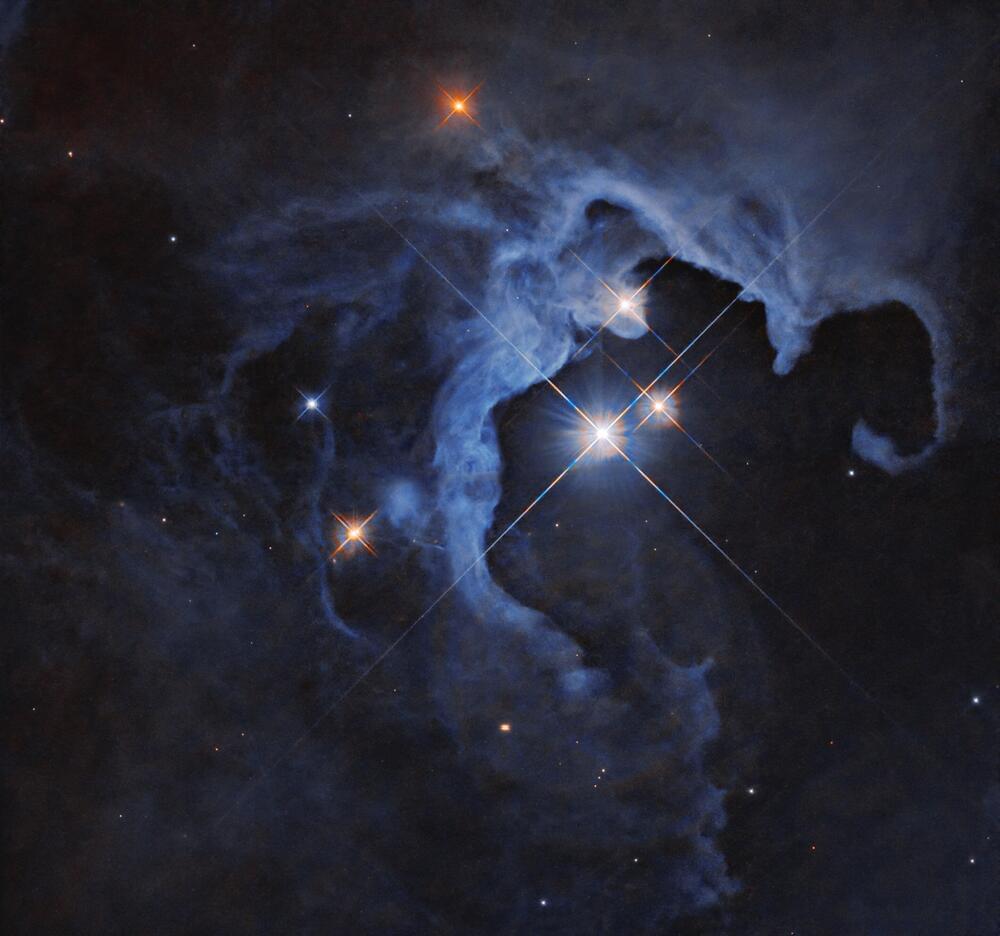
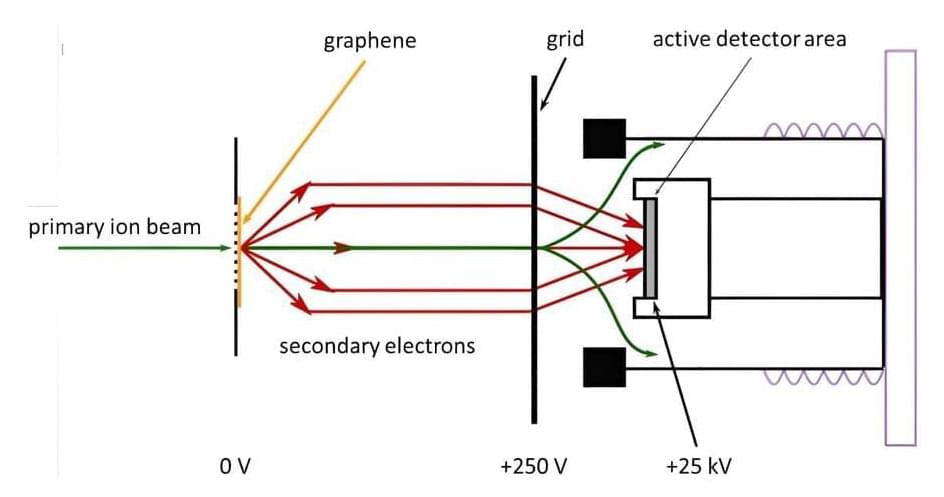
Looking like a glittering cosmic geode, a trio of dazzling stars blaze from the hollowed-out cavity of a reflection nebula in this new image from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The triple-star system is made up of the variable star HP Tau, HP Tau G2, and HP Tau G3.
HP Tau is known as a T Tauri star, a type of young variable star that hasn’t begun nuclear fusion yet but is beginning to evolve into a hydrogen-fueled star similar to our sun. T Tauri stars tend to be younger than 10 million years old―in comparison, our sun is around 4.6 billion years old―and are often found still swaddled in the clouds of dust and gas from which they formed.
As with all variable stars, HP Tau’s brightness changes over time. T Tauri stars are known to have both periodic and random fluctuations in brightness. The random variations may be due to the chaotic nature of a developing young star, such as instabilities in the accretion disk of dust and gas around the star, material from that disk falling onto the star and being consumed, and flares on the star’s surface. The periodic changes may be due to giant sunspots rotating in and out of view.