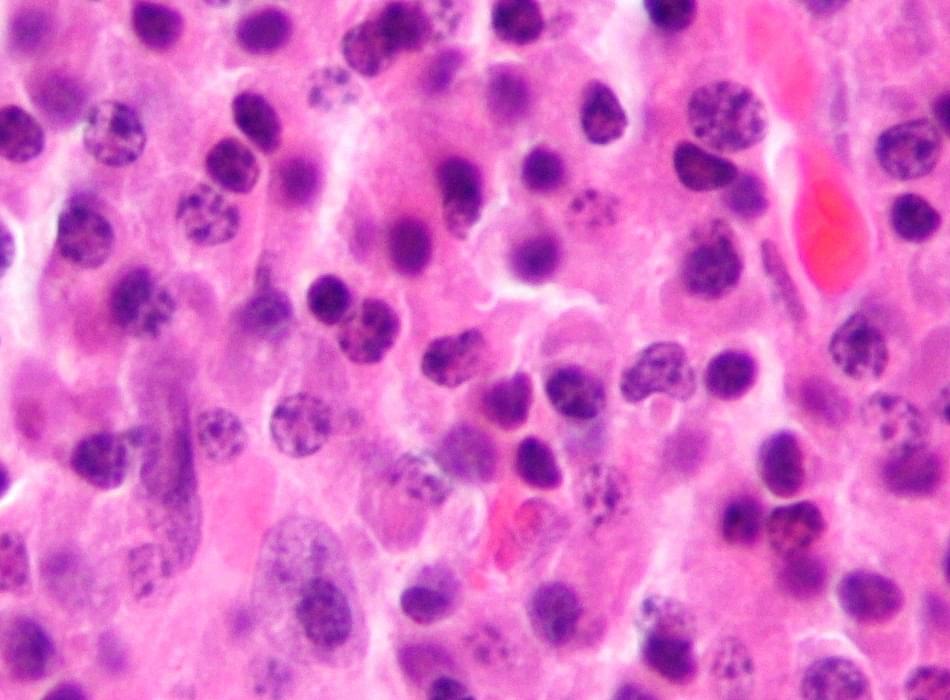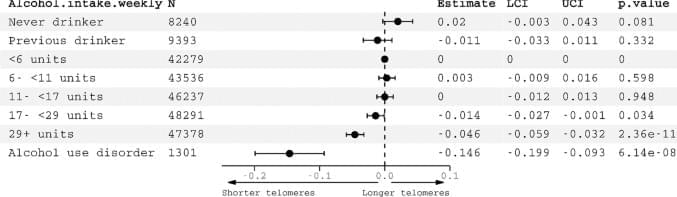
Observational studies of the relationship between alcohol use and telomere length have produced conflicting results. The largest such study to date, of 4,567 individuals, found no association between alcohol intake and either baseline or longitudinal change in telomere length [9]. Another analysis of two American cohorts (n = 2623) also reported null findings [10]. On the other hand, a few small studies (sample size range: 255‑1800) have observed associations with heavy drinking or AUD. Participants with AUD have been reported to have shorter telomeres compared to healthy controls [11]. A longitudinal study of Helsinki businessmen observed that higher midlife alcohol consumption was associated with shorter telomere length in older age [8]. Drinking 30 g/day of alcohol in older participants was associated with shorter telomeres in a Korean study [12]. Associations were stronger in those experiencing the alcohol flush reaction, raising the intriguing possibility that acetaldehyde, ethanol’s toxic breakdown product, is mechanistically involved. In a recent review of 27 studies, 10 showed significant associations between alcohol use and telomere length [13]. The studies included cross-sectional and longitudinal designs. The majority comprised European participants with ages ranging from the third to seventh decade. Most studies observed positive associations between alcohol and LTL. However heterogeneity between studies in methods of quantifying telomere length and categorizing alcohol intake hindered meta-analysis and aggregation of the data.
MR seeks to identify potentially causal determinants of an outcome. It estimates the association between genetically predicted levels of an exposure and an outcome of interest. Residual confounding and reverse causation aim to be less of a concern than in most other methods of analyzing observational data [14]. With MR, genetic proxies can be used to study the effects of genetically-predicted variability in alcohol consumption or AUD risk. To our knowledge, no MR study of alcohol and telomere length has yet been attempted.
We conducted a large observational study of two alcohol phenotypes, alcohol consumption and AUD, and leucocyte. We then performed linear MR analyses to investigate the evidence for a causal effect between alcohol consumption/AUD and LTL. Estimates generated by our observational and genetic methods were compared. Genetic distinction between different alcohol use traits motivates their separate analysis. Quantity/frequency measures such as drinks per week and AUDIT-C (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Consumption, a 3 item screening tool), while moderately genetically correlated with AUD, have distinct patterns of genetic correlation with other traits [13]. Furthermore, as there has been much speculation about potential J-shaped relationships between alcohol and health outcomes [15], we performed a non-linear MR analysis to examine the shape of the relationship between alcohol consumption and telomere length.