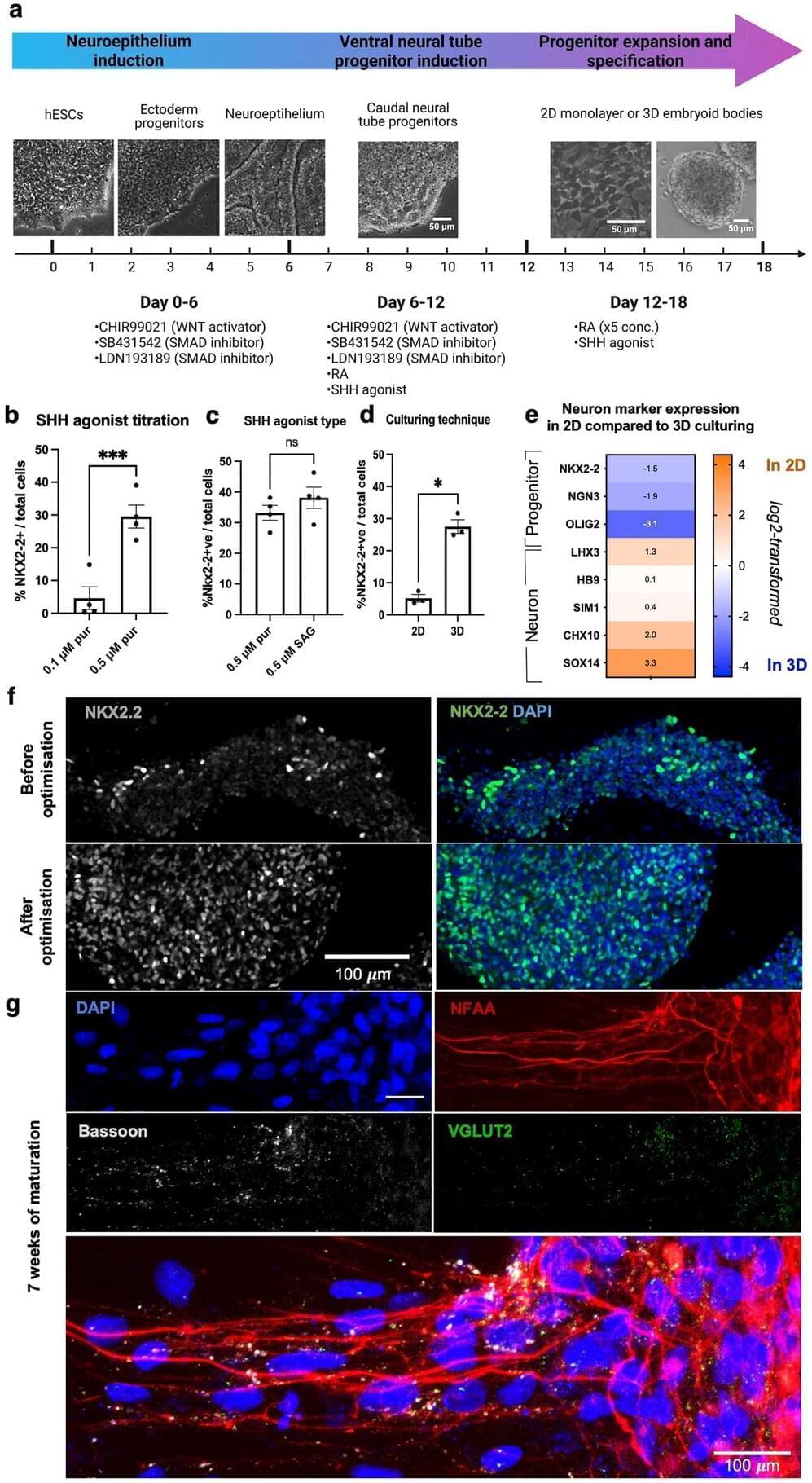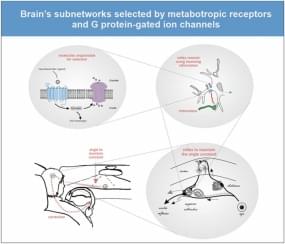
I am proud to announce that today came out probably my most important scientific paper. I propose a whole new paradigm in neuroscience. To understand the mind, synapses are not so important any more. Instead, critical are some other type of proteins on the neural membrane. These proteins have the capability to transiently select subnetworks that will be functional in the next few seconds or minutes. The paradigm proposes that cognition emerges from those transient subnetwork selections (and not from network computations of the classical, so-called connectionist paradigm). The proteins in question are metabotropic receptor and G protein-gated ion channels. Simply put, we think with those proteins. A result of a thought is a new state of network pathways, not the activity of neurons.
One can download the paper here:
Perhaps the most important question posed by brain research is: How the brain gives rise to the mind. To answer this question, we have primarily relied on the connectionist paradigm: The brain’s entire knowledge and thinking skills are thought to be stored in the connections; and the mental operations are executed by network computations. I propose here an alternative paradigm: Our knowledge and skills are stored in metabotropic receptors (MRs) and the G protein-gated ion channels (GPGICs). Here, mental operations are assumed to be executed by the functions of MRs and GPGICs. As GPGICs have the capacity to close or open branches of dendritic trees and axon terminals, their states transiently re-route neural activity throughout the nervous system. First, MRs detect ligands that signal the need to activate GPGICs. Next, GPGICs transiently select a subnetwork within the brain. The process of selecting this new subnetwork is what constitutes a mental operation – be it in a form of directed attention, perception or making a decision. Synaptic connections and network computations play only a secondary role, supporting MRs and GPGICs. According to this new paradigm, the mind emerges within the brain as the function of MRs and GPGICs whose primary function is to continually select the pathways over which neural activity will be allowed to pass. It is argued that MRs and GPGICs solve the scaling problem of intelligence from which the connectionism paradigm suffers.