Who was rumored to be a pedophile.
“The over-all number of minds is just one.”

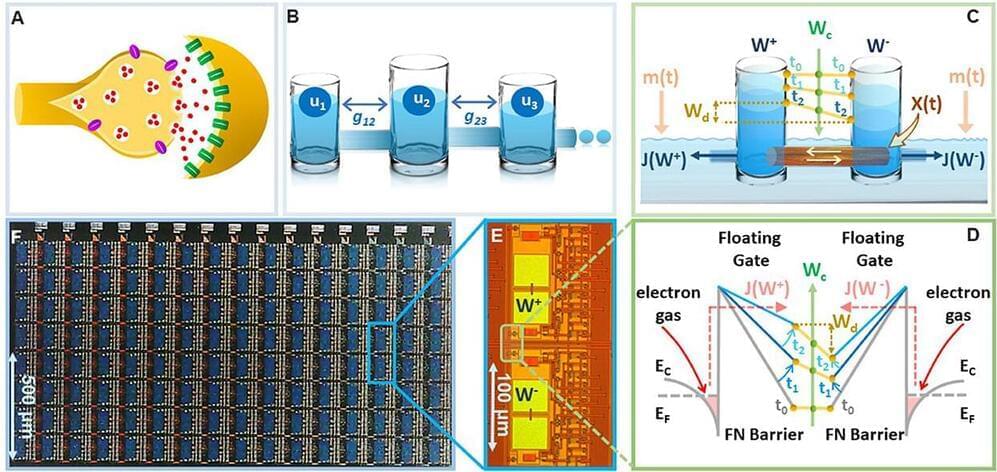
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have made tremendous progress in the past few years including the recent launch of ChatGPT and art generators, but one thing that is still outstanding is an energy-efficient way to generate and store long-and short-term memories at a form factor that is comparable to a human brain. A team of researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has developed an energy-efficient way to consolidate long-term memories on a tiny chip.
Shantanu Chakrabartty, the Clifford W. Murphy Professor in the Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering, and members of his lab developed a relatively simple device that mimics the dynamics of the brain’s synapses, connections between neurons that allows signals to pass information. The artificial synapses used in many modern AI systems are relatively simple, whereas biological synapses can potentially store complex memories due to an exquisite interplay between different chemical pathways.
Chakrabartty’s group showed that their artificial synapse could also mimic some of these dynamics that can allow AI systems to continuously learn new tasks without forgetting how to perform old tasks. Results of the research were published Jan. 13 in Frontiers in Neuroscience.
A trailblazing experiment could yield results that help prove the existence of a quantum gravity particle.


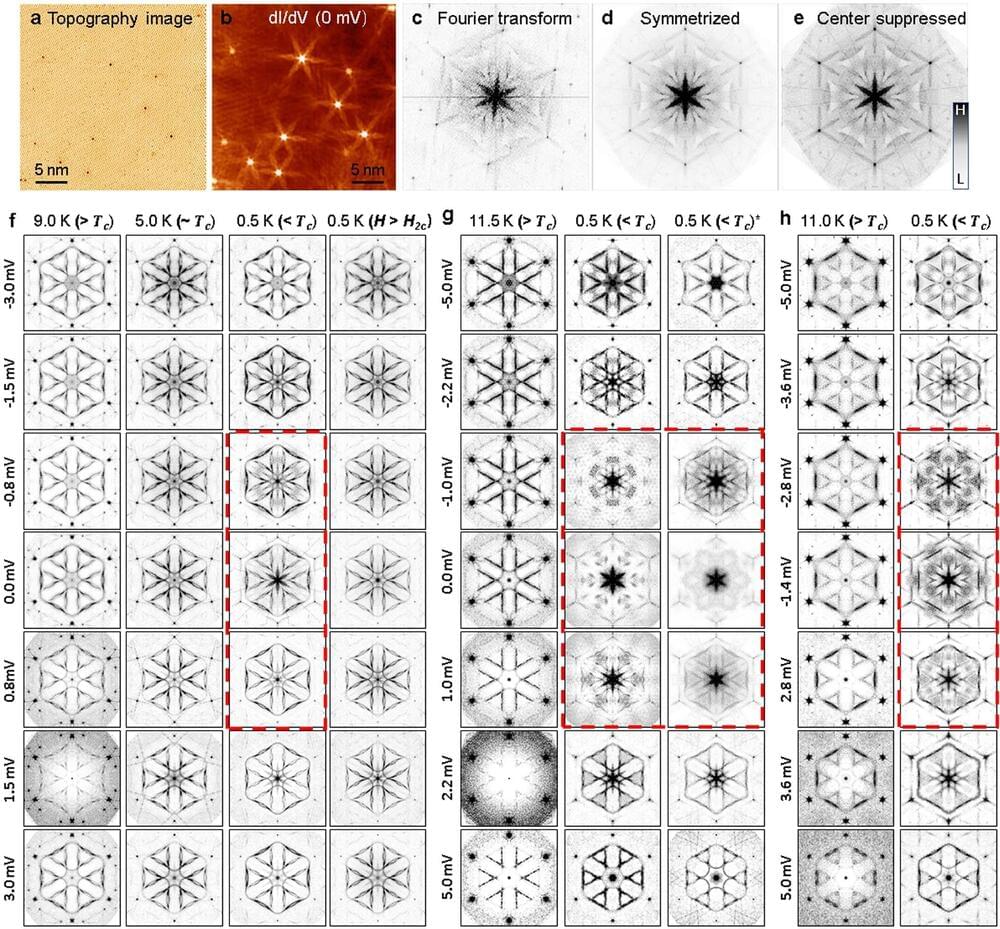
The University of Tennessee’s physicists have led a scientific team that found silicon—a mainstay of the soon-to-be trillion-dollar electronics industry—can host a novel form of superconductivity that could bring rapidly emerging quantum technologies closer to industrial scale production.
The findings are reported in Nature Physics and involve electron theft, time reversal, and a little electronic ambidexterity.
