It’s not every day that someone comes across a new state of matter in quantum physics, the scientific field devoted to describing the behavior of atomic and subatomic particles in order to elucidate their properties.
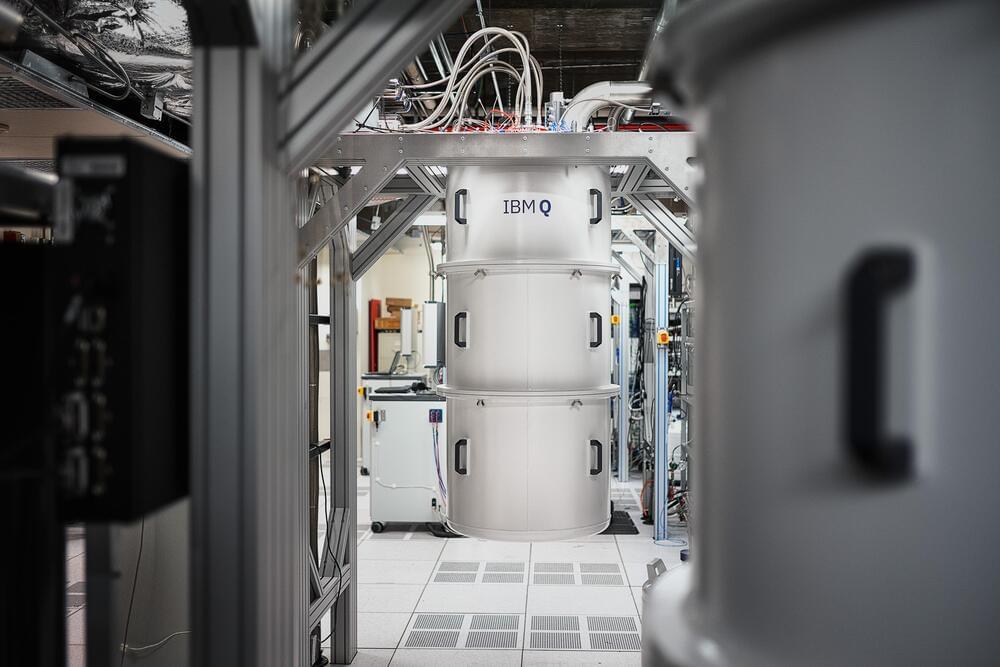



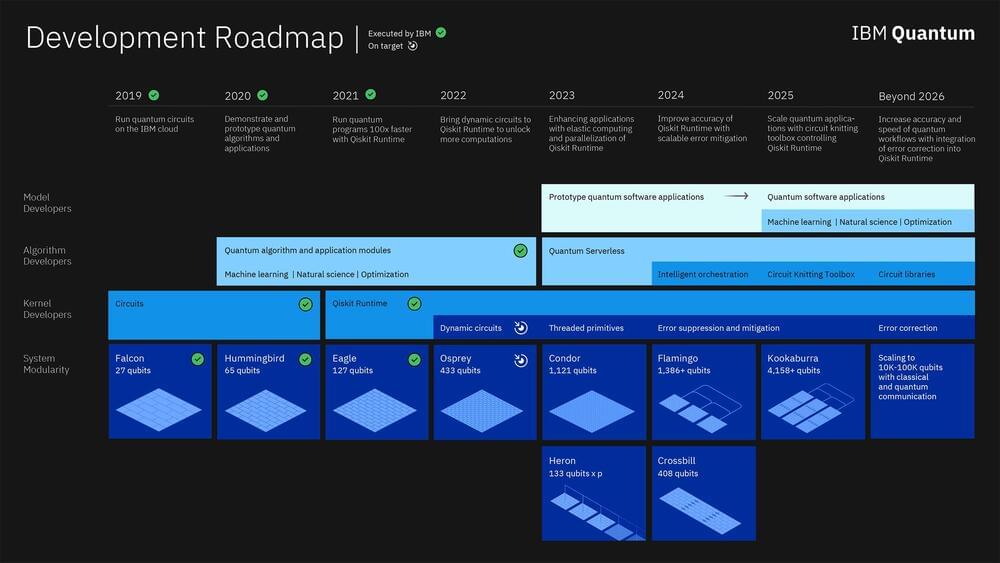
Forty years after it first began to dabble in quantum computing, IBM is ready to expand the technology out of the lab and into more practical applications — like supercomputing! The company has already hit a number of development milestones since it released its previous quantum roadmap in 2020, including the 127-qubit Eagle processor that uses quantum circuits and the Qiskit Runtime API. IBM announced on Wednesday that it plans to further scale its quantum ambitions and has revised the 2020 roadmap with an even loftier goal of operating a 4,000-qubit system by 2025.
