An international team of astronomers has employed a set of space telescopes to observe a peculiar nuclear transient known as AT 2019avd. Results of the observational campaign, presented in a paper published December 21 on the pre-print server arXiv, deliver important insights into the properties and behavior of this transient.
Nuclear astrophysics is key to understanding supernova explosions, and in particular the synthesis of the chemical elements that evolved after the Big Bang. Therefore, detecting and investigating nuclear transient events could be essential in order to advance our knowledge in this field.
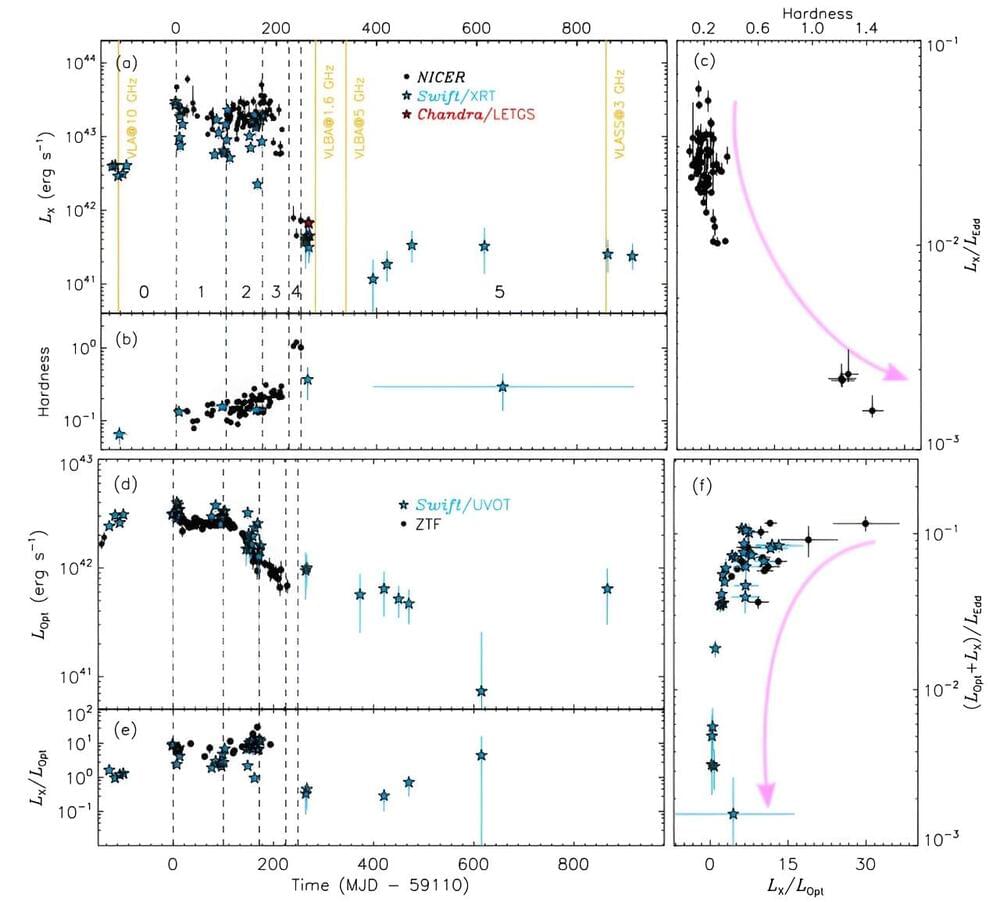
At a redshift of 0.028, AT 2019avd is a peculiar nuclear transient discovered by the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) in 2009. The transient has been detected in various wavelengths, from radio to soft X-rays, and has recently exhibited two continuous flaring episodes with different profiles, spanning over two years.


















