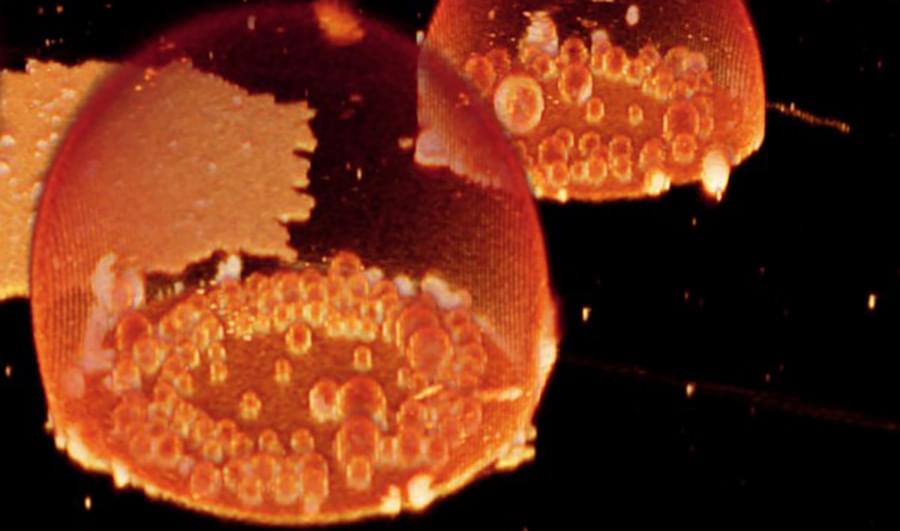
(Inside Science) – Primitive “protocells” like those that evolved into the first living cells can form in bubbles on mineral surfaces that were plentiful on the early Earth, according to new research.
The researchers created artificial protocells that they believe may be similar to the protocells that may have formed on Earth about 3.8 billion years ago. The artificial protocells can absorb other small molecules by forming a barrier membrane around them — behavior that is strikingly like that of modern living cells when they absorb cellular fuel and other essential materials while blocking off harmful substances.
And the artificial protocells also exhibit a primitive form of “division,” where the outer membrane of a protocell ruptures and leaves behind several “daughter” protocells with the same capabilities.