Before it sets about building the biggest quantum computer to date, IBM plans release its 433-qubit Osprey chip later this year and migrate the Qiskit Runtime to the cloud in 2023, “bringing a serverless approach into the core quantum software stack,” per Wednesday’s release. Those products will be followed later that year by Condor, a quantum chip IBM is billing as “the world’s first universal quantum processor with over 1,000 qubits.”
This rapid four-fold jump in quantum volume (the number of qubits packed into a processor) will enable users to run increasingly longer quantum circuits, while increasing the processing speed — measured in CLOPS (circuit layer operations per second) — from a maximum of 2,900 OPS to over 10,000. Then it’s just a simple matter of quadrupaling that capacity in the span of less than 24 months.
Leonard Susskind (Stanford University)
https://simons.berkeley.edu/events/quantum-colloquium-black-…ing-thesis.
Quantum Colloquium.
A few years ago three computer scientists named Adam Bouland, Bill Fefferman, and Umesh Vazirani, wrote a paper that promises to radically change the way we think about the interiors of black holes. Inspired by their paper I will explain how black holes threaten the QECTT, and how the properties of horizons rescue the thesis, and eventually make predictions for the complexity of extracting information from behind the black hole horizon. I’ll try my best to explain enough about black holes to keep the lecture self contained.
Panel featuring Scott Aaronson (UT Austin), Geoffrey Penington (UC Berkeley), and Edward Witten (IAS); Umesh Vazirani (UC Berkeley; moderator). 1:27:30.
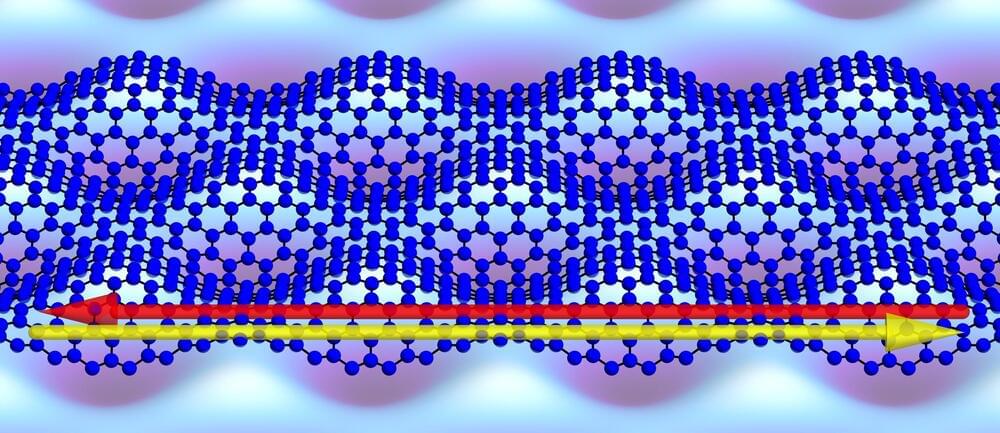
Since graphene was first isolated and characterized in the early 2000s, researchers have been exploring ways to use this atomically thin nanomaterial because of its unique properties such as high tensile strength and conductivity.
In more recent years, twisted bilayer graphene, made of two sheets of graphene twisted to a specific “magic” angle, has been shown to have superconductivity, meaning that it can conduct electricity with very little resistance. However, using this approach to make devices remains challenging because of the low yield of fabricating twisted bilayer graphene.
