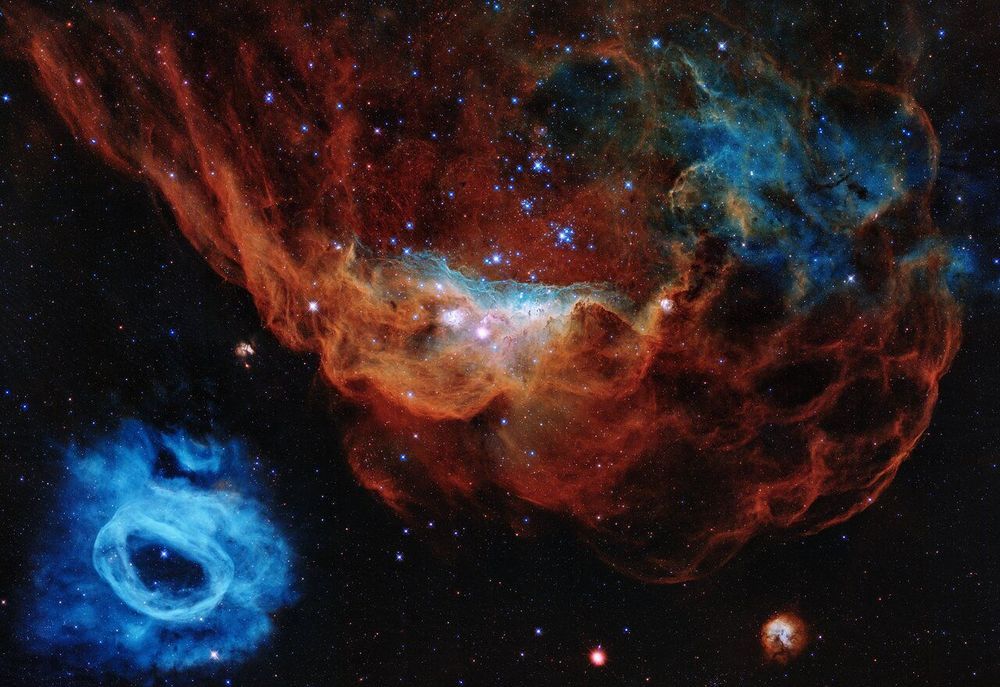
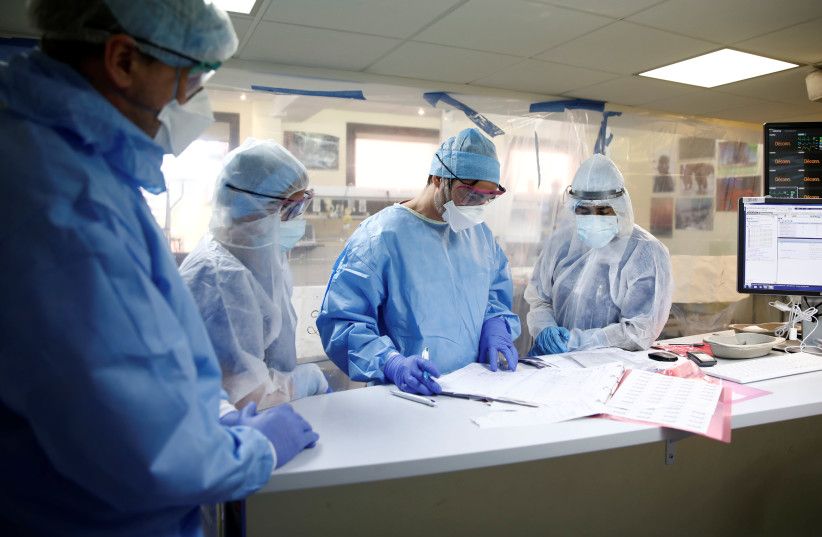
Hubble Space Telescope’s iconic images and scientific breakthroughs have redefined our view of the Universe. To commemorate three decades of scientific discoveries, this image is one of the most photogenic examples of the many turbulent stellar nurseries the telescope has observed during its 30-year lifetime. The portrait features the giant nebula NGC 2014 and its neighbour NGC 2020 which together form part of a vast star-forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, approximately 163 000 light-years away. The image is nicknamed the “Cosmic Reef” because it resembles an undersea world.
On 24 April 1990 the Hubble Space Telescope was launched aboard the space shuttle Discovery, along with a five-astronaut crew. Deployed into low-Earth orbit a day later, the telescope has since opened a new eye onto the cosmos that has been transformative for our civilization.
Hubble is revolutionising modern astronomy not only for astronomers, but also by taking the public on a wondrous journey of exploration and discovery. Hubble’s seemingly never-ending, breathtaking celestial snapshots provide a visual shorthand for its exemplary scientific achievements. Unlike any other telescope before it, Hubble has made astronomy relevant, engaging, and accessible for people of all ages. The mission has yielded to date 1.4 million observations and provided data that astronomers around the world have used to write more than 17 000 peer-reviewed scientific publications, making it one of the most prolific space observatories in history. Its rich data archive alone will fuel future astronomy research for generations to come.