Jumping genes — not jumping beans.
“Jumping genes” are ubiquitous. Every domain of life hosts these sequences of DNA that can “jump” from one position to another along a chromosome; in fact, nearly half the human genome is made up of jumping genes. Depending on their specific excision and insertion points, jumping genes can interrupt or trigger gene expression, driving genetic mutation and contributing to cell diversification. Since their discovery in the 1940s, researchers have been able to study the behavior of these jumping genes, generally known as transposons or transposable elements (TE), primarily through indirect methods that infer individual activity from bulk results. However, such techniques are not sensitive enough to determine precisely how or why the transposons jump, and what factors trigger their activity.
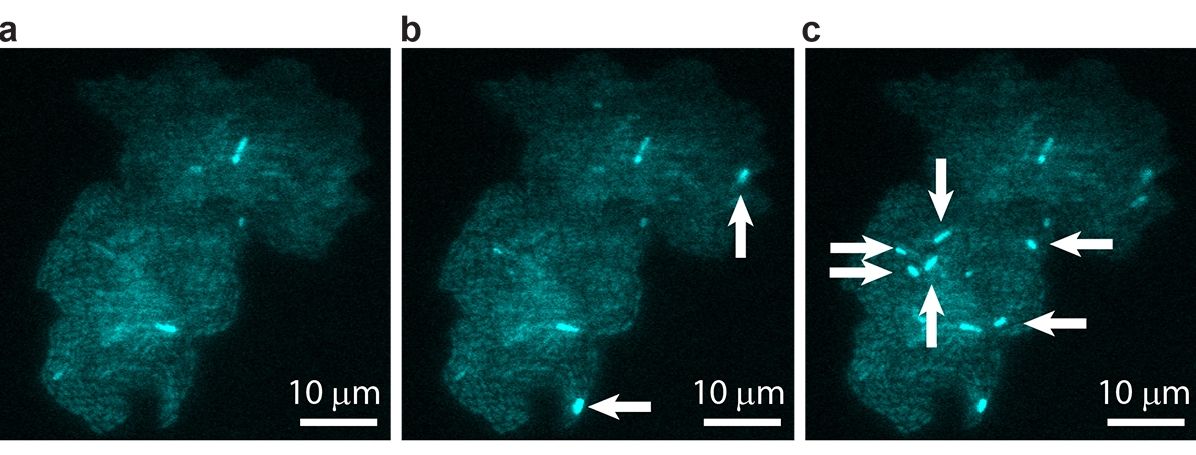
Reporting in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have observed jumping gene activity in real time within living cells. The study is the collaborative effort of physics professors Thomas Kuhlman and Nigel Goldenfeld, at the Center for the Physics of Living Cells, a National Science Foundation Physics Frontiers Center.
Continue reading “Watching ‘jumping genes’ in action” »