Superconductors conduct electric current without resistance or energy dissipation. Their uses range from powerful electromagnets for particle accelerators and medical MRI devices to ultrasensitive magnetic sensors to quantum computers. Superconductivity is a spectacular display of quantum mechanics in action on a macroscopic scale. It all comes down to the electrons.
A certain amount of noise is inherent in any quantum system. For instance, when researchers want to read information from a quantum computer, which harnesses quantum mechanical phenomena to solve certain problems too complex for classical computers, the same quantum mechanics also imparts a minimum level of unavoidable error that limits the accuracy of the measurements.
Scientists can effectively get around this limitation by using “parametric” amplification to “squeeze” the noise—a quantum phenomenon that decreases the noise affecting one variable while increasing the noise that affects its conjugate partner. While the total amount of noise remains the same, it is effectively redistributed. Researchers can then make more accurate measurements by looking only at the lower-noise variable.
A team of researchers from MIT and elsewhere has now developed a new superconducting parametric amplifier that operates with the gain of previous narrowband squeezers while achieving quantum squeezing over much larger bandwidths. Their work is the first to demonstrate squeezing over a broad frequency bandwidth of up to 1.75 gigahertz while maintaining a high degree of squeezing (selective noise reduction). In comparison, previous microwave parametric amplifiers generally achieved bandwidths of only 100 megahertz or less.
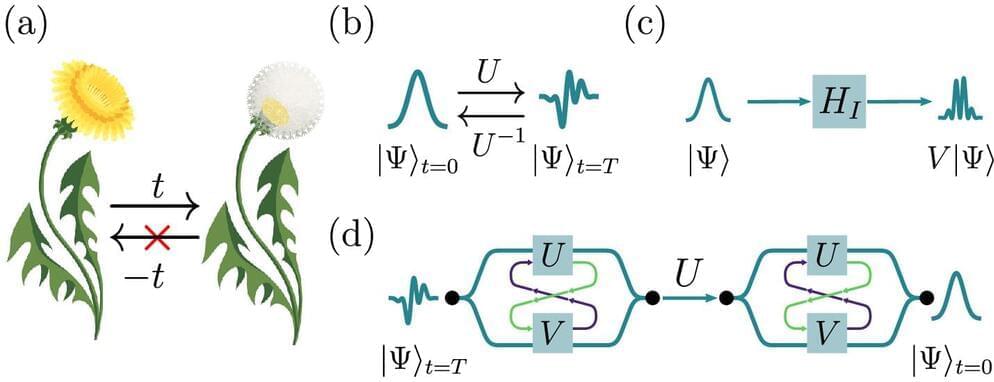
In the world around us, processes appear to follow a certain time-direction: Dandelions eventually turn into blowballs. However, the quantum realm does not play by the same rules. Physicists from the University of Vienna and IQOQI Vienna have now shown that for certain quantum systems, the time-direction of processes can be reversed. This demonstration of a so-called rewinding protocol has been published in Optica.
