Opinions: Give your opinions in the comments section.
3D printed lab meat, and plant based meats will be more widespread in our future. Would you eat stem cell 3D printed lab meat or plant based meat? Why or why not? What are the differences between natural vs unnatural. Growing up in Texas I know most Texans frown on it, as BBQ is a religion. Is 3D printing meat sustainable\.
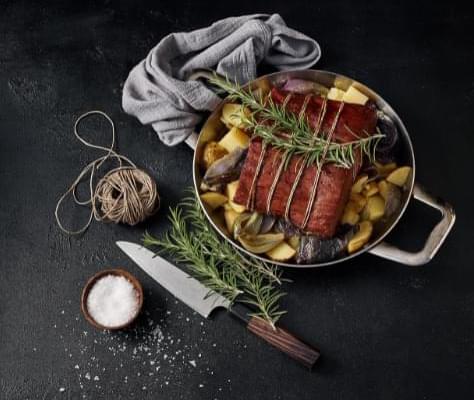
Whether it comes from a plant or the cells of an animal, it’s becoming increasingly clear that the meat of the future will probably not be coming from the flesh of slaughtered animals. Instead, whether made from plants or cells, it will be formed into ‘meat’ by a 3D printer. In September of 2021, a Japanese team of researchers at the University of Osaka announced that they had 3D printed Wagyu beef. Beef connoisseurs will recognize the name; Wagyu beef is prized (and suitably priced) for its flavor and fat marbling. Legends abound about the cows such beef derives from, how they are allegedly coddled and massaged, fed a special diet that includes beer — but much of those tales are either exaggerated or pure urban legend. As Joe Heitzeberg, the co-founder and CEO of Crowd Cow explains, There are four breeds native to Japan. Of those four breeds, one of the breeds is genetically unique. It has a genetic predisposition to create this crazy marbling of fat on the inside of muscle tissue. No other livestock does that. The researchers at the University of Osaka used two different types of stem cells from Wagyu cows to create cultured meat, growing living animal cells onto some type of matrix where they are then incubated and grown into animal tissue that has never been part of a living animal. There are currently no reports on the taste of the cultured Wagyu beef but we can assume it’s ‘good’ and given a little time, the technology should be able to produce excellent Wagyu cultured meat — at what price, however, is another big question mark. But there’s another simpler solution that could be a better meat replacement than cultured meat, as even meat grown from stem cells still contains cholesterol and some of the negative health concerns associated with animal protein. Plant-based imitation meat is also being created with 3D printers, and the results are surprising even hardcore meat lovers.
Continue reading “Staking a Claim on the Steak of Tomorrow: 3D Printing Tech is Making ‘Meat’” »