Archive for the ‘internet’ category: Page 272
Dec 6, 2016
The Institute for Critical Infrastructure Technology
Posted by Roman Mednitzer in categories: cybercrime/malcode, internet
New report: rise of the machines: the dyn attack was just A practice run.
As the adversarial threat landscape continues to hyper-evolve, America’s treasure troves of public and private data, IP, and critical infrastructure continues to be pilfered, annihilated, and disrupted. The Mirai IoT botnet has inspired a renaissance in adversarial interest in DDoS botnet innovation based on the lack of fundamental security-by-design in the Internet and in IoT devices, and based on the lack of basic cybersecurity and cyber-hygiene best practices by Internet users.
http://icitech.org/icit-publication-the-rise-of-the-machines…ctice-run/
Continue reading “The Institute for Critical Infrastructure Technology” »
Dec 2, 2016
Free, built-in VPN in Opera for computers
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, internet
Right in your browser.
Now, you don’t have to download VPN extensions or pay for VPN subscriptions to access blocked websites and to shield your browsing when on public Wi-Fi.
Nov 28, 2016
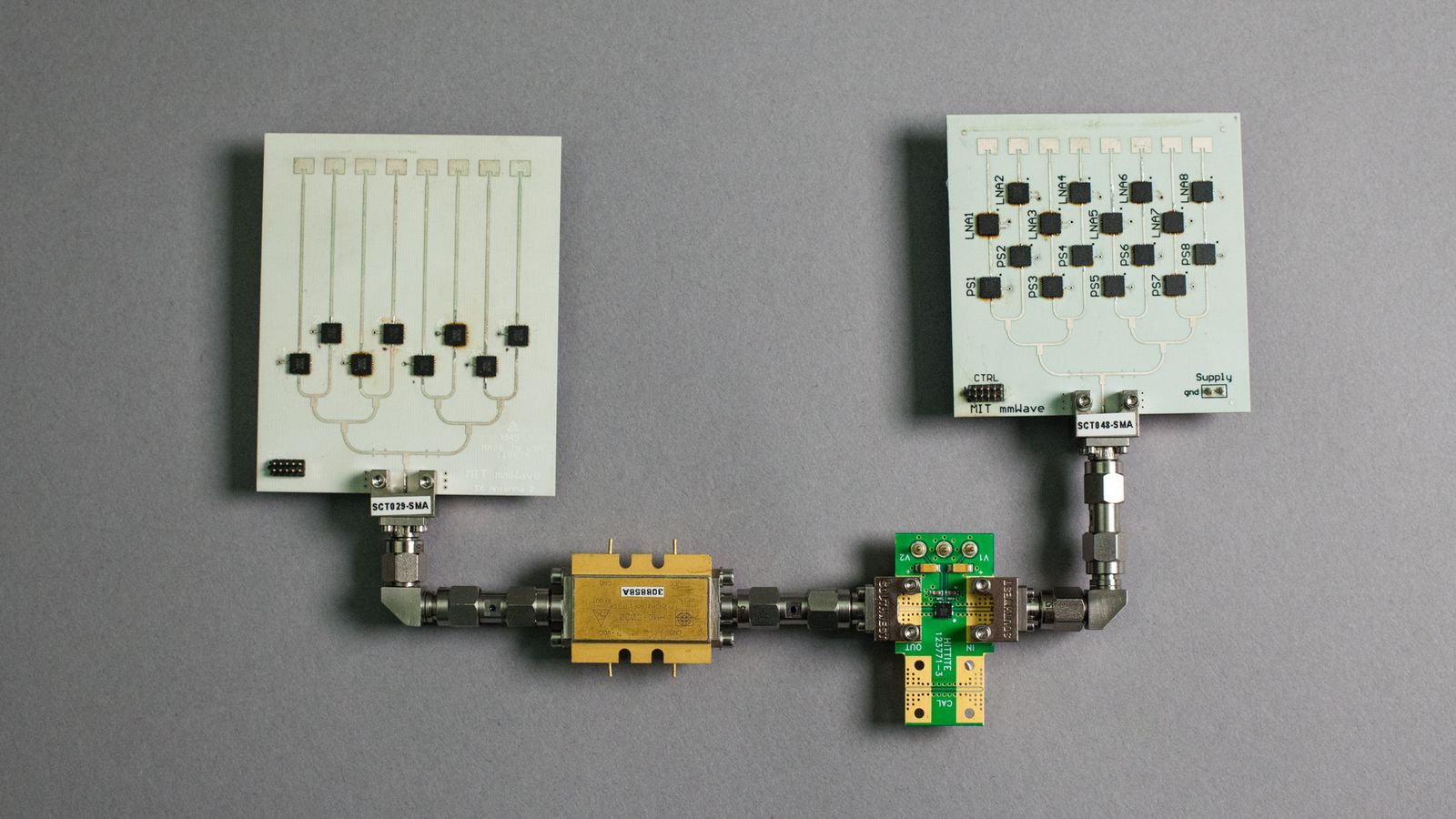
MIT’s new method of radio transmission could one day make wireless VR a reality
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: internet, mobile phones, robotics/AI, supercomputing, virtual reality
If you want to use one of today’s major VR headsets, whether the Oculus Rift, the HTC Vive, or the PS VR, you have to accept the fact that there will be an illusion-shattering cable that tethers you to the small supercomputer that’s powering your virtual world.
But researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) may have a solution in MoVr, a wireless virtual reality system. Instead of using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth to transmit data, the research team’s MoVR system uses high-frequency millimeter wave radio to stream data from a computer to a headset wirelessly at dramatically faster speeds than traditional technology.
There have been a variety of approaches to solving this problem already. Smartphone-based headsets such as Google’s Daydream View and Samsung’s Gear VR allow for untethered VR by simply offloading the computational work directly to a phone inside the headset. Or the entire idea of VR backpacks, which allow for a more mobile VR experience by building a computer that’s more easily carried. But there are still a lot of limitations to either of these solutions.
Continue reading “MIT’s new method of radio transmission could one day make wireless VR a reality” »
Nov 27, 2016
What happens when bots start writing code instead of humans
Posted by Elmar Arunov in categories: internet, robotics/AI
Shift 2: Open-source code, Node, and frameworks
Once widely considered a toy language, Node has quickly taken over the web and fostered an incredible open-source community. For those who are unfamiliar, Node is a way for JavaScript to run on a server. What’s so incredible about Node is that the same developers who were only writing client-side code (front-end web development) can now write backend code without switching languages.
In addition, there is an incredible community that rallies around and thrives off of open-source contributions. The infrastructure and open-source packages are very powerful, allowing developers to not just solve their own problems, but also to build in a way that solves problems for the entire community. Building a software product with Node today is like playing with Lego blocks; you spend most of your time simply connecting them.
Continue reading “What happens when bots start writing code instead of humans” »
Nov 27, 2016
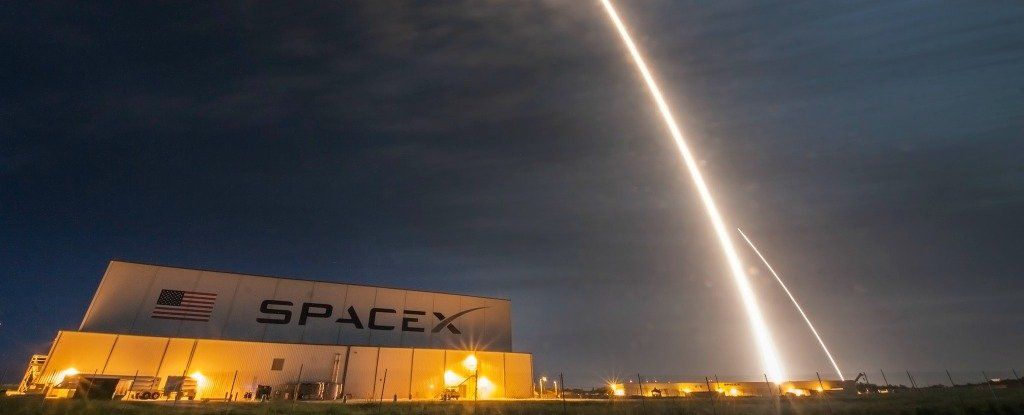
SpaceX Wants to Surround Earth With an Internet Service That’s 200 Times Faster
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: Elon Musk, internet, satellites
SpaceX, the aerospace company founded by the Mars-hungry tech entrepreneur Elon Musk, just made a big move to enshroud the planet in high-speed internet coverage.
