A breakthrough Cu-Ta-Li alloy has the potential to revolutionize aerospace, defense, and industrial applications. Researchers from the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) and Lehigh University have developed an advanced nanostructured copper alloy that sets a new benchmark for high-temperature perf
Category: nanotechnology – Page 5
Image quality often makes the difference between an amazing multimedia experience, like feeling immersed in a high-definition movie, and a visual letdown. When it comes to biomolecular imaging, the details matter even more. When scientists increase resolution in quantitative imaging, they improve accuracy and confidence in results, ultimately facilitating discoveries in studies of proteins, cells and other biomedical applications.
Scientists have long been able to look at single molecules to study their nanoscale structures and dynamics in biological systems. However, distinguishing between two closely spaced dipole emitters, which are fluorescent molecules that can emit light in specific directions and intensities, has remained a major challenge, especially when such molecules emit light at the same time and are spatially coincident, or located at nearly the same point in space.
This limitation has hindered researchers’ ability to measure the orientation and angular separation of dipoles accurately, which is vital to understanding their rotational dynamics in crowded cellular environments.
Polymer-coated nanoparticles loaded with therapeutic drugs show significant promise for cancer treatment, including ovarian cancer. These particles can be targeted directly to tumors, where they release their payload while avoiding many of the side effects of traditional chemotherapy.
Over the past decade, MIT Institute Professor Paula Hammond and her students have created a variety of these particles using a technique known as layer-by-layer assembly. They’ve shown that the particles can effectively combat cancer in mouse studies.
To help move these nanoparticles closer to human use, the researchers have now come up with a manufacturing technique that allows them to generate larger quantities of the particles, in a fraction of the time.
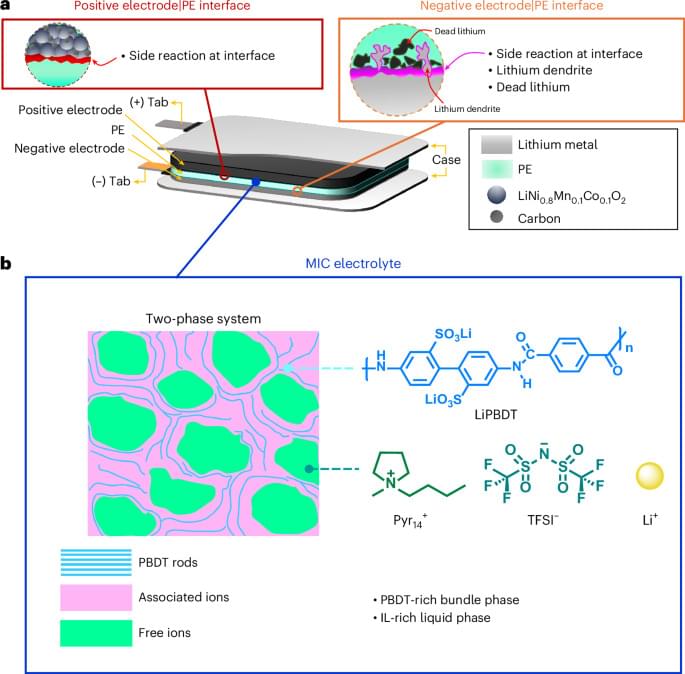
Investigating the effect of heterogeneities across the electrode|multiphase polymer electrolyte interfaces in high-potential lithium batteries Nanotechnology
Posted in nanotechnology | Leave a Comment on Investigating the effect of heterogeneities across the electrode|multiphase polymer electrolyte interfaces in high-potential lithium batteries Nanotechnology
X-ray synchrotron measurements reveal heterogeneities at electrode|electrolyte interfaces of lithium metal batteries operating at high potentials. Here the authors demonstrate the rearrangement of ionically conductive phases in polymer electrolytes that lead to battery performance degradation.