Now, a new study shows how patterned, periodic deformations of a single layer of graphene transforms it into a material with electronic properties previously seen in twisted graphene bilayers. This system also hosts additional unexpected and interesting conducting states at the boundary. Through a better understanding of how unique properties occur when single sheets of graphene are subjected to periodic strain, this work has the potential to create quantum devices such as orbital magnets and superconductors in the future. The study, published in Physical Review Letters, was conducted by graduate student Võ Tiến Phong and professor Eugene Mele in Penn’s Department of Physics & Astronomy in the School of Arts & Sciences.
We’re excited to present an update to the IBM Quantum roadmap, and our plan to weave quantum processors, CPUs, and GPUs into a compute fabric capable of solving problems beyond the scope of classical resources.
Two years ago, we issued our first draft of that map to take our first steps: our ambitious three-year plan to develop quantum computing technology, called our development roadmap. Since then, our exploration has revealed new discoveries, gaining us insights that have allowed us to refine that map and travel even further than we’d planned. Today, we’re excited to present to you an update to that map: our plan to weave quantum processors, CPUs, and GPUs into a compute fabric capable of solving problems beyond the scope of classical resources alone.
Our goal is to build quantum-centric supercomputers. The quantum-centric supercomputer will incorporate quantum processors, classical processors, quantum communication networks, and classical networks, all working together to completely transform how we compute. In order to do so, we need to solve the challenge of scaling quantum processors, develop a runtime environment for providing quantum calculations with increased speed and quality, and introduce a serverless programming model to allow quantum and classical processors to work together frictionlessly.
But first: where did this journey begin? We put the first quantum computer on the cloud in 2016, and in 2017, we introduced an open source software development kit for programming these quantum computers, called Qiskit. We debuted the first integrated quantum computer system, called the IBM Quantum System One, in 2019, then in 2020 we released our development roadmap showing how we planned to mature quantum computers into a commercial technology.

Physicists sometimes come up with crazy stories that sound like science fiction. Some turn out to be true, like how the curvature of space and time described by Einstein was eventually borne out by astronomical measurements. Others linger on as mere possibilities or mathematical curiosities.
In a new paper in Physical Review Research, JQI Fellow Victor Galitski and JQI graduate student Alireza Parhizkar have explored the imaginative possibility that our reality is only one half of a pair of interacting worlds. Their mathematical model may provide a new perspective for looking at fundamental features of reality—including why our universe expands the way it does and how that relates to the most miniscule lengths allowed in quantum mechanics. These topics are crucial to understanding our universe and are part of one of the great mysteries of modern physics.
The pair of scientists stumbled upon this new perspective when they were looking into research on sheets of graphene—single atomic layers of carbon in a repeating hexagonal pattern. They realized that experiments on the electrical properties of stacked sheets of graphene produced results that looked like little universes and that the underlying phenomenon might generalize to other areas of physics. In stacks of graphene, new electrical behaviors arise from interactions between the individual sheets, so maybe unique physics could similarly emerge from interacting layers elsewhere—perhaps in cosmological theories about the entire universe.
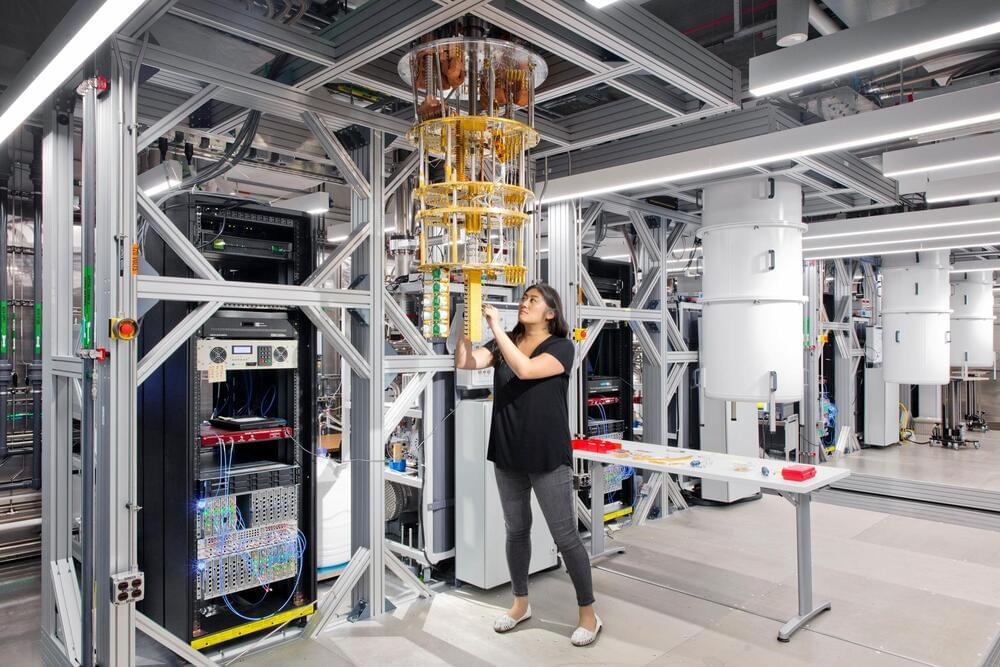

Today’s classical supercomputers can do a lot. But because their calculations are limited to binary states of 0 or 1, they can struggle with enormously complex problems such as natural science simulations. This is where quantum computers, which can represent information as 0, 1, or possibly both at the same time, might have an advantage.
