Archive for the ‘nanotechnology’ category: Page 250
Jan 9, 2018
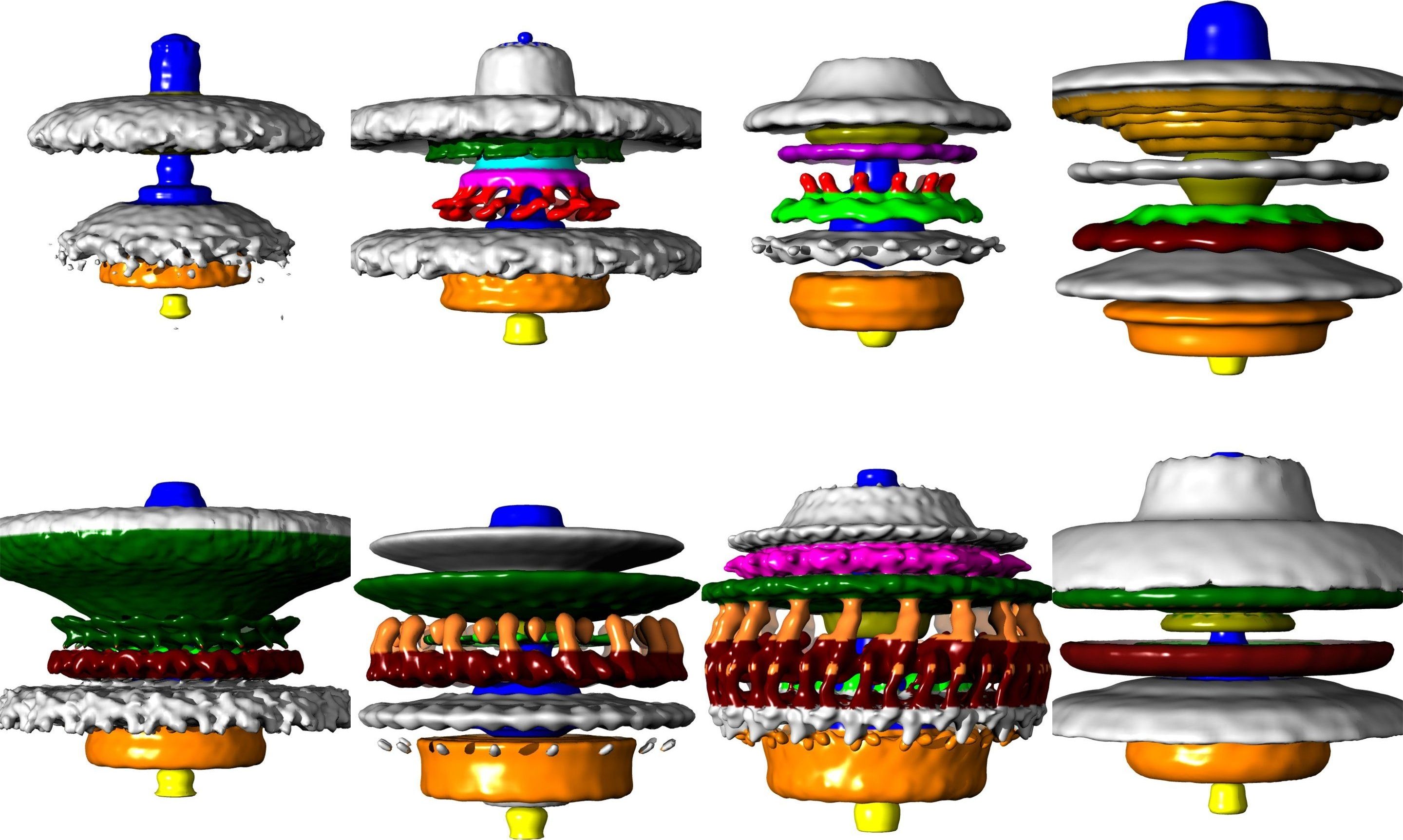
How bacteria turbocharged their motors
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: evolution, habitats, nanotechnology
Using detailed 3D images, researchers have shown how bacteria have evolved molecular motors of different powers to optimize their swimming.
The discovery, by a team from Imperial College London, provides insights into evolution at the molecular scale.
