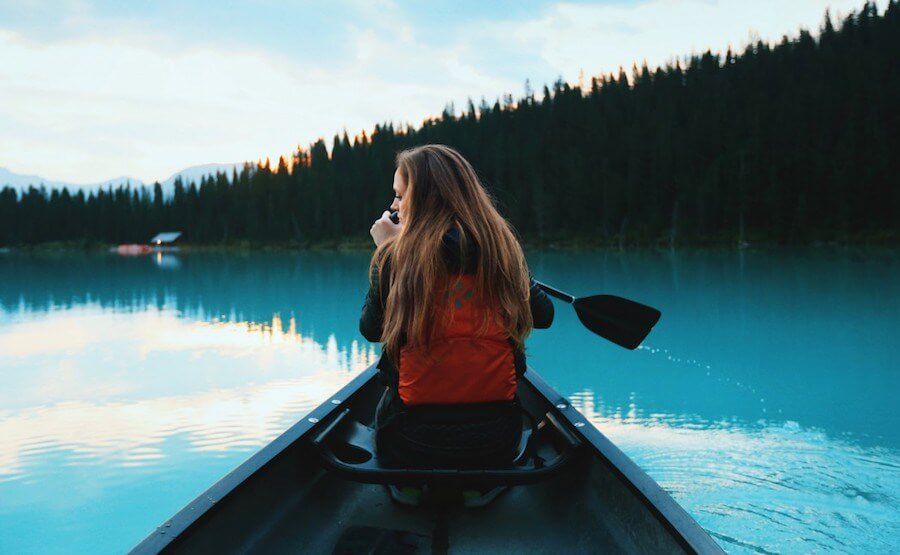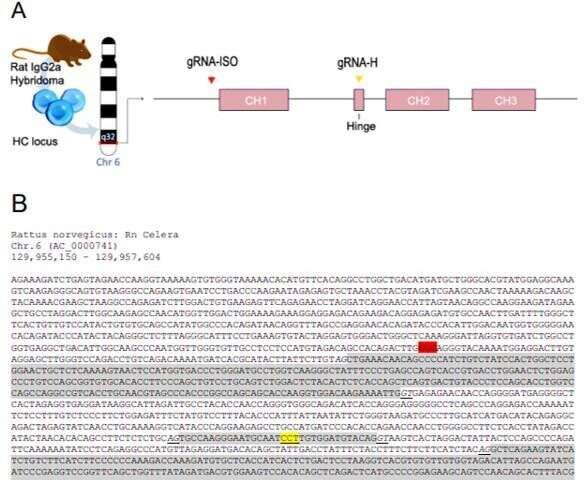
Bioengineers and life scientists incorporate hybridoma technology to produce large numbers of identical antibodies, and develop new antibody therapeutics and diagnostics. Recent preclinical and clinical studies on the technology highlight the importance of antibody isotypes for therapeutic efficacy. In a new study, a research team in Netherlands have developed a versatile Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindrome Repeats (CRISPR) and homology directed repair (HDR) platform to rapidly engineer immunoglobin domains and form recombinant hybridomas that secrete designer antibodies of a preferred format, species or isotype. In the study, Johan M. S. van der Schoot and colleagues at the interdisciplinary departments of immunology, proteomics, immunohematology, translational immunology and medical oncology, used the platform to form recombinant hybridomas, chimeras and mutants. The stable antibody products retained their antigen specificity. The research team believes the versatile platform will facilitate mass-scale antibody engineering for the scientific community to empower preclinical antibody research. The work is now published on Science Advances.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) have revolutionized the medical field with applications to treat diseases that were once deemed incurable. Hybridoma technology is widely used since 1975 for mAb discovery, screening and production, as immortal cell lines that can produce large quantities of mAbs for new antibody-based therapies. Scientists had generated, validated and facilitated a large number of hybridomas in the past decade for preclinical research, where the mAb format and isotypes were important to understand their performance in preclinical models. Genetically engineered mAbs are typically produced with recombinant technology, where the variable domains should be sequenced, cloned into plasmids and expressed in transient systems. These processes are time-consuming, challenging and expensive, leading to outsourced work at contract research companies, which hamper the process of academic early-stage antibody development and preclinical research.
In its mechanism of action, the constant antibody domains forming the fragment crystallizable – (Fc) domain are central to the therapeutic efficacy of mAbs since they engage with specific Fc receptors (FcRs). Preceding research work had highlighted the central role of Fc in antibody-based therapeutics to emphasize this role. Since its advent, CRISPR and associated protein Cas-9 (CRISPR-Cas9)-targeted genome editing technology has opened multitudes of exciting opportunities for gene therapy, immunotherapy and bioengineering. Researchers had used CRISPR-Cas9 to modulate mAb expression in hybridomas, generate a hybridoma platform and engineer hybridomas to introduce antibody modification. However, a platform for versatile and effective Fc substitution from foreign species within hybridomas with constant domains remains to be genetically engineered.