Quantum computer: One of the obstacles for progress in the quest for a working quantum computer has been that the working devices that go into a quantum computer and perform the actual calculations, the qubits, have hitherto been made by universities and in small numbers. But in recent years, a pan-European collaboration, in partnership with French microelectronics leader CEA-Leti, has been exploring everyday transistors—that are present in billions in all our mobile phones—for their use as qubits. The French company Leti makes giant wafers full of devices, and, after measuring, researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, have found these industrially produced devices to be suitable as a qubit platform capable of moving to the second dimension, a significant step for a working quantum computer. The result is now published in Nature Communications.
Quantum dots in two dimensional array is a leap ahead
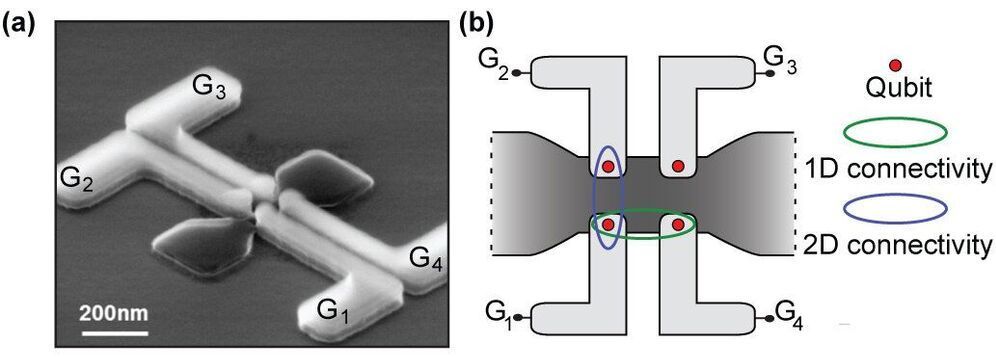
One of the key features of the devices is the two-dimensional array of quantum dots. Or more precisely, a two by two lattice of quantum dots. “What we have shown is that we can realize single electron control in every single one of these quantum dots. This is very important for the development of a qubit, because one of the possible ways of making qubits is to use the spin of a single electron. So reaching this goal of controlling the single electrons and doing it in a 2-D array of quantum dots was very important for us”, says Fabio Ansaloni, former Ph.D. student, now postdoc at center for Quantum Devices, NBI.