Archive for the ‘quantum physics’ category: Page 731
Feb 21, 2017
A quantum leap for computers
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, quantum physics
More on the QC Blueprint which enables others to use as a reference when building a QC.
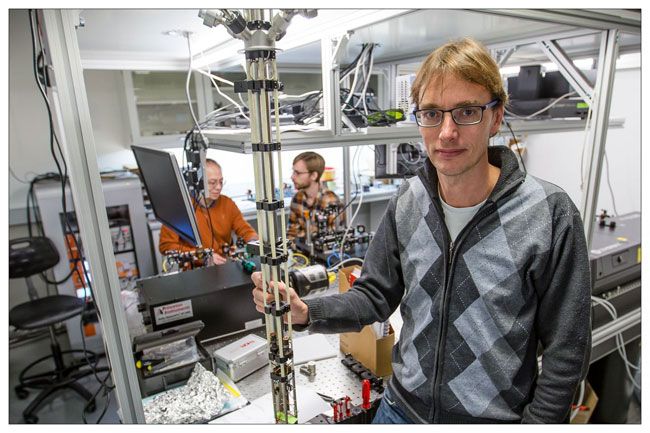
According to Prof Winfried Hensinger of the University of Sussex in the United Kingdom, he and his team have the first practical design for a quantum computer. Like millions of others, I have struggled to come to an understanding of quantum mechanics and how a quantum computer might work.
It would use qubits rather than standard on/off or 1 and 0 bits used in traditional computers. A qubit can have a state of anywhere between zero and one, including all the “states” in between. Theoretically, a quantum computer can perform a very large number of calculations simultaneously using the ideas of super positioning and quantum entanglement. The theory is that all the necessary calculations are carried out at virtually the same time, e.g. working out all the factors of a very large number. This kind of problem can take a regular computer quite a while.
Feb 21, 2017
Photon Gun Could Further Development of Photonic Quantum Network
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: nanotechnology, quantum physics
A photonic nanostructure for constructing quantum photonic circuits for quantum networks has been developed, which could impact the optics and photoni.
Feb 21, 2017
NSCI Seminar: Quantum Applications and Microsoft’s unique approach to Quantum Computing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: chemistry, engineering, quantum physics, robotics/AI
Sharing in case folks would like to listen in.
Microsoft’s Station Q was founded in 2006. The focus of the team has always been topological quantum computing. By taking a full systems architecture approach, we have reached the point where we now able to start engineering a scalable quantum computer. The goal is to be able to solve major problems in areas of interest (e.g., Chemistry, Materials and Machine Learning). This talk will focus on the types of applications that we will be trying to solve as well as the unique approach to quantum computation that we’ve developed. For reference, see:
Current Approach: https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.05289 Chemistry Application: https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.03590 Other papers: https://arxiv.org/find/all/1/all:+wecker_d/0/1/0/all/0/1
Feb 21, 2017
Quantum Entanglement is Just as Einstein Predicted
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: particle physics, quantum physics
I never doubt the theory.
We owe a lot to Einstein, and this week physicists have confirmed another of his theories by unraveling and proving that quantum entanglement does in fact exist. Under the standard quantum theory, nothing has a definitive state until it’s measured, and when two particles interact they become entangled. Being entangled means no longer do the particles have their probabilities but one that includes both particles together. Even though two photons become entangled, they can still travel light years apart from each other, but they will always remain linked.