Bacteria use molecular motors just tens of nanometres wide to spin a tail (or ‘flagellum’) that pushes them through their habitat. Like human-made motors, the structure of these nanoscale machines determines their power and the bacteria’s swimming ability.
Jan 4, 2018
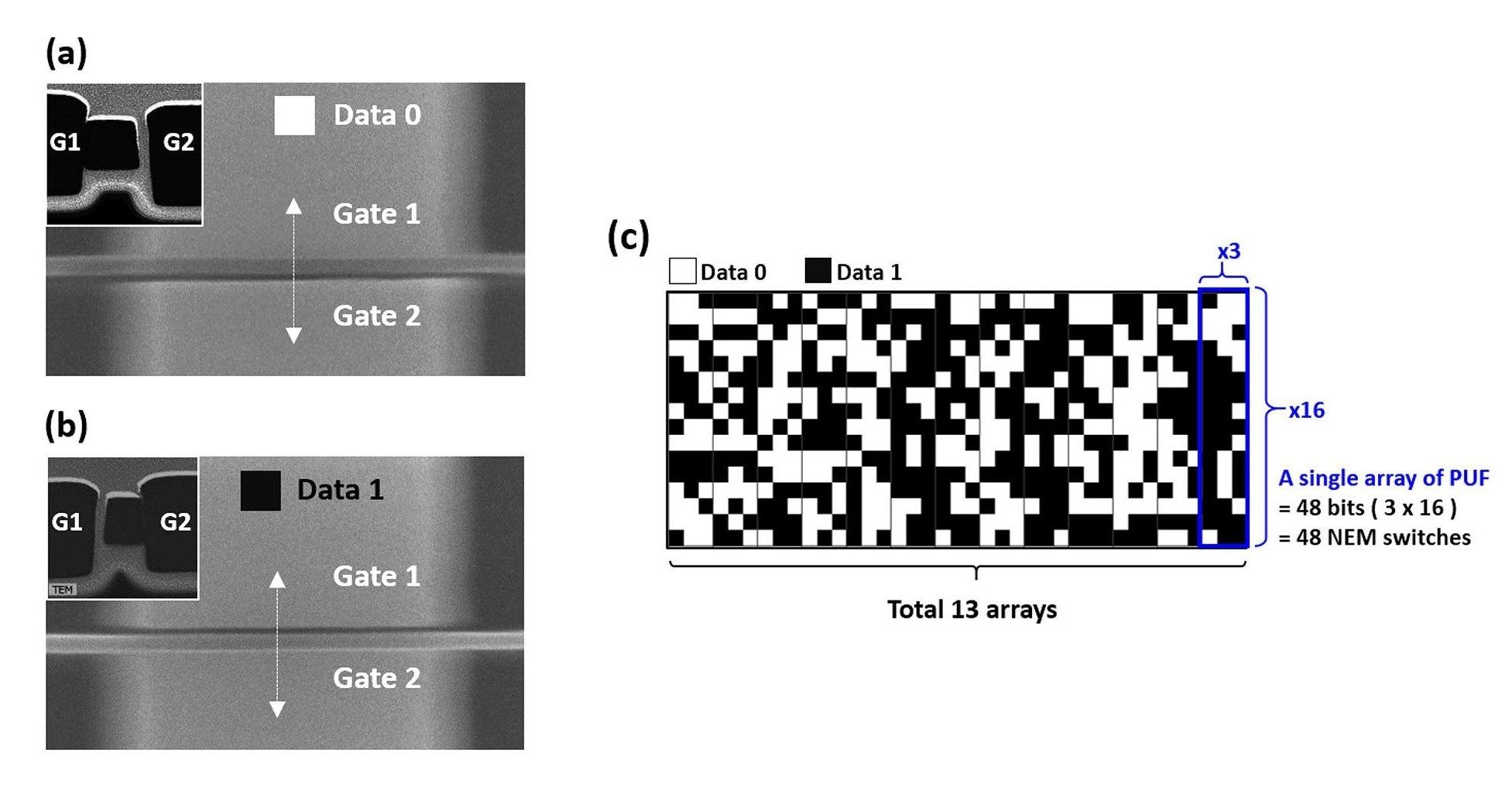
Nanoscale cryptography method gains robustness from stiction
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: encryption, internet, nanotechnology, security
Most of the cryptographic methods that keep important data secure use complex encryption software, and as a result, consume large amounts of power. As more and more electronic devices are being connected to the internet, there is a growing need for alternative low-power security methods, and this is often done by basing the security on hardware rather than software.