On November 15, the company filed a lengthy application with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to launch 4,425 satellites. (We first heard about the filing through the r/SpaceX community on Reddit.) That is a hell of a lot of satellites.
According to a database compiled by the Union of Concerned Scientists, there are 1,419 active satellites currently orbiting Earth.
Continue reading “SpaceX Wants to Surround Earth With an Internet Service That’s 200 Times Faster” »
Nov 25, 2016
SynBio is gearing up
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, economics, internet
We’re only starting in this space.
Synthetic Biology (SynBio) includes a large field of applications. Within this area biochemists combine engineering concepts and techniques with biology to design new genes that produce a specific protein. When this protein is an enzyme, bacteria and yeast in which such a gene is implanted can produce specific chemicals through a fermentation process. A large and growing number of businesses is active in this field. This became apparent once again at the EFIB-conference in Glasgow, last October. The workshop was chaired by John Cumbers, founder of the American SynBioBeta, an internet-site dedicated to sharing information and news on synthetic biology.

Nov 23, 2016
Microsoft Sets Sights on Building Practical Quantum Computer
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: cybercrime/malcode, encryption, internet, quantum physics
DAILY VIDEO: Microsoft Starts Quantum Computer Development Program; Cerber Ransomware Expands Database Encryption Attacks; IBM Debuts Watson Internet of Things Services Practice; and there’s more.
Today’s topics include Microsoft’s plan to build a Quantum computer, Trend Micro’s find that the Cerber malware is seeking out database files to encrypt and hold for ransom, IBM’s new Watson internet of things services for the automotive, electronics and insurance industries, and the release of the Microsoft Office Online Server update.
Microsoft is on a mission to build a quantum computer, and the company has appointed Todd Holmdahl to manage the project. Holmdahl is the corporate vice president of Microsoft Quantum, a unit dedicated to turning the company’s quantum computing research into real-world products.
Continue reading “Microsoft Sets Sights on Building Practical Quantum Computer” »
Nov 22, 2016
What are Molecular Machines?
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: economics, evolution, food, information science, internet, nanotechnology, robotics/AI
Machines lace almost all social, political cultural and economic issues currently being discussed. Why, you ask? Clearly, because we live in a world that has all its modern economies and demographic trends pivoting around machines and factories at all scales.
We have reached the stage in the evolution of our civilization where we cannot fathom a day without the presence of machines or automated processes. Machines are not only used in sectors of manufacturing or agriculture but also in basic applications like healthcare, electronics and other areas of research. Although, machines of varying types had entered the industrial landscape long ago, technologies like nanotechnology, the Internet of Things, Big Data have altered the scenario in an unprecedented manner.
The fusion of nanotechnology with conventional mechanical concepts gives rise to the perception of ‘molecular machines’. Foreseen to be a stepping stone into nano-sized industrial revolution, these microscopic machines are molecules designed with movable parts that behave in a way that our regular machines operate in. A nano-scale motor that spins in a given direction in presence of directed heat and light would be an example of a molecular machine.
Nov 22, 2016
Single photon converter: key component of quantum internet
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, internet, quantum physics
A Polish-British team of physicists has constructed and tested a compact, efficient converter capable of modifying the quantum properties of individual photons. The new device should facilitate the construction of complex quantum computers, and in the future may become an important element in global quantum networks, the successors of today’s Internet.
Quantum internet and hybrid quantum computers, built out of subsystems that operate by means of various physical phenomena, are now becoming more than just the stuff of imagination. In an article just published in the journal Nature Photonics, physicists from the University of Warsaw’s Faculty of Physics (FUW) and the University of Oxford have unveiled a key element of such systems: an electro-optical device that enables the properties of individual photons to be modified. Unlike existing laboratory constructions, this new device works with previously unattainable efficiency and is at the same time stable, reliable, and compact.
Building an efficient device for modifying the quantum state of individual photons was an exceptionally challenging task, given the fundamental differences between classical and quantum computing.