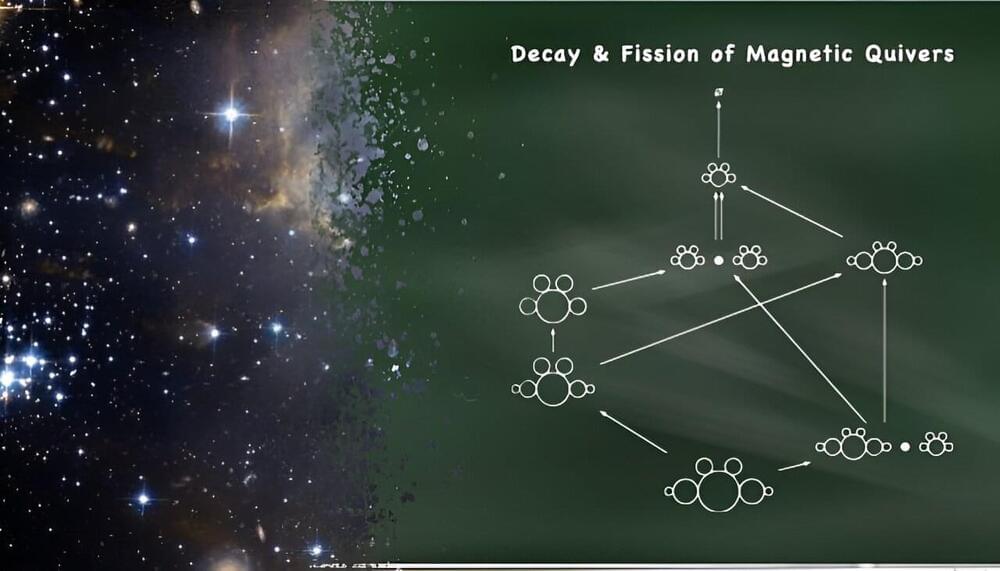
A simple concept of decay and fission of “magnetic quivers” helps to clarify complex quantum physics and mathematical structures.
Category: quantum physics – Page 184
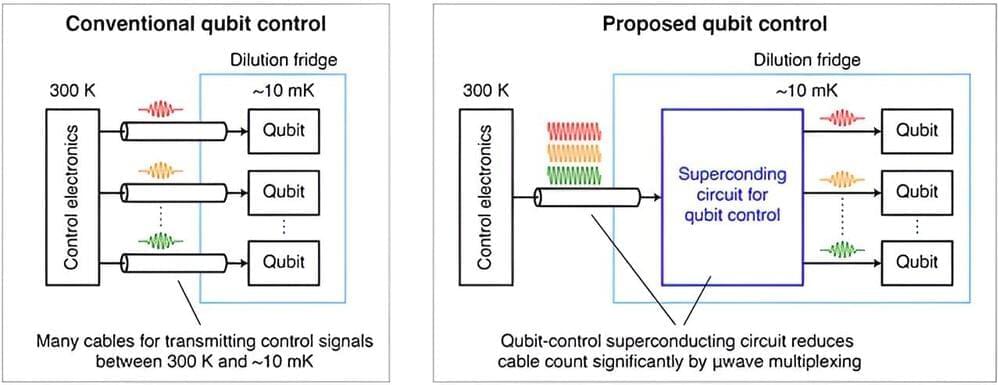
In support of the development of large-scale superconducting quantum computers, researchers with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), one of the largest public research organizations in Japan, in collaboration with Yokohama National University, Tohoku University, and NEC Corporation, proposed and successfully demonstrated a superconducting circuit that can control many qubits at low temperature.
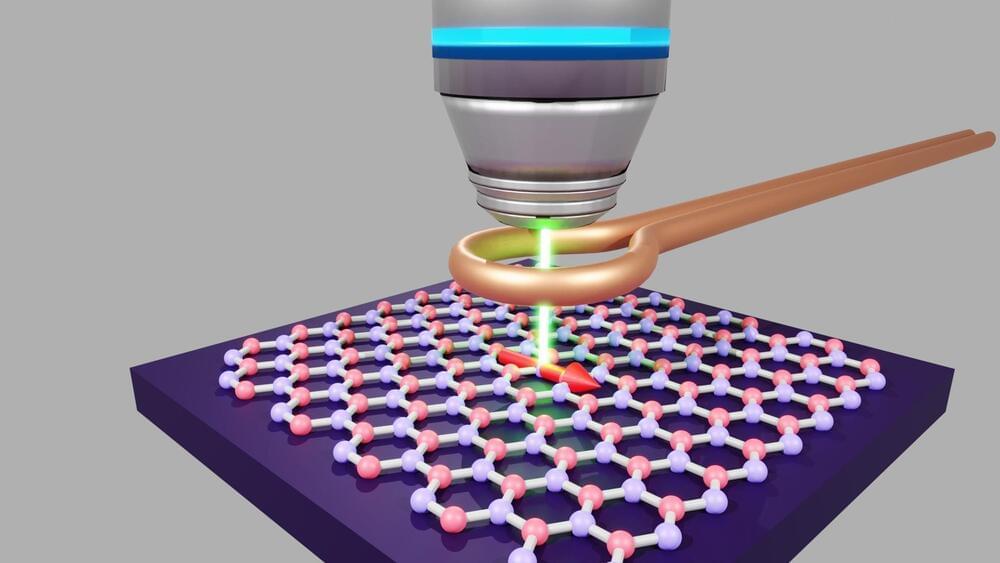
A collaborative study by researchers at Lancaster and Radboud universities has pioneered a method to generate and control spin waves at the nanoscale, offering a new, energy-efficient approach to quantum computing.