One of the most promising approaches to hardware-based, low-power security is to derive cryptographic keys from the randomness that inherently and uncontrollably emerges during the fabrication process of nanoscale devices. These methods, called “physical unclonable functions” (PUFs), convert the random variations in the physical devices into the binary states of “0” and “1” to create unique, random cryptographic keys. These keys can then be used to encrypt data into cipher text, as well as decrypt it back into plain text, in a process that remains secure as long as the key remains private.
However, one of the biggest challenges facing PUF technology is its vulnerability to harsh environments. Since the physical randomness that forms the basis of the key usually arises from variations in electrical characteristics, and electrical characteristics are affected by external factors such as high temperatures and radiation, these devices often do not preserve their states when exposed to such conditions.
Continue reading “Nanoscale cryptography method gains robustness from stiction” »
Jan 3, 2018
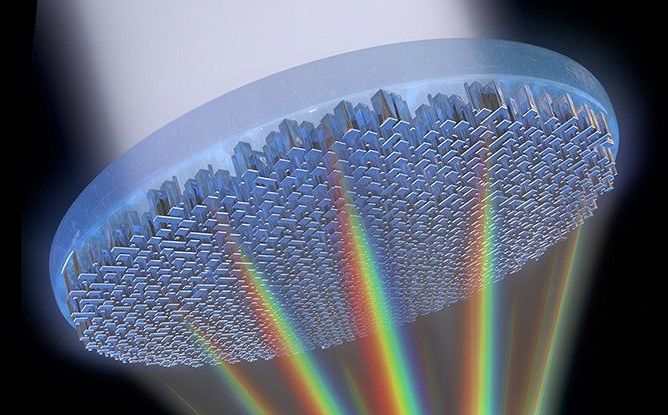
A Revolutionary New Type of Lens Focuses All The Colours of The Rainbow Into a Single Point
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: nanotechnology
A brand new type of lens called a metalens has just passed a major hurdle. A metalens is a flat surface that use nanostructures to focus light, and it could change optics forever by replacing the traditional bulky, curved lenses we know.
Up until now these ultra-compact lenses have had enormous potential, but they’ve struggled to focus a broad spectrum of light. Well, that just changed.
For the first time researchers have managed to develop a single metalens capable of focusing all the colours of the rainbow – the entire visible spectrum of light, making white light – into one point at a high resolution, something that has required multiple lenses in the past.
Dec 24, 2017
MIT Just Created Living Plants That Glow Like A Lamp, And Could Grow Glowing Trees To Replace Streetlights
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: innovation, nanotechnology
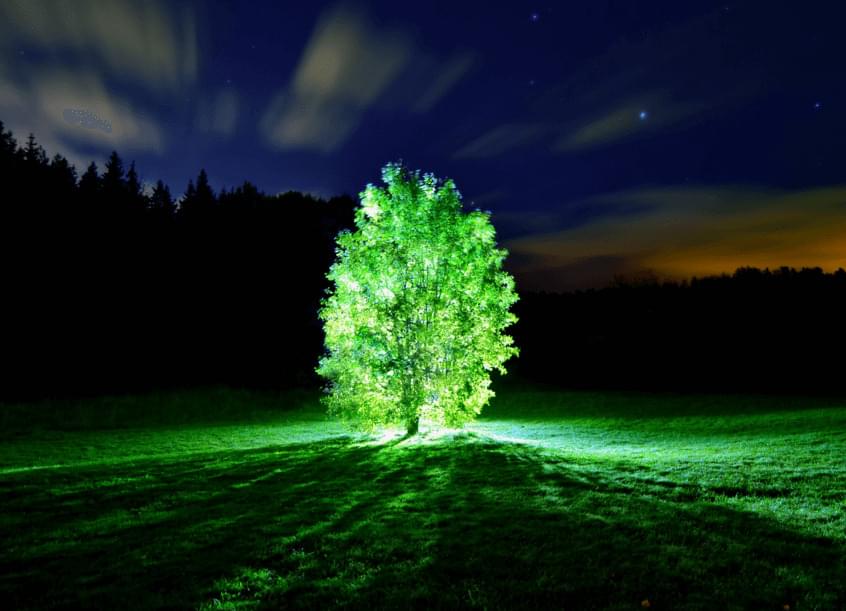

Roads of the future could be lit by glowing trees instead of streetlamps, thanks to a breakthrough in creating bioluminescent plants. Experts injected specialized nanoparticles into the leaves of a watercress plant, which caused it to give off a dim light for nearly four hours. This could solve lots of problems.