Everyday life is full of changes that are well understood, yet practically impossible to reverse; for example, the metamorphosis of a dandelion into a blowball. However, one could imagine undoing this transformation, step by step, if one knew precisely how each molecule in the plant moved in time. In the quantum realm the problem gets even trickier: One of the core principles of quantum physics is that simply observing a system causes it to change.
This makes it impossible, even in principle, to track a system’s change in time and reverse the process. However, at the same time, the laws of quantum mechanics also open up new possibilities such as universal rewinding protocols. These allow for reversing changes in a quantum system without knowing what they were.
O.o! If the universe is some sorta hologram then this could be a clue to our actual reality.
Last December, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded for experimental evidence of a quantum phenomenon that has been known for more than 80 years: entanglement. As envisioned by Albert Einstein and his collaborators in 1935, quantum objects can be mysteriously correlated even when separated by great distances. But as strange as the phenomenon may seem, why is such an old idea still worthy of the most prestigious award in physics?
Coincidentally, just weeks before the new Nobel laureates were honored in Stockholm, another team of respected scientists from Harvard, MIT, Caltech, Fermilab and Google reported that they ran a process on Google’s quantum computer that could be interpreted as a wormhole. Wormholes are tunnels through the universe that can function as a shortcut through space and time and are loved by science fiction fans, and although the tunnel realized in this latest experiment only exists in a two-dimensional toy universe, it could be a breakthrough for the future represent research at the forefront of physics.
But why does entanglement have to do with space and time? And how can it be important for future breakthroughs in physics? Properly understood, entanglement means that the universe is what philosophers call “monistic,” that is, at the most fundamental level, everything in the universe is part of a single, unified whole. It is a defining property of quantum mechanics that its underlying reality is described in terms of waves, and a monistic universe would require universal functioning. Decades ago, researchers such as Hugh Everett and Dieter Zeh showed how our everyday reality can emerge from such a universal quantum mechanical description. But it is only now that researchers such as Leonard Susskind and Sean Carroll are developing ideas as to how this hidden quantum reality could explain not only matter but also the structure of space and time.

Researchers have learned much about neutrinos over the past few decades, but some mysteries remain unsolved. For example, the standard model predicts that neutrinos are massless, but experiments say otherwise. One possible solution to this mass mystery involves another group of neutrinos that does not interact directly via the weak nuclear force and is therefore extremely difficult to detect. David Moore of Yale University and his colleagues have proposed a way to search for these so-called sterile neutrinos using a radioactive nanoparticle suspended in a laser beam [1].
Moore and his colleagues suggest levitating a 100-nm-diameter silica sphere in an optical trap and cooling it to its motional ground state. If the nanoparticle is filled with nuclei that decay by emitting neutrinos—such as certain argon or phosphorous isotopes—then electrons and neutrinos zipping from decaying nuclei should give it a momentum kick. By measuring the magnitude of this kick, the team hopes to determine the neutrinos’ momenta. Although most of these neutrinos will be the familiar three neutrino flavors, sterile neutrinos—if they exist—should also occasionally be emitted, producing unexpectedly small momentum kicks. Moore says that monitoring a single nanoparticle for one month would equate to a sterile-neutrino sensitivity 10 times better than that of any experiment tried so far.
Moore and his team are currently working on a proof-of-principle experiment using alpha-emitting by-products of radon, which result in a larger momentum kick. Once the techniques are optimized, they expect that switching to beta-decaying isotopes will let them see heavy sterile neutrinos in the 0.1–1 MeV mass range. Introducing more quantum tricks to manipulate the nanoparticle’s quantum state will make future experiments sensitive to even lighter sterile neutrinos.