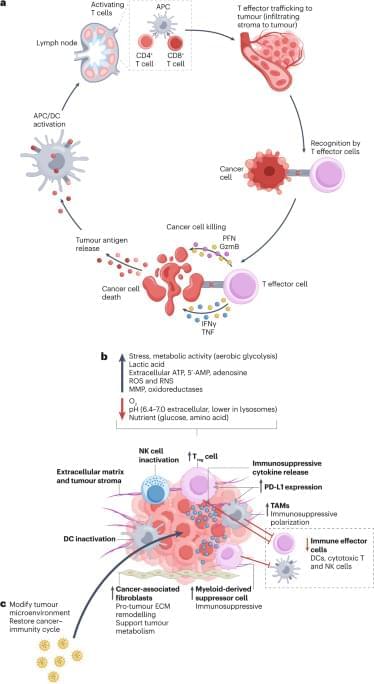
Immunotherapies, predominantly immune-checkpoint inhibitors and chimaeric antigen receptor T cells, have transformed oncology. Nonetheless, these systemically administered agents have several limitations, including the risk of off-target toxicities and a lack of activity owing to an inability to overcome an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment (TME). In this Review, the authors describe the potential to overcome these challenges using functionalized nanomaterials that are designed to release a wide range of immunotherapeutic cargoes in response to specific TME characteristics, including hypoxia, differences in pH, the presence of specific enzymes, reactive oxygen species and/or high levels of extracellular ATP.
A team of chemists led by Feng Lin and Louis Madsen found a way to see into battery interfaces, which are tight, tricky spots buried deep inside the cell. The research findings were published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
A new collaboration between Brown University and TU Delft has brought us closer to interstellar travel using light-powered sails. By combining ultra-thin, highly reflective materials with AI-optimized nanoscale design, researchers created a revolutionary lightsail that’s cheaper, faster to make.
These nano-PeLEDs feature pixel lengths as small as 90 nanometers, enabling an unprecedented pixel density of 127,000 pixels per inch (PPI). For comparison, a typical 27-inch 4K gaming monitor has a pixel density of just 163 PPI.
“Making electronic devices smaller is an everlasting pursuit for scientists and engineers,” said Professor Di Dawei, Deputy Director of the International Research Center for Advanced Photonics at Zhejiang University.
He explained that while micro-LEDs based on III-V semiconductors are considered state-of-the-art, their efficiency drops sharply when pixel sizes fall below 10 micrometers – a limitation that has hindered their use in ultra-high-resolution displays.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects approximately 1% of people over the age of 60 and 5% of those over the age of 85. Current drugs for Parkinson’s disease mainly affect the symptoms and cannot stop its progression. Nanotechnology provides a solution to address some challenges in therapy, such as overcoming the blood-brain barrier (BBB), adverse pharmacokinetics, and the limited bioavailability of therapeutics. The reformulation of drugs into nanoparticles (NPs) can improve their biodistribution, protect them from degradation, reduce the required dose, and ensure target accumulation. Furthermore, appropriately designed nanoparticles enable the combination of diagnosis and therapy with a single nanoagent.
In recent years, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been studied with increasing interest due to their intrinsic nanozyme activity. They can mimic the action of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase. The use of 13-nm gold nanoparticles (CNM-Au8®) in bicarbonate solution is being studied as a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease and other neurological illnesses. CNM-Au8® improves remyelination and motor functions in experimental animals.
Among the many techniques for nanoparticle synthesis, green synthesis is increasingly used due to its simplicity and therapeutic potential. Green synthesis relies on natural and environmentally friendly materials, such as plant extracts, to reduce metal ions and form nanoparticles. Moreover, the presence of bioactive plant compounds on their surface increases the therapeutic potential of these nanoparticles. The present article reviews the possibilities of nanoparticles obtained by green synthesis to combine the therapeutic effects of plant components with gold.
University of Queensland researchers are designing nanotechnology they believe could improve how we treat the most aggressive form of breast cancer.
Professor Chengzhong (Michael) Yu and his team are developing novel nanoparticles that could dramatically increase the effectiveness of immunotherapies when treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
TNBC is aggressive, fast-growing and accounts for 30 per cent of all breast cancer deaths in Australia each year, despite making up only 10 to 15 per cent of new cases.
Professor Yu, from UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (AIBN), said a new solution was needed because TNBC cancer cells lacked the proteins targeted by some of the treatments used against other cancers.
UQ researchers are designing nanotechnology they believe could improve how we treat the most aggressive form of breast cancer.