Researchers at Lancaster University and Radboud University Nijmegen have successfully produced propagating spin waves on the nanoscale, unveiling a new method to modulate and amplify these waves.
Their discovery, published in Nature, could pave the way for the development of dissipation-free quantum information technologies. As the spin waves do not involve electric currents these chips will be free from associated losses of energy.
Explore the fascinating world of quantum teleportation. Discover its principles, applications, and the profound impact it could have on our future.
Introduction to Quantum Teleportation
Quantum teleportation, a term that sounds like it’s straight out of science fiction, is a very real and advancing field in quantum physics. This groundbreaking technology is not about transporting matter from one place to another but rather involves the transfer of information between quantum particles. This article delves into the science behind quantum teleportation, its potential applications, and the impact it could have on various aspects of our lives.
There’s a hot new BEC in town that has nothing to do with bacon, egg, and cheese. You won’t find it at your local bodega, but in the coldest place in New York: the lab of Columbia physicist Sebastian Will, whose experimental group specializes in pushing atoms and molecules to temperatures just fractions of a degree above absolute zero.
Scientists at the Cavendish Laboratory have discovered spin coherence in Hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) under normal conditions, offering new prospects for quantum technology applications.
Cavendish Laboratory researchers have discovered that a single ‘atomic defect’ in a material known as Hexagonal Boron Nitride (hBN) maintains spin coherence at room temperature and can be manipulated using light.
Spin coherence refers to an electronic spin being capable of retaining quantum information over time. The discovery is significant because materials that can host quantum properties under ambient conditions are quite rare.
To reliably perform complex, large-scale calculations, computing systems rely on so-called error correction schemes, techniques designed to protect information against errors. These techniques are perhaps even more essential when it comes to quantum computers, devices that perform computations leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics.
Industry and academia in Japan and the United States are collaborating on research to pioneer quantum-centric supercomputing.
In the general formulation of quantum information, quantum states are represented by a special class of matrices called density matrices. This lesson describes the basics of how density matrices work and explains how they relate to quantum state vectors. It also introduces the Bloch sphere, which provides a useful geometric representation of qubit states, and discusses different types of correlations that can be described using density matrices.
0:00 — Introduction.
1:46 — Overview.
2:55 — Motivation.
4:40 — Definition of density matrices.
9:55 — Examples.
12:58 — Interpretation.
15:37 — Connection to state vectors.
20:13 — Probabilistic selections.
25:23 — Completely mixed state.
28:41 — Probabilistic states.
32:03 — Spectral theorem.
37:36 — Bloch sphere (introduction)
38:36 — Qubit quantum state vectors.
41:30 — Pure states of a qubit.
43:52 — Bloch sphere.
47:38 — Bloch sphere examples.
51:36 — Bloch ball.
55:40 — Multiple systems.
56:46 — Independence and correlation.
1:00:55 — Reduced states for an e-bit.
1:04:16 — Reduced states in general.
1:08:53 — The partial trace.
1:12:23 — Conclusion.
Find the written content for this lesson on IBM Quantum Learning: https://learning.quantum.ibm.com/cour…
#ibmquantum #learnquantum #qiskit
Since Nobel-Prize-winning physicist Frank Wilczek first proposed his theory over a decade ago, researchers have been on the search for elusive “time crystals”—many-body systems composed of particles and quasiparticles like excitons, photons, and polaritons that, in their most stable quantum state, vary periodically in time.
Wilczek’s theory centered around a puzzling question: Can the most stable state of a quantum system of many particles be periodic in time? That is, can it display temporal oscillations characterized by a beating with a well-defined rhythm?
It was quite rapidly shown that time crystal behavior cannot occur in isolated systems (systems which do not exchange energy with the surrounding environment). But far from closing the subject, this disturbing question motivated scientists to search for the conditions under which an open system (i.e., one that exchanges energy with the environment) may develop such time crystal behavior.