Sep 20, 2015
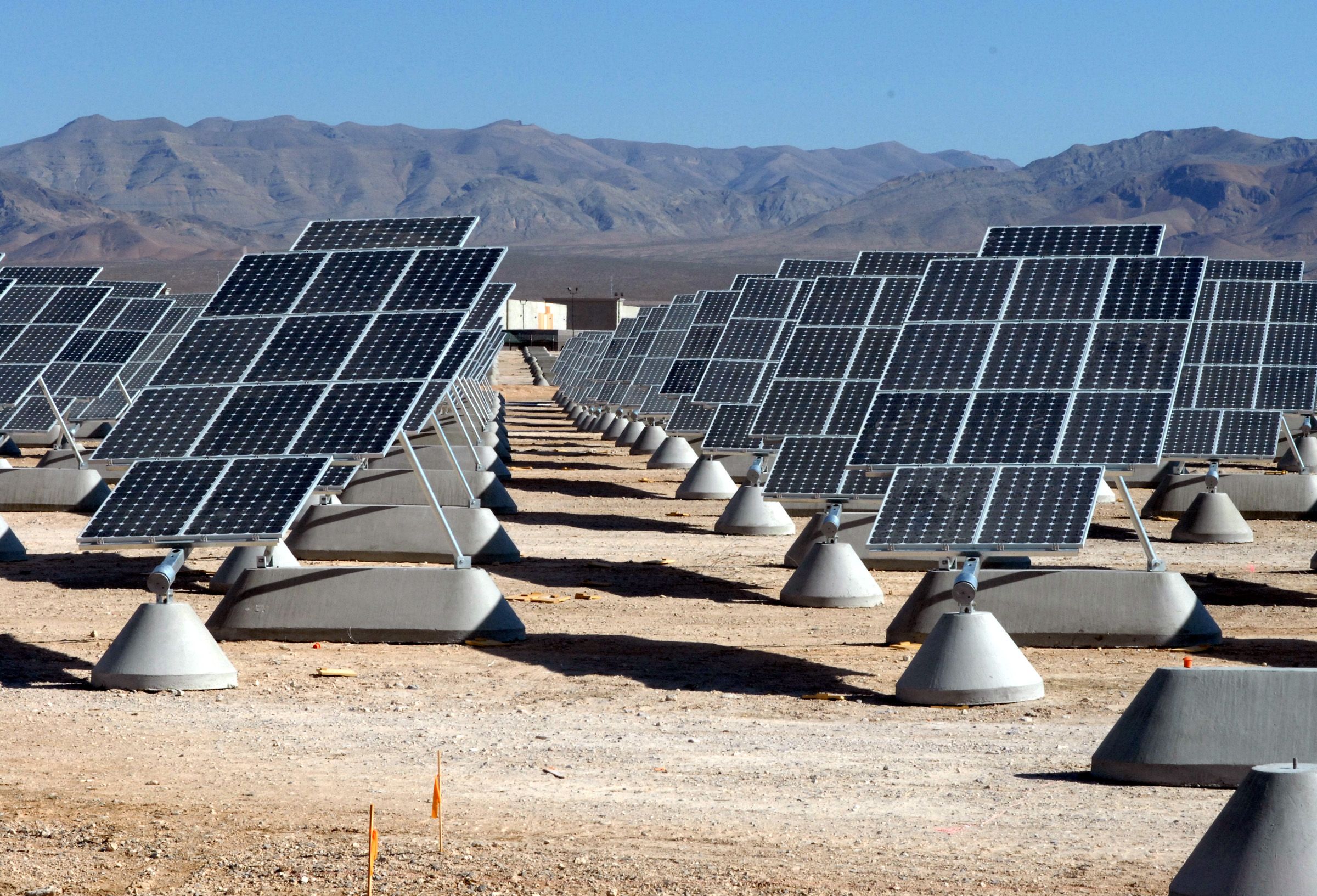
Solar panels as inexpensive as paint?
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: engineering, materials, solar power, sustainability
Fortunately, that is changing because researchers such as Qiaoqiang Gan, University at Buffalo assistant professor of electrical engineering, are helping develop a new generation of photovoltaic cells that produce more power and cost less to manufacture than what’s available today.
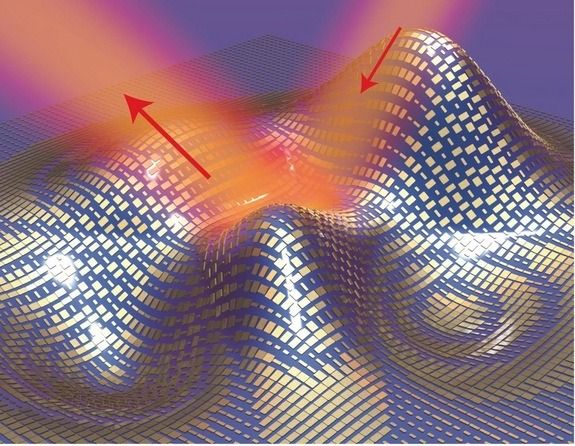
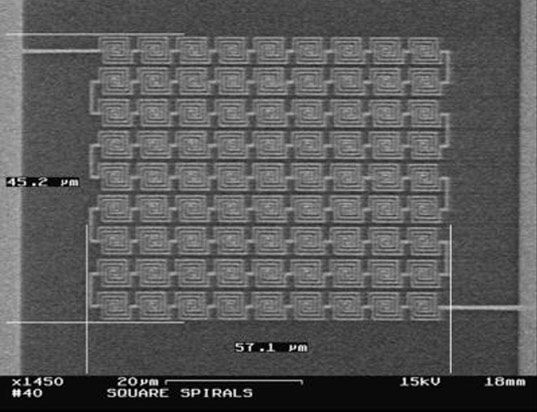
One of the more promising efforts, which Gan is working on, involves the use of plasmonic-enhanced organic photovoltaic materials. These devices don’t match traditional solar cells in terms of energy production but they are less expensive and — because they are made (or processed) in liquid form — can be applied to a greater variety of surfaces.
Gan detailed the progress of plasmonic-enhanced organic photovoltaic materials in the May 7 edition of the journal Advanced Materials. Co-authors include Filbert J. Bartoli, professor of electrical and computer engineering at Lehigh University, and Zakya Kafafi of the National Science Foundation.
 The dimensionless aspect, since it has no dimensions, is outside of space and time. This is the key aspect to existence: an aspect outside of space and time perpetually interacting dialectically with an aspect inside space and time. All of the weird and wonderful phenomena of the universe are the products of this ultimate dichotomy.
The dimensionless aspect, since it has no dimensions, is outside of space and time. This is the key aspect to existence: an aspect outside of space and time perpetually interacting dialectically with an aspect inside space and time. All of the weird and wonderful phenomena of the universe are the products of this ultimate dichotomy.