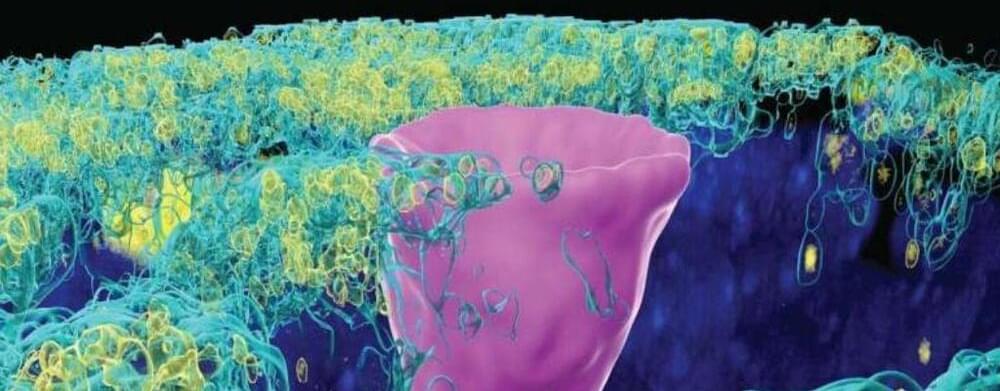
The naked mole rat won’t win any beauty contests, but it could possibly win in the talent category. Its superpower: fighting the aging process to live several times longer than other animals its size, in a state of youthful vigor.
It’s believed that naked mole rats experience all the normal processes of wear and tear over their lifespan, but that they’re exceptionally good at repairing the damage from oxygen free radicals and the DNA errors that accumulate over time. Even though they possess genes that make them vulnerable to cancer, they rarely develop the disease, or any other age-related disease, for that matter. Naked mole rats are known to live for over 40 years without any signs of aging, whereas mice live on average about two years and are highly prone to cancer.
Now, these remarkable animals may be able to share their superpower with other species. In August, a study provided what may be the first proof-of-principle that genetic material transferred from one species can increase both longevity and healthspan in a recipient animal.




 Fyodor Urnov, PhD, is a pioneer in the field of genome editing and one of the scientists most invested in expanding the availability and utility of CRISPR-based therapies to the broadest possible population. He envisions a world in which genome editing can treat the nearly 400 million people who are suffering from one of the 7,000 diseases brought on by gene mutations.
Fyodor Urnov, PhD, is a pioneer in the field of genome editing and one of the scientists most invested in expanding the availability and utility of CRISPR-based therapies to the broadest possible population. He envisions a world in which genome editing can treat the nearly 400 million people who are suffering from one of the 7,000 diseases brought on by gene mutations.