A team of physicists at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel has successfully demonstrated the inverse Mpemba effect at the quantum level using single trapped ions. In their study, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the group demonstrated the effect by trapping a strontium-88 ion coupled to an external thermal bath.
Category: quantum physics – Page 185
Superconductivity is a fascinating phenomenon, which allows a material to sustain an electrical current without any loss. This collective quantum behavior of matter only appears in certain conductors at temperatures far below ambient.
Physicists have struggled to understand the nature of time since the field began. But a new theoretical study suggests time could be an illusion woven at the quantum level.
Google’s Sycamore quantum computer was the first to demonstrate quantum supremacy – solving calculations that would be unfeasible on a classical computer – but now ordinary machines have pulled ahead again.
Engineers at EPFL have developed a device capable of transforming heat into electrical voltage efficiently at temperatures even colder than those found in outer space. This breakthrough could significantly advance quantum computing technologies by addressing a major obstacle.
To perform quantum computations, quantum bits (qubits) need to be cooled to temperatures in the millikelvin range (close to-273 degrees Celsius) to reduce atomic motion and minimize noise. However, the electronics used to control these quantum circuits generate heat, which is challenging to dissipate at such low temperatures. Consequently, most current technologies must separate the quantum circuits from their electronic components, resulting in noise and inefficiencies that impede the development of larger quantum systems beyond the laboratory.
Researchers in EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES), led by Andras Kis, in the School of Engineering have now fabricated a device that not only operates at extremely low temperatures, but does so with efficiency comparable to current technologies at room temperature.
A new study in Nature Physics demonstrates a novel method for generating quantum entanglement using a quantum dot, which violates the Bell inequality. This method uses ultra-low power levels and could pave the way for scalable and efficient quantum technologies.