Feb 21, 2017
Shell-Dependent Photoluminescence Studies Provide Mechanistic Insights into the Off-Grey-On Transitions of Blinking Quantum Dots
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: materials, quantum physics
The majority of quantum dot (QD) blinking studies have used a model of switching between two distinct fluorescence intensity levels, “on” and “off”. However, a distinct intermediate intensity level has been identified in some recent reports – a so-called “grey” or “dim” state, which has brought this binary model into question. While this grey state has been proposed to result from the formation of a trion, it is still unclear under which conditions it is present in a QD. By performing shell-dependent blinking studies on CdSe QDs, we report that the populations of the grey state and the on state are strongly dependent on both the shell material and its thickness. We found that adding a ZnS shell did not result in a significant population of the grey state. Using ZnSe as the shell material resulted in a slightly higher population of the grey state, although it was still poorly resolved. However, adding a CdS shell resulted in the population of a grey state, which depended strongly on its thickness up to 5 ML. Interestingly, while the frequency of transitions to and from the grey state showed a very strong dependence on CdS shell thickness, the brightness of and the dwell time in the grey state did not. Moreover, we found that the grey state acts as an on-pathway intermediate state between on and off states, with the thickness of the shell determining the transition probability between them. We also identified two types of blinking behavior in QDs, one that showed long-lived but lower intensity on states and another that showed short-lived but brighter on states that also depended on the shell thickness. Intensity-resolved single QD fluorescence lifetime analysis was used to identify the relationship between the various exciton decay pathways and the resulting intensity levels. We used this data to propose a model in which multiple on, grey and off states exist whose equilibrium populations vary with time that give rise to the various intensity levels of single QDs, and which depends on shell composition and thickness.
View: PDF | PDF w/ Links.
Feb 21, 2017
A.I. Machines Are Learning Quantum Physics And Solving Complex Problems On Their Own
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: particle physics, quantum physics, robotics/AI, supercomputing
In the past, traditional methods to understand the behavior of quantum interacting systems have worked well, but there are still many unsolved problems. To solve them, Giuseppe Carleo of ETH Zurich, Switzerland, used machine learning to form a variational approach to the quantum many-body problem.
Before digging deeper, let me tell you a little about the many-body problem. It deals with the difficulty of analyzing “multiple nontrivial relationships encoded in the exponential complexity of the many-body wave function.” In simpler language, it’s the study of interactions between many quantum particles.
If we take a look at our current computing power, modeling a wave function will need lot more powerful supercomputers. But, according to Carleo, the neural networks are pretty good at generalizing. Hence, they need only limited information to infer something. So, fiddling with this idea, Carleo and Matthias Troyer created a simple neural network to reconstruct such multi-body wave function.
Feb 18, 2017
EmDrive: Chinese space agency to put controversial tech onto satellites ‘as soon as possible’
Posted by Andreas Matt in categories: government, quantum physics, satellites
Chinese government confirms it has been funding EmDrive research since 2010 and believes in its benefits.
Feb 16, 2017
All inherited diseases including cancer ‘could be cured in the next 20 years’
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, quantum physics
Definitely yes on gene mutations; however, those where the disease has already appeared, or cancer that has occurred before will require another form of eradication/ prevention. And, that is where Quantum Biosystem technology will be effective in eliminating disease.
ALL inherited diseases could be cured within 20 years, a leading British expert claims.
It includes eradicating life-limiting conditions such as cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease.
Continue reading “All inherited diseases including cancer ‘could be cured in the next 20 years’” »
Feb 16, 2017
Revolutionary New Technique Visualizes Biomolecules Without Crystallization
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: particle physics, quantum physics
Quantum interpolation makes viewing Biomolecules at room temp. possible without freezing. This technique will enable more powerful sensors than we have ever had before.
In the latest issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from MIT and Singapore University of Technology and Design are describing a new technique that may finally give life scientists a detailed view into many of the biomolecules they work with. These days, X-ray diffraction is typically used to see the structure of a molecule. But this requires crystallization, a process not all molecules, including many proteins, are unwilling to undergo.
The technology uses tiny diamond crystals that have a nitrogen atom in place of a single carbon atom. These so-called “nitrogen vacancy centers” make the crystals react to minute fluctuations of magnetic and electric fields surrounding them. They’re so sensitive that the spins of individual atoms of a nearby molecule affect them enough to be detected by an external device.
Continue reading “Revolutionary New Technique Visualizes Biomolecules Without Crystallization” »