Aug 17, 2022
2D boundaries could create electricity
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: energy, materials
There’s still plenty of room at the bottom to generate piezoelectricity. Engineers at Rice University and their colleagues are showing the way.
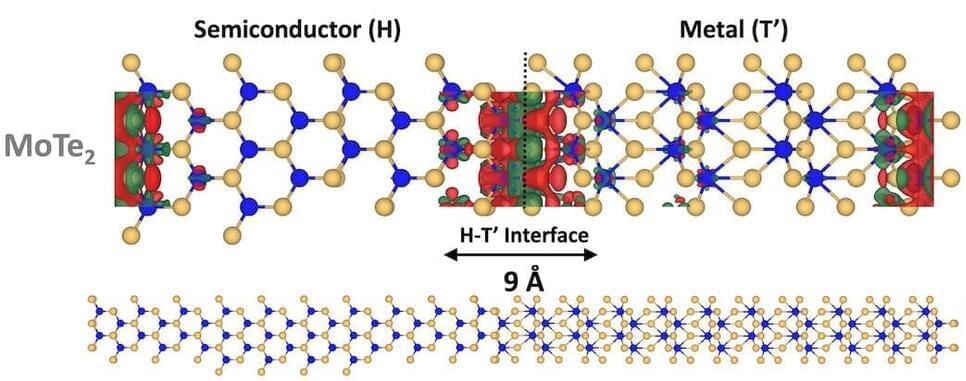
A new study describes the discovery of piezoelectricity—the phenomenon by which mechanical energy turns into electrical energy —across phase boundaries of two-dimensional materials.
The work led by Rice materials scientists Pulickel Ajayan and Hanyu Zhu and their colleagues at Rice’s George R. Brown School of Engineering, the University of Southern California, the University of Houston, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base Research Laboratory and Pennsylvania State University appears in Advanced Materials.