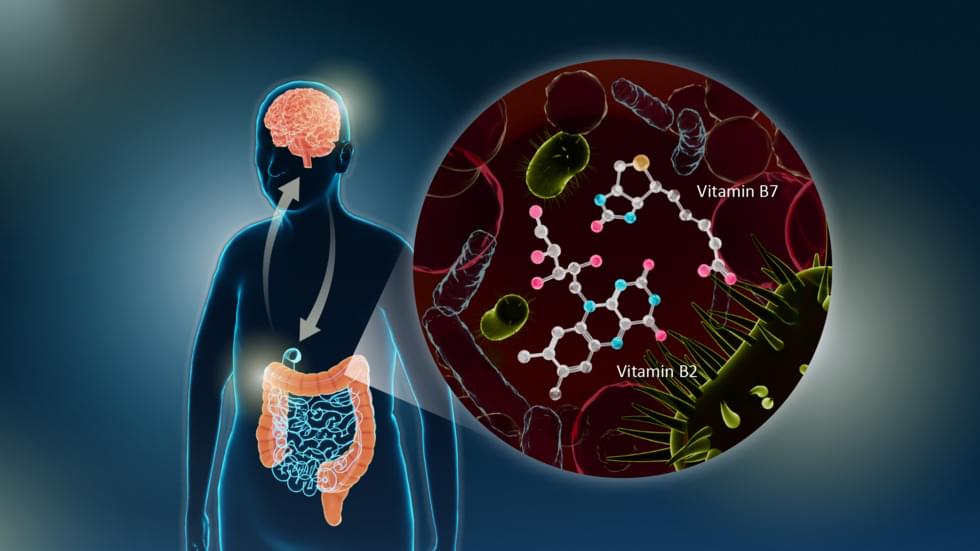
A study led by Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan has revealed a link between gut microbiota and Parkinson’s disease (PD). The researchers found a reduction in the gut bacteria of genes responsible for synthesizing the essential B vitamins B2 and B7. They also identified a relationship between the lack of these genes and low levels of agents that help maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier. This barrier prevents toxins from entering the bloodstream, which causes the inflammation seen in PD. Their findings, published in npj Parkinson’s Disease, suggest that treatment with B vitamins to address these deficiencies can be used to treat PD.
PD is characterized by a variety of physical symptoms that hinder daily activities and mobility, such as shaking, slow movement, stiffness, and balance problems. While the frequency of PD may vary between different populations, it is estimated to affect approximately 1–2% of individuals aged 55 years or older.
Various physiological processes are heavily influenced by the microorganisms found in the gut, which are collectively known as gut microbiota. In ideal conditions, gut microbiota produce SCFAs and polyamines, which maintain the intestinal barrier that prevents toxins entering the bloodstream. Toxins in the blood can be carried to the brain where they cause inflammation and affect neurotransmission processes that are critical for maintaining mental health.