Nov 17, 2020
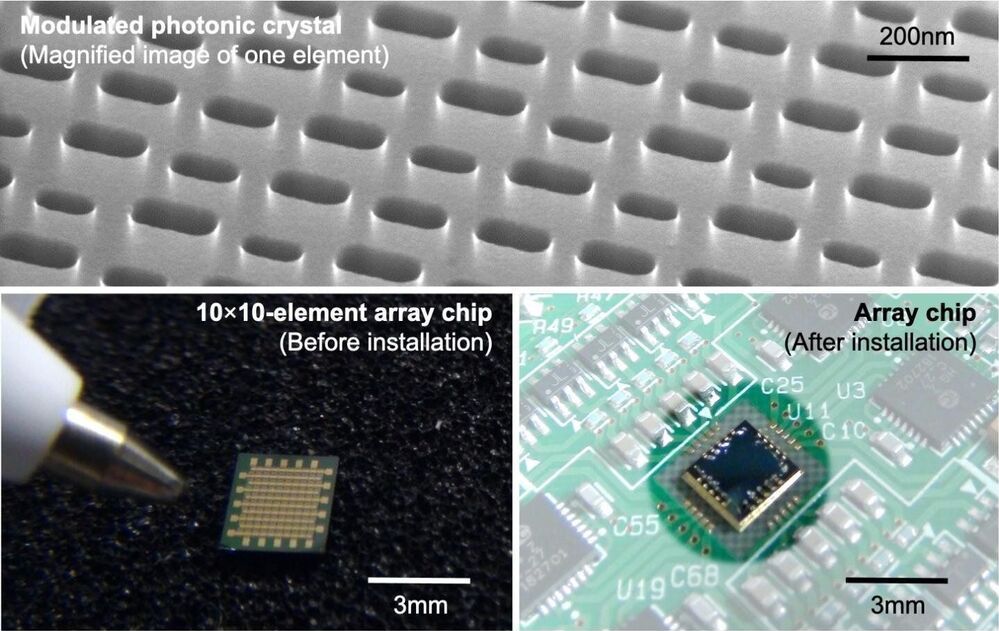
Researchers describe a new beam scanning device utilizing ‘photonic crystals
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: food, mobile phones, robotics/AI
Scanning lasers—from barcode scanners at the supermarket to cameras on newer smartphones—are an indispensable part of our daily lives, relying on lasers and detectors for pinpoint precision.
Distance and object recognition using LiDAR—a portmanteau of light and radar—is becoming increasingly common: reflected laser beams record the surrounding environment, providing crucial data for autonomous cars, agricultural machines, and factory robots.
Current technology bounces the laser beams off of moving mirrors, a mechanical method that results in slower scanning speeds and inaccuracies, not to mention the large physical size and complexity of devices housing a laser and mirrors.