Dec 8, 2022
Levitation Breakthrough Achieved in New Study of Acoustic Radiation Force Phenomenon
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: mathematics, particle physics
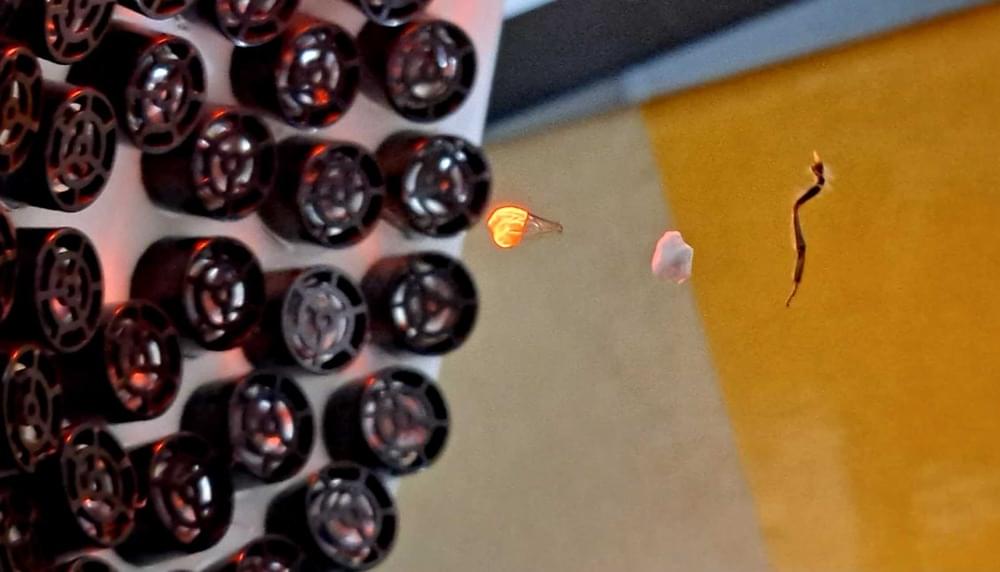
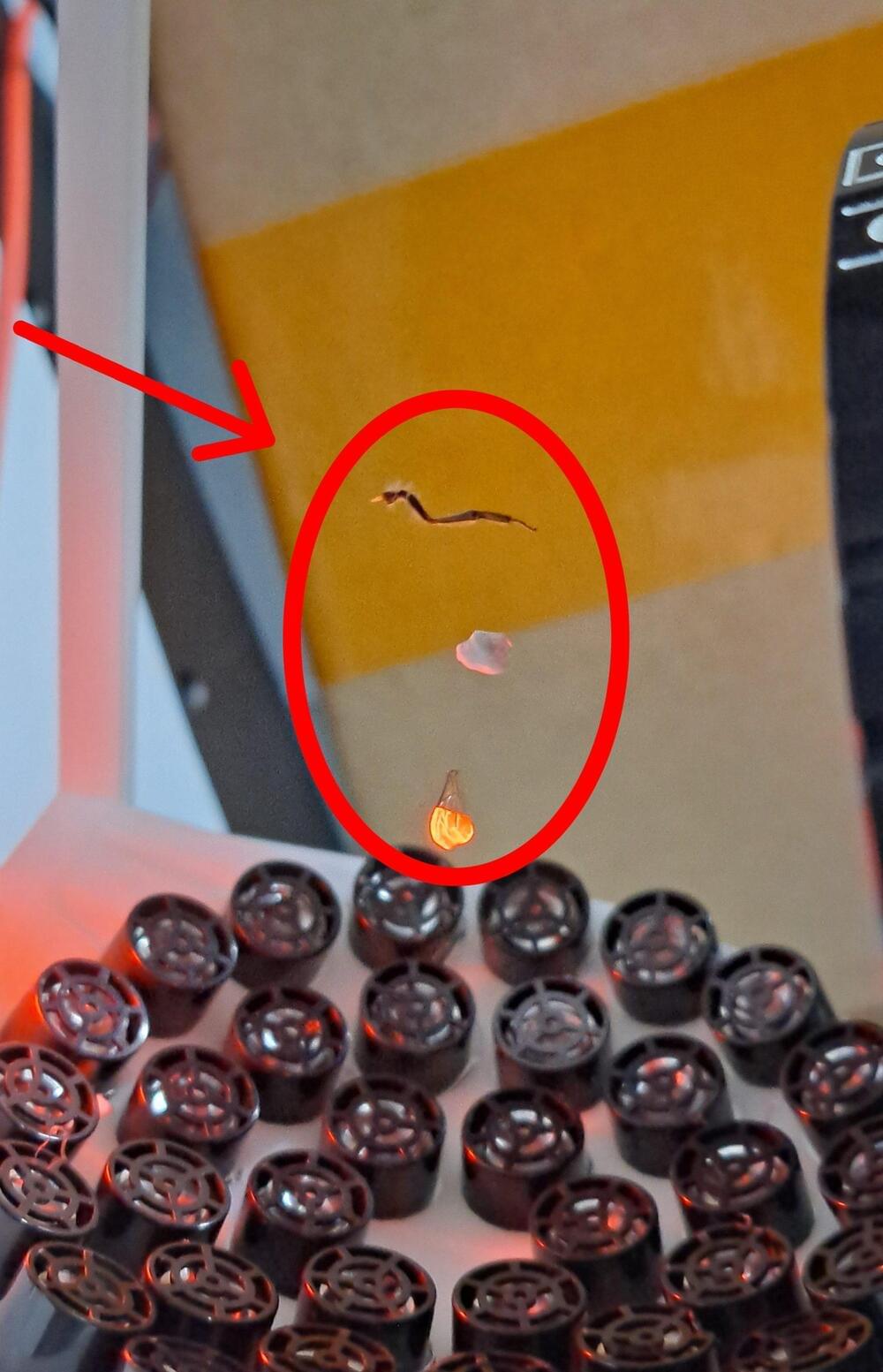
Scientists with the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) and the University of New South Wales (UNSW) have developed a method that helps to fine-tune the control of particles using ultrasonic waves according to new research, which they say expands our understanding of the field of acoustic levitation.
The levitation of objects, once a phenomenon seen only in science fiction and fantasy, now represents a field in acoustics with practical applications in multiple research areas, industries, and even among hobbyists. However, the use of high-intensity sound waves to suspend small objects in the air is nothing new. The theoretical basis for overcoming gravity with the help of acoustic radiation pressure goes as far back as the 1930s, when researcher Louis King first studied the suspension of particles in the field of a sound wave, and how this demonstrates acoustic radiation force being exerted against them.
Later calculations beginning in the 1950s helped to further refine our understanding of the acoustic radiation force produced by the scattering of sound waves. However, the modern foundation for acoustic levitation science draws mainly from the work of superconductivity pioneer Lev. P. Gorkov, who was the first to synthesize previous studies and provide a solid mathematical basis for the phenomenon.