The idea of time travel has dazzled sci-fi enthusiasts for years. Science tells us that traveling to the future is technically feasible, at least if you’re willing to go near the speed of light, but going back in time is a no-go. But what if scientists could leverage the advantages of quantum physics to uncover data about complex systems that happened in the past?
New research indicates that this premise may not be that far-fetched. In a paper published June 27, 2024, in Physical Review Letters, Kater Murch, the Charles M. Hohenberg Professor of Physics and Director of the Center for Quantum Leaps at Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues Nicole Yunger Halpern at NIST and David Arvidsson-Shukur at the University of Cambridge demonstrate a new type of quantum sensor that leverages quantum entanglement to make time-traveling detectors.
Murch describes this concept as analogous to being able to send a telescope back in time to capture a shooting star that you saw out of the corner of your eye. In the everyday world, this idea is a non-starter. But in the mysterious and enigmatic land of quantum physics, there may be a way to circumvent the rules. This is thanks to a property of entangled quantum sensors that Murch refers to as “hindsight.”
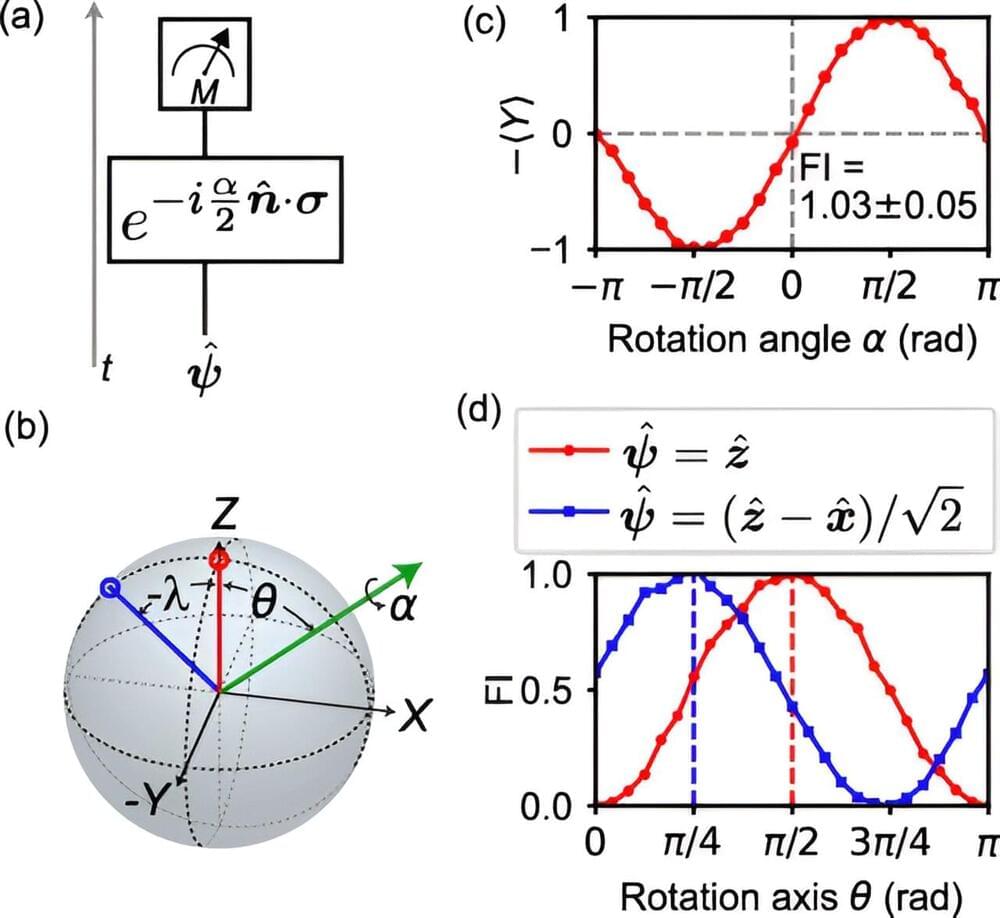
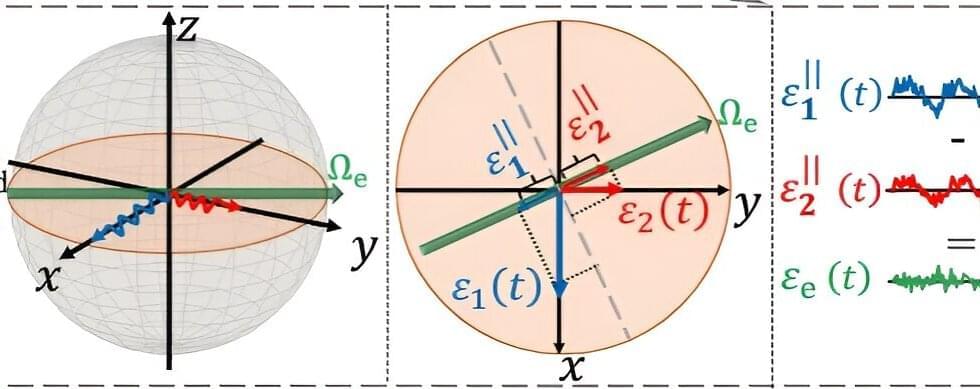
Researchers have developed a new method to significantly enhance quantum technology performance by using the cross-correlation of two noise sources to extend coherence time, improve control fidelity, and increase sensitivity for high-frequency sensing. This innovative strategy addresses key challenges in quantum systems, offering a tenfold increase in stability and paving the way for more reliable and versatile quantum devices.
The work is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in quantum technology by developing a novel method that dramatically improves the stability and performance of quantum systems. This pioneering work addresses the longstanding challenges of decoherence and imperfect control, paving the way for more reliable and sensitive quantum devices.
