Sep 2, 2024
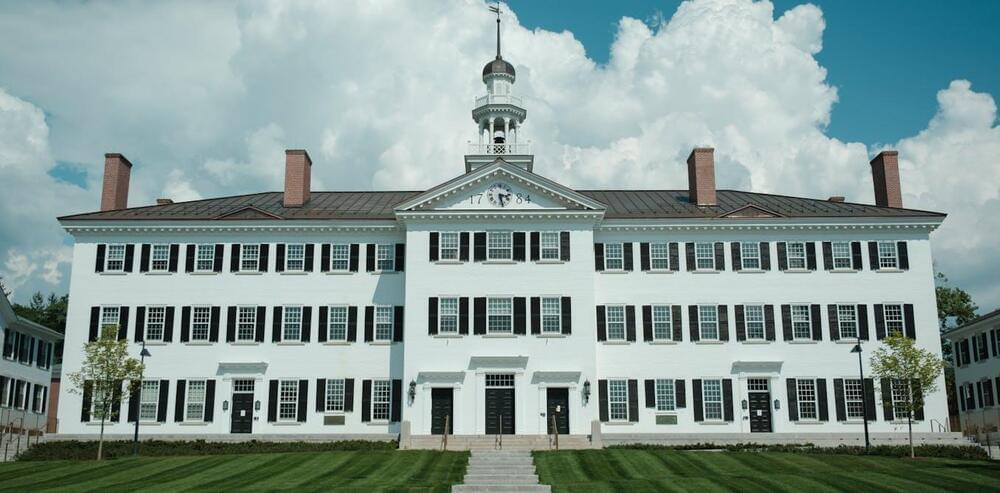
AI was born at a US summer camp 68 years ago. Here’s why that event still matters today
Posted by Rx Sobolewski in category: robotics/AI
Let’s also emphasise ethical considerations. The Dartmouth participants didn’t spend much time discussing the ethical implications of AI. Today, we know better, and must do better.
We must also refocus research directions. Let’s emphasise research into AI interpretability and robustness, interdisciplinary AI research and explore new paradigms of intelligence that aren’t modelled on human cognition.
Finally, we must manage our expectations about AI. Sure, we can be excited about its potential. But we must also have realistic expectations, so that we can avoid the disappointment cycles of the past.