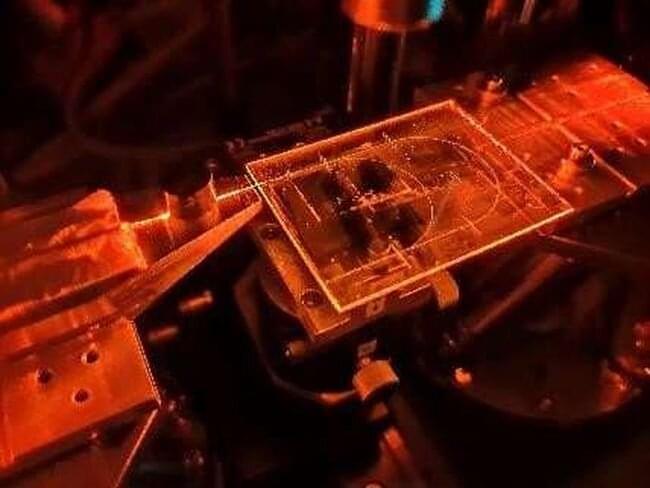
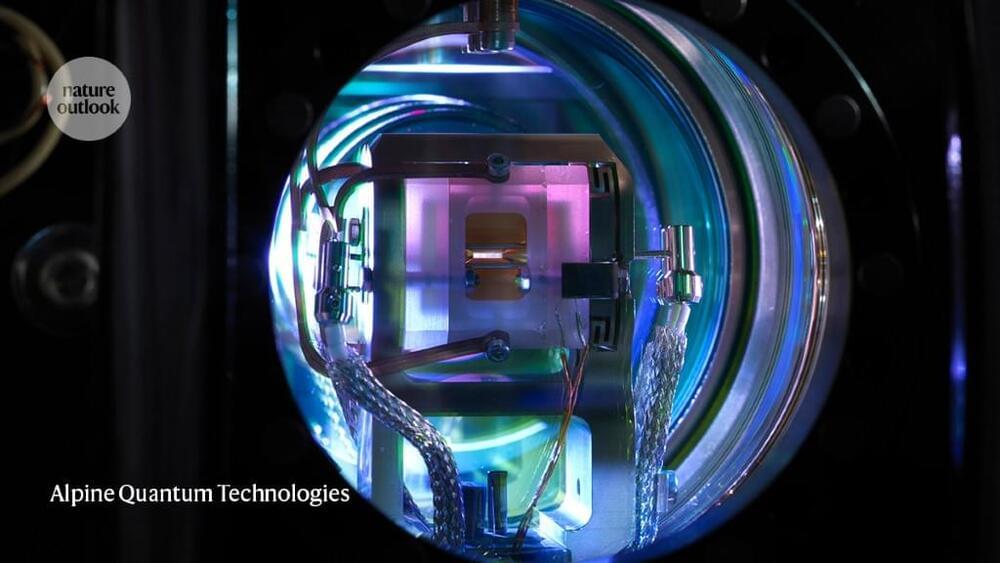
Researchers have developed a quantum key distribution (QKD) system based on integrated photonics that can transmit secure keys at unprecedented speeds. The proof-of-principle experiments represent an important step toward real-world application of this highly secure communication method.
QKD is a well-established method of providing secret keys for secure communication between distant parties. By using the quantum properties of light to generate secure random keys for encrypting and decrypting data, its security is based on the laws of physics, rather than computational complexity like today’s communication protocols.
“A key goal for QKD technology is the ability to simply integrate it into a real-world communications network,” said research team member Rebecka Sax from the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “An important and necessary step toward this goal is the use of integrated photonics, which allows optical systems to be manufactured using the same semiconductor technology used to make silicon computer chips.”