Collaboration will seek to advance the development of a quantum internet.


Quantum computing looks like a world of imagination where we’ll be processing data beyond our thoughts. Many Industries are working to make a powerful Quantum computer that will solve all the issues. But what IBM has done is really something exceptional. They have developed the world’s first Quantum computer that will change history.
In a classical computer, data is stored and processed in bits, represented by either a zero or a one. But in quantum computers, qubits can not only be in a zero or one state but a superposition of both simultaneously: the more qubits, the more computing power, and the more possibilities. IBM’s quantum computer journey started with a 5-qubit quantum computer on the cloud called the Quantum Experience and led to the Eagle chip that began in 2016. Since then, the company has released a succession of chips with increasing numbers of qubits, all named after birds, each with its own set of technological challenges.
Watch How artificial Intelligence is changing the world:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=trhLQi9RuZ4&t.
#Quantumcomputer #Quantumcomputeribm
face_with_colon_three circa 2018.
Understanding the fundamental constituents of the universe is tough. Making sense of the brain is another challenge entirely. Each cubic millimetre of human brain contains around 4 km of neuronal “wires” carrying millivolt-level signals, connecting innumerable cells that define everything we are and do. The ancient Egyptians already knew that different parts of the brain govern different physical functions, and a couple of centuries have passed since physicians entertained crowds by passing currents through corpses to make them seem alive. But only in recent decades have neuroscientists been able to delve deep into the brain’s circuitry.
On 25 January, speaking to a packed audience in CERN’s Theory department, Vijay Balasubramanian of the University of Pennsylvania described a physicist’s approach to solving the brain. Balasubramanian did his PhD in theoretical particle physics at Princeton University and also worked on the UA1 experiment at CERN’s Super Proton Synchrotron in the 1980s. Today, his research ranges from string theory to theoretical biophysics, where he applies methodologies common in physics to model the neural topography of information processing in the brain.
“We are using, as far as we can, hard mathematics to make real, quantitative, testable predictions, which is unusual in biology.” — Vijay Balasubramanian

Circa 2016 memory transfer between two organisms.
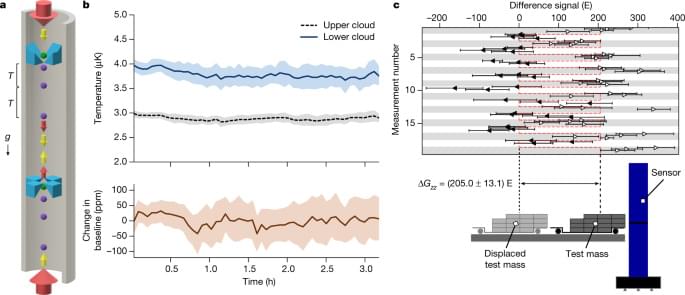
Schrödinger’s thought experiment to prepare a cat in a superposition of both alive and dead states reveals profound consequences of quantum mechanics and has attracted enormous interests. Here we propose a straightforward method to create quantum superposition states of a living microorganism by putting a small cryopreserved bacterium on top of an electromechanical oscillator. Our proposal is based on recent developments that the center-of-mass oscillation of a 15-μm-diameter aluminum membrane has been cooled to its quantum ground state (Teufel et al. in Nature 475:359, 2011), and entangled with a microwave field (Palomaki et al. in Science 342:710, 2013). A microorganism with a mass much smaller than the mass of the electromechanical membrane will not significantly affect the quality factor of the membrane and can be cooled to the quantum ground state together with the membrane.
The company’s engineers said that the new device may not be slated for use with any of the current IBM Quantum processors but that building it taught them important lessons on how to overcome these challenges.
In this video I discuss 5 Types of Compute which can replace our traditional Computers in the Future.
Watch Next:
➞ Analog Compute: https://youtu.be/f4A85foHPZY
➞ Biological Compute: https://youtu.be/FuzoLdrRX5Q
➞ Compute with Light: https://youtu.be/mt8I71VUazw.
➞ Quantum Computers: https://youtu.be/j9eYQ_ggqJk.
➞ RF compute paper: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345970494_Radio-Fre…c_Synapses.
➞ Support me on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/AnastasiInTech.