Last year, IBM debuted a 127-qubit computing chip and a structure called the IBM Quantum System Two, intended to house components like the chandelier cryostat, wiring, and electronics for these bigger chips down the line. These developments edged IBM ahead of other big tech companies like Google and Microsoft in the race to build the most powerful quantum computer. Today, the company is laying out its three-year-plan to reach beyond 4,000-qubits by 2025 with a processor it is calling “Kookaburra.” Here’s how it is planning to get there.”
To get to its 2025 goal of a 4,000 qubit plus chip, IBM has micro-milestones it wants to hit on both the hardware and software side.

A group of researchers from Pisa, Jyväskylä, San Sebastian and MIT have demonstrated how a heterostructure consisting of superconductors and magnets can be used to create unidirectional current like that found in semiconductor diodes.
These novel superconductor diodes, however, operate at much lower temperatures than their semiconductor counterparts and are therefore useful in quantum technologies.
The current state of affairs, however, is a bit more complicated. While quantum computers have officially gone from theory to fact—a remarkable achievement—none are yet practical.
To realize a useful quantum computer, Google, IBM, Microsoft, Amazon, and others are pouring resources into machines that run on a menagerie of qubits. The most popular approach, favored by Google and IBM, involves tiny loops of superconducting wire. Honeywell and IonQ are pursuing atomic qubits made of trapped ions. Researchers in China are building intricate, Rube-Goldberg-like machines on lab benches to run quantum computations with mirrors and light.
The quantum race is anything but settled, and as outlined in a paper published this week in Nature, there’s a new horse on the track. Instead of superconducting loops, ions, or photons, a team of scientists led by the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, made qubits from single electrons.
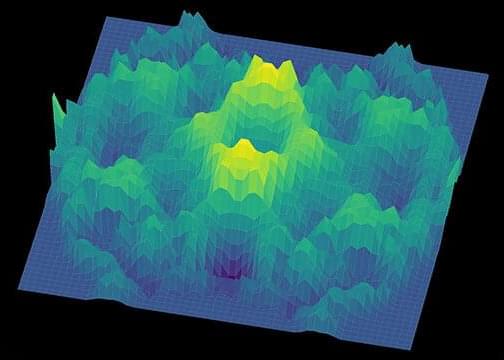
Computational detective work by U.S. and German physicists has confirmed that cerium zirconium pyrochlore is a 3D quantum spin liquid.
Despite the name, quantum spin liquids are solid materials in which quantum entanglement and the geometric arrangement of atoms frustrate the natural tendency of electrons to magnetically order themselves in relation to one another. The geometric frustration in a quantum spin liquid is so severe that electrons fluctuate between quantum magnetic states no matter how cold they become.
Theoretical physicists routinely work with quantum mechanical models that manifest quantum spin liquids, but finding convincing evidence that they exist in actual physical materials has been a decades-long challenge. While a number of 2D or 3D materials have been proposed as possible quantum spin liquids, Rice University physicist Andriy Nevidomskyy has said there’s no established consensus among physicists that any of them qualify.