The chemical involved, which produced enough light to read a book by, is the same as is used by fireflies to create their characteristic shine. To create their glowing plants, engineers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) turned to an enzyme called luciferase. Luciferase acts on a molecule called luciferin, causing it to emit light.
Dec 19, 2017
Bio-programming toolkit maker Asimov launches with $4.7M from Andreessen Horowitz
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: biotech/medical, computing, nanotechnology
Biotech is one of today’s many hot frontiers of technology, but one thing holding it back is that it’s significantly less amenable to traditional computing techniques than other areas. A new startup called Asimov, spun off from research at MIT, is working on bridging the gap between the digital and the biological by creating, essentially, a set of computer-aided biology design tools. It’s a prescient enough idea that it has attracted $4.7 million in seed funding.
The problem that Asimov addresses is this. Say you’re a pharmaceutical company trying to make a tiny biocompatible machine that holds a certain amount of medication and releases it when it senses some other molecule.
In order to do so, you’d have to — well, among about a million other things — design what amounts to a logic gate and signal processor that works at the molecular scale. This is a daunting prospect, as creating molecular machinery is a labor-intensive process often involving creating thousands of variations of a given structure and testing them repeatedly to see which works.
Dec 18, 2017
Using Nanotechnology, not Water, to Clean Solar Panels
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: nanotechnology, particle physics, solar power, space, sustainability
Although solar panels might appear bright and shiny, in desert environments, where they are most frequently installed, layers of dust and other particles can quickly coat their surface. These coatings can affect the panels’ ability to absorb sunlight and drastically reduce the conversion of the sun’s rays into energy, making it necessary to periodically wash the panels with water. But often, in areas like Nevada, water resources are scarce.
Consequently, NEXUS scientists have turned their attention toward developing technologies for waterless cleaning. NASA has already been using such techniques to wash panels in the lunar and Mars missions, but their developed methodologies prove too expensive for widespread public application. NEXUS scientist Biswajit Das of UNLV and his team are aiming to develop a water-free cleaning technology that will be cost-effective for large-scale photovoltaic generation, whereby they look to nanotechnology, rather than water, to clean the panels. “Our mission is to develop a waterless, or at least a less-water cleaning technique to address the effect of dust on solar panels,” Das says. “Once developed, this method will significantly reduce water use for the future PV generation.”
Continue reading “Using Nanotechnology, not Water, to Clean Solar Panels” »
Dec 16, 2017
IBM Stuffs a Whopping 330TB of Data into a Tiny Cartridge
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, nanotechnology, particle physics
Some of the earliest computers relied upon tape drives for storage, but we’ve since moved on to faster and more versatile storage technologies. Still, tape drives continue to exist in enterprise, and they’ve been advancing by leaps and bounds while you haven’t been paying attention. IBM just announced a new record in data storage density — 201 gigabits per square inch on a magnetic tape (that’s one square inch of it above). That works out to a whopping 330TB of uncompressed data on a single tape drive cartridge.
IBM reached this plateau in magnetic tape density by developing several new technologies. Older versions of IBM’s magnetic tape used a thin film of barium ferrite particles applied to the surface like paint. “Sputtered tape” uses several layers of thin metal film that are applied using a new vacuum technology. A layer of lubricant is also applied to the reading surface of the tape to keep the tape in good working order as it’s run through the drive. The higher density arrangement of magnetic nanoparticles will, of course, require new drive technology to read.
Continue reading “IBM Stuffs a Whopping 330TB of Data into a Tiny Cartridge” »
Dec 16, 2017
First-of-its-kind chemical oscillator offers new level of molecular control
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, nanotechnology
Researchers successfully constructed a first-of-its-kind chemical oscillator that uses DNA components. DNA molecules that follow specific instructions could offer more precise molecular control of synthetic chemical systems, a discovery that opens the door for engineers to create molecular machines…