➞ Subscribe to my Newsletter: https://anastasiintech.substack.com
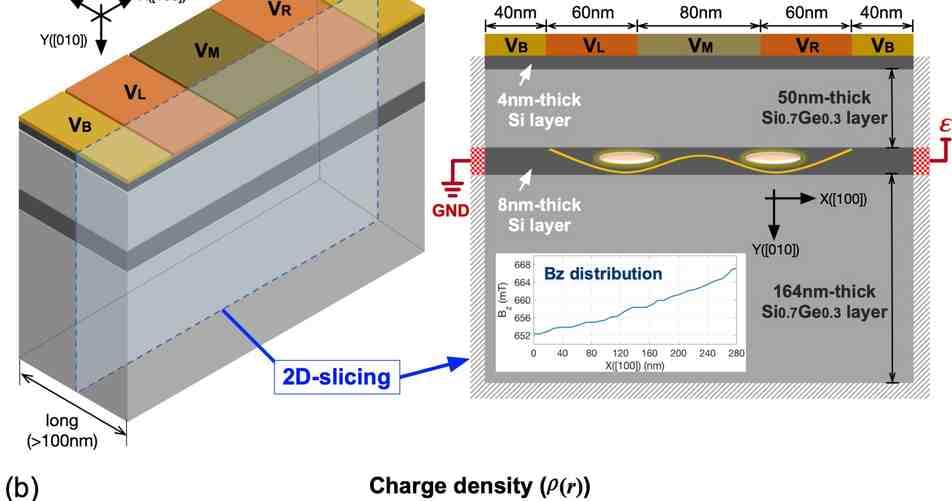
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center in diamond is a promising quantum sensor with remarkably versatile sensing capabilities. While scanning NV magnetometry is well-established, NV electrometry has been so far limited to bulk diamonds. Here we demonstrate imaging external alternating (AC) and direct (DC) electric fields with a single NV at the apex of a diamond scanning tip under ambient conditions. A strong electric field screening effect is observed at low frequencies. We quantitatively measure its frequency dependence and overcome this screening by mechanically oscillating the tip for imaging DC fields. Our scanning NV electrometry achieved an AC E-field sensitivity of 26‰mV‰Î¼m ˆ’1‰Hz ˆ’1/2, a DC E-field gradient sensitivity of 2‰V‰Î¼m ˆ’2‰Hz ˆ’1/2, and sub-100‰nm resolution limited by the NV-sample distance. Our work represents an important step toward building a scanning-probe-based multimodal quantum sensing platform.
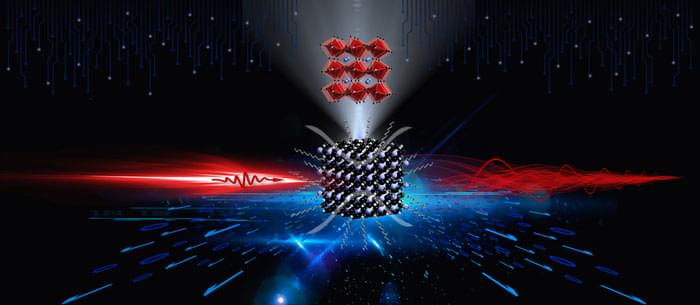
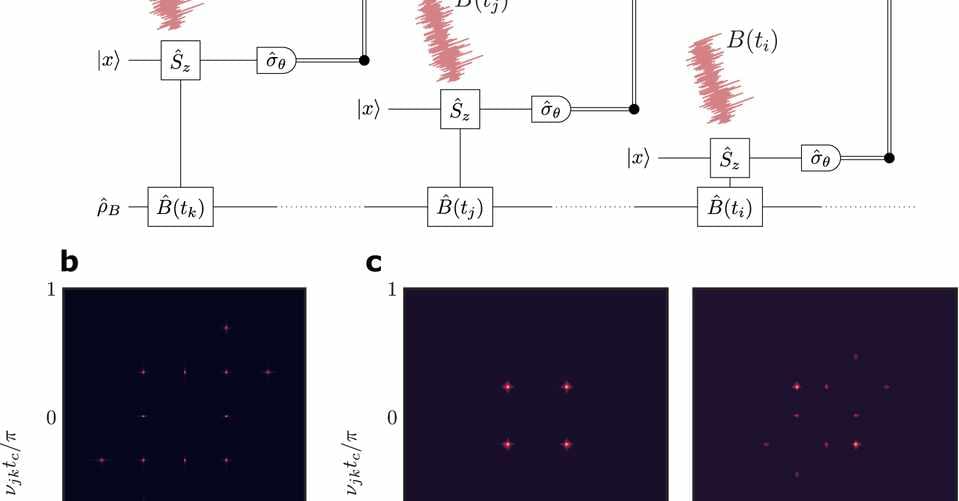
A research group led by Prof. WU Kaifeng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Dr. Peter C. Sercel from the Center for Hybrid Organic Inorganic Semiconductors for Energy, recently reported the utilization of lattice distortion in lead halide perovskite quantum dots (QDs) to control their exciton fine structure.
The study was published in Nature Materials (“Lattice distortion inducing exciton splitting and coherent quantum beating in CsPbI 3 perovskite quantum dots”).
Lattice distortion of perovskite quantum dots induces coherent quantum beating. (Image: DICP)