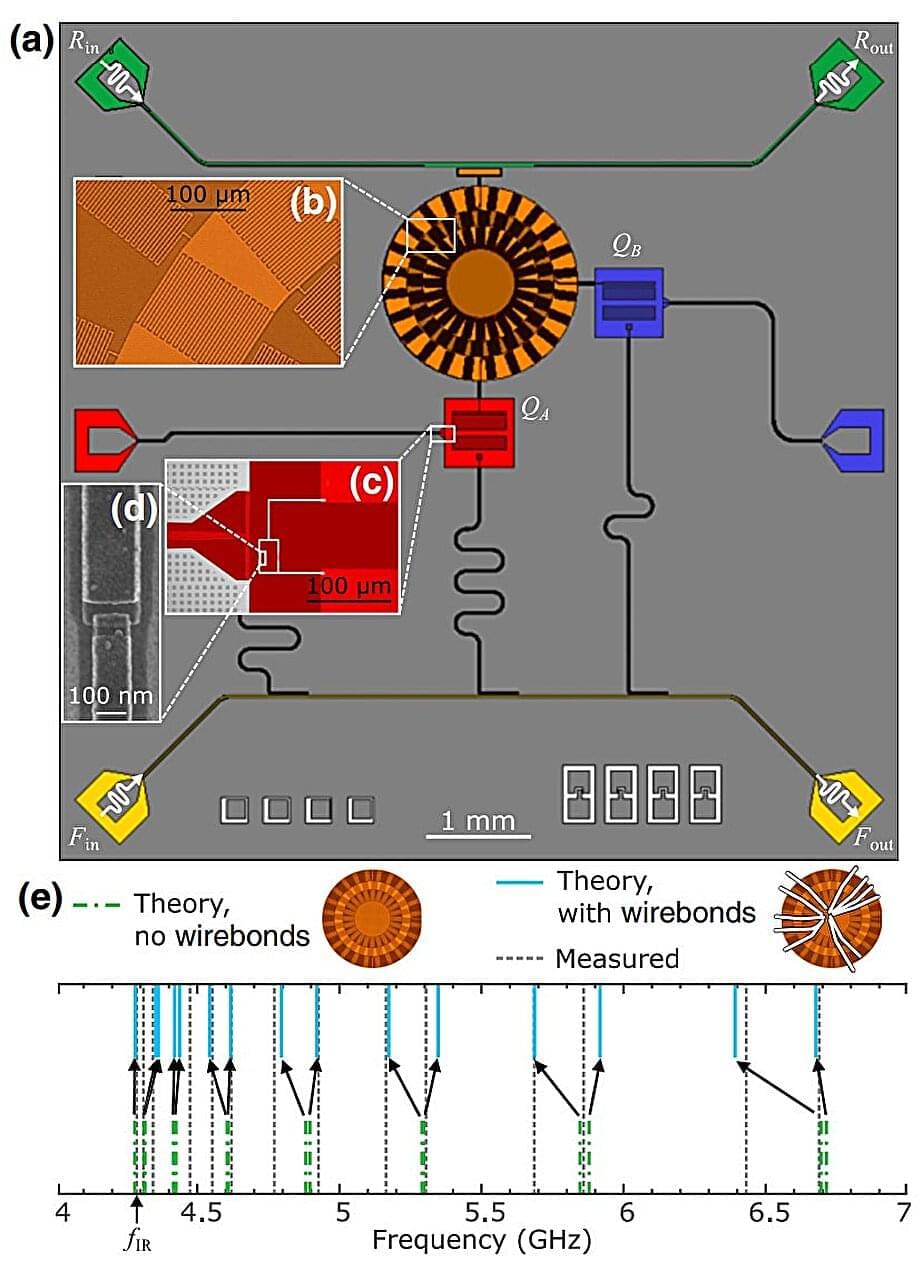
Implementing a fault-tolerant quantum processor requires coupling qubits to generate entanglement. Superconducting qubits are a promising platform for quantum information processing, but scaling up to a full-scale quantum computer necessitates interconnecting many qubits with low error rates. Traditional methods often limit coupling to nearest neighbors, require large physical footprints, and involve numerous couplers, complicating fabrication.
For instance, coupling 100 qubits pairwise demands a vast number of couplers. Moreover, controlling individual circuit elements and couplers with separate cables for even 1,000 qubits would require an impractically large volume of cables, making it infeasible to fit such a system in a large lab, let alone manage millions of qubits. This highlights the need for more efficient and scalable coupling methods.
A team of theoretical physicists led by Mohd Ansari at FZJ, in collaboration with the experimental team of Britton Plourde at Syracuse University, introduced a novel approach using a multimode coupler that enables tunable coupling strength between any pair of qubits.
Charge density waves are quantum phenomena occurring in some materials, which involve a static modulation of conduction electrons and the periodic distortion of the lattice. These waves have been observed in numerous condensed matter materials, including high-temperature superconductors and quantum Hall systems.
While many studies have investigated these states, so far experimental observations of the boundary states that emerge from charge density waves are still scarce. In a recent paper, published in Nature Physics, researchers at Princeton University and other institutes worldwide have visualized the bulk and boundary modes of the charge density wave in the topological material Ta2Se8I.
“Our research group focuses on discovering and investigating novel topological properties of quantum matter utilizing various state-of-the-art experimental techniques that probe electronic structure of the materials,” Maksim Litskevich, co-author of the paper, told Phys.org. “In recent years, the physics community has experienced excitement exploring the intriguing and rich properties of Kagome materials, which intricately intertwine geometry, topology, and